
일본은 1992년 6월 30일 유네스코 세계 유산 협약을 받아들였습니다. 2021년 7월 현재, 25개의 문화재가 세계 유산 목록에 등재되었습니다: 20개의 문화 유산과 5개의 자연 유산. 추가적인 5개의 유적지와 1개의 유적지 확장물이 향후 등재를 위해 제출되었고 2017년 현재 잠정 목록에 있습니다.
Japan accepted the UNESCO World Heritage Convention on 30 June 1992. As of July 2021, twenty-five properties have been inscribed on the World Heritage List: twenty cultural sites and five natural sites. A further five sites and one site extension have been submitted for future inscription and are currently on the Tentative List as of 2017.
@ Buddhist Monuments in the Hōryū-ji Area
호류지 지역의 유네스코 세계문화유산 불교기념물은 일본 나라현 이카루가시의 호류지와 홋카이도에서 발견된 다양한 건물들을 포함하고 있습니다. 이 건물들은 주변 경관과 함께 1993년에 몇 가지 기준으로 지정되었습니다. 새겨진 건축물들은 7세기에서 8세기로 거슬러 올라가는 현존하는 가장 오래된 목조 건물들 중 일부입니다. 많은 건축물들은 또한 일본의 국보이고, 일본 불교의 영향의 중요한 시대를 반영하고 있습니다. 그 건축물들은 호류지 동사에 있는 21개의 건물들, 서사에 있는 9개의 건물들, 17개의 수도원들과 다른 건물들, 그리고 홋카이도에 있는 탑을 포함하고 있습니다.
The UNESCO World Heritage Site Buddhist Monuments in the Hōryū-ji Area includes a variety of buildings found in Hōryū-ji and Hokki-ji in Ikaruga, Nara Prefecture, Japan. These buildings were designated in 1993 along with the surrounding landscape, under several criteria. The structures inscribed are some of the oldest extant wooden buildings in the world, dating from the 7th to 8th centuries. Many of the monuments are also National Treasures of Japan, and reflect an important age of Buddhist influence in Japan. The structures include 21 buildings in the Hōryū-ji East Temple, 9 in the West Temple, 17 monasteries and other buildings, and the pagoda in Hokki-ji.


@ Himeji-jō
히메지 성(히메지 姫路城 Himeji-jō)은 일본 효고현 히메지시에 위치한 언덕 꼭대기에 있는 성입니다. 이 성은 봉건 시대의 고급 방어 시설을 갖춘 83개의 방으로 이루어진 전형적인 일본 성의 건축 양식 중 현존하는 가장 훌륭한 예로 여겨집니다. 이 성은 밝은 흰색 외관과 새가 날아다니는 것과 비슷하게 생겼기 때문에 자주 하쿠로조 또는 시라사기조로 알려져 있습니다.
Himeji Castle (姫路城, Himeji-jō) ([çimeʑiꜜʑoː] ) is a hilltop Japanese castle complex situated in Himeji, a city in the Hyōgo Prefecture of Japan. The castle is regarded as the finest surviving example of prototypical Japanese castle architecture, comprising a network of 83 rooms with advanced defensive systems from the feudal period.[7] The castle is frequently known as Hakuro-jō or Shirasagi-jō ("White Egret Castle" or "White Heron Castle") because of its brilliant white exterior and supposed resemblance to a bird taking flight.


@ Historic Monuments of Ancient Kyoto
유네스코 세계문화유산 고대 교토의 역사 유적 (교토, 우지, 오츠 시)은 일본 내 교토시와 그 바로 근처의 17개 지역을 포함하고 있습니다. 794년, 일본 황실은 수도를 헤이안쿄로 옮겼습니다. 그 장소들은 세 개의 도시에 있습니다: 교토 현의 교토와 우지, 그리고 시가 현의 오츠, 남쪽과 북쪽으로 각각 교토와 접하고 있습니다. 그 유적들 중, 13개는 불교 사원, 3개는 신사, 그리고 1개는 성입니다. 그 문화재들은 일본 정부에 의해 국보로 지정된 38개의 건물, 중요 문화재로 지정된 160개의 재산, 경치가 아름다운 특별한 곳으로 지정된 8개의 정원, 그리고 경치가 아름다운 곳으로 지정된 4개의 장소를 포함하고 있습니다. 유네스코는 1994년에 그 장소를 세계 문화 유산으로 등재했습니다.
The UNESCO World Heritage Site Historic Monuments of Ancient Kyoto (Kyoto, Uji and Otsu Cities) encompasses 17 locations in Japan within the city of Kyoto and its immediate vicinity. In 794, the Japanese imperial family moved the capital to Heian-kyō. The locations are in three cities: Kyoto and Uji in Kyoto Prefecture; and Ōtsu in Shiga Prefecture; Uji and Ōtsu border Kyoto to the south and north, respectively. Of the monuments, 13 are Buddhist temples, three are Shinto shrines, and one is a castle. The properties include 38 buildings designated by the Japanese government as National Treasures, 160 properties designated as Important Cultural Properties, eight gardens designated as Special Places of Scenic Beauty, and four designated as Places of Scenic Beauty. UNESCO listed the site as World Heritage in 1994.


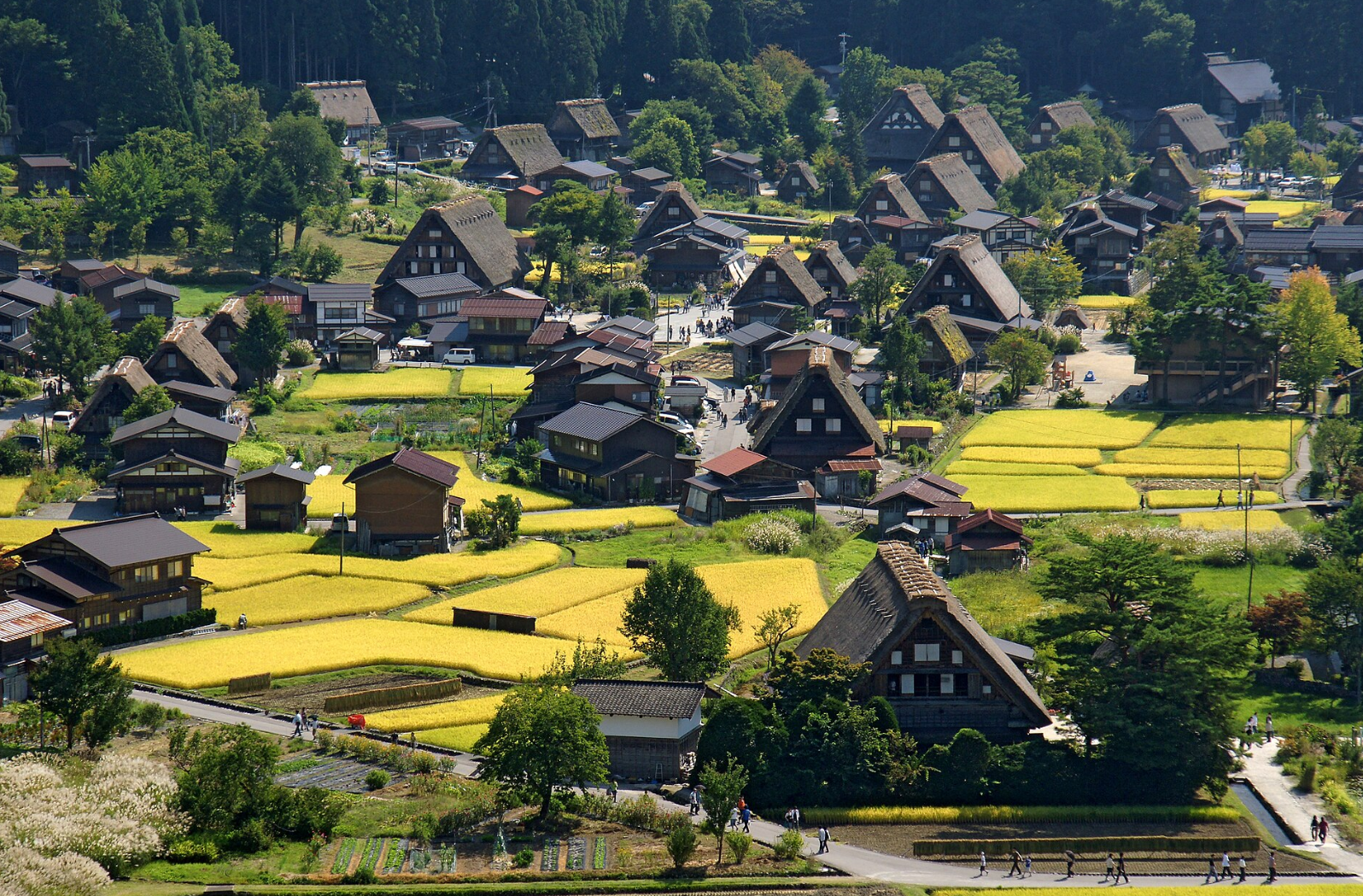
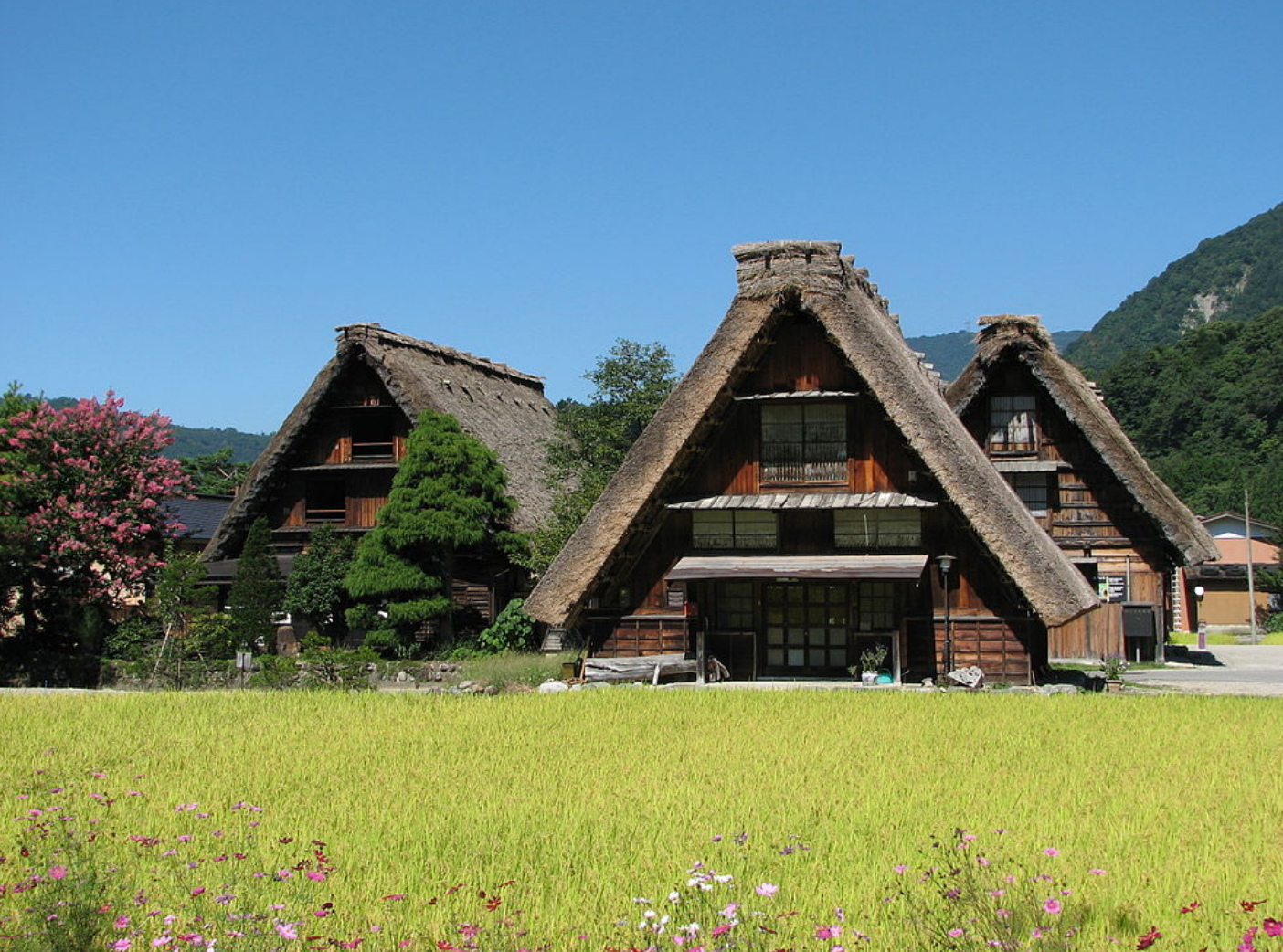
@ Historic Villages of Shirakawa-gō and Gokayama
시라카와고와 고카야마의 역사적인 마을은 일본의 유네스코 세계 문화 유산 중 하나입니다. 그 문화재는 일본 중부의 기후현과 도야마현의 경계에 걸쳐 뻗어 있는 쇼가와 강 외딴 곳에 있는 68 헥타르 (170 에이커)의 면적에 걸쳐 있는 세 개의 역사적인 산 마을로 이루어져 있습니다. 시라카와고 (白川郷, "백하 구")는 기후현의 시라카와 마을에 위치하고 있습니다. 고카야마 (五箇山, "다섯 개의 산") 지역은 도야마현 난토시의 가미타이라 마을과 타이라 마을 사이에 있습니다.
The Historic Villages of Shirakawa-gō and Gokayama are one of Japan's UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The cultural property consists of three historic mountain villages over an area of 68 hectares (170 acres) in the remote Shogawa river valley, stretching across the border of Gifu and Toyama Prefectures in central Japan. Shirakawa-gō (白川郷, "White River Old-District") is located in the village of Shirakawa in Gifu Prefecture. The Gokayama (五箇山, "Five Mountains") area is divided between the former villages of Kamitaira and Taira in Nanto, Toyama Prefecture.


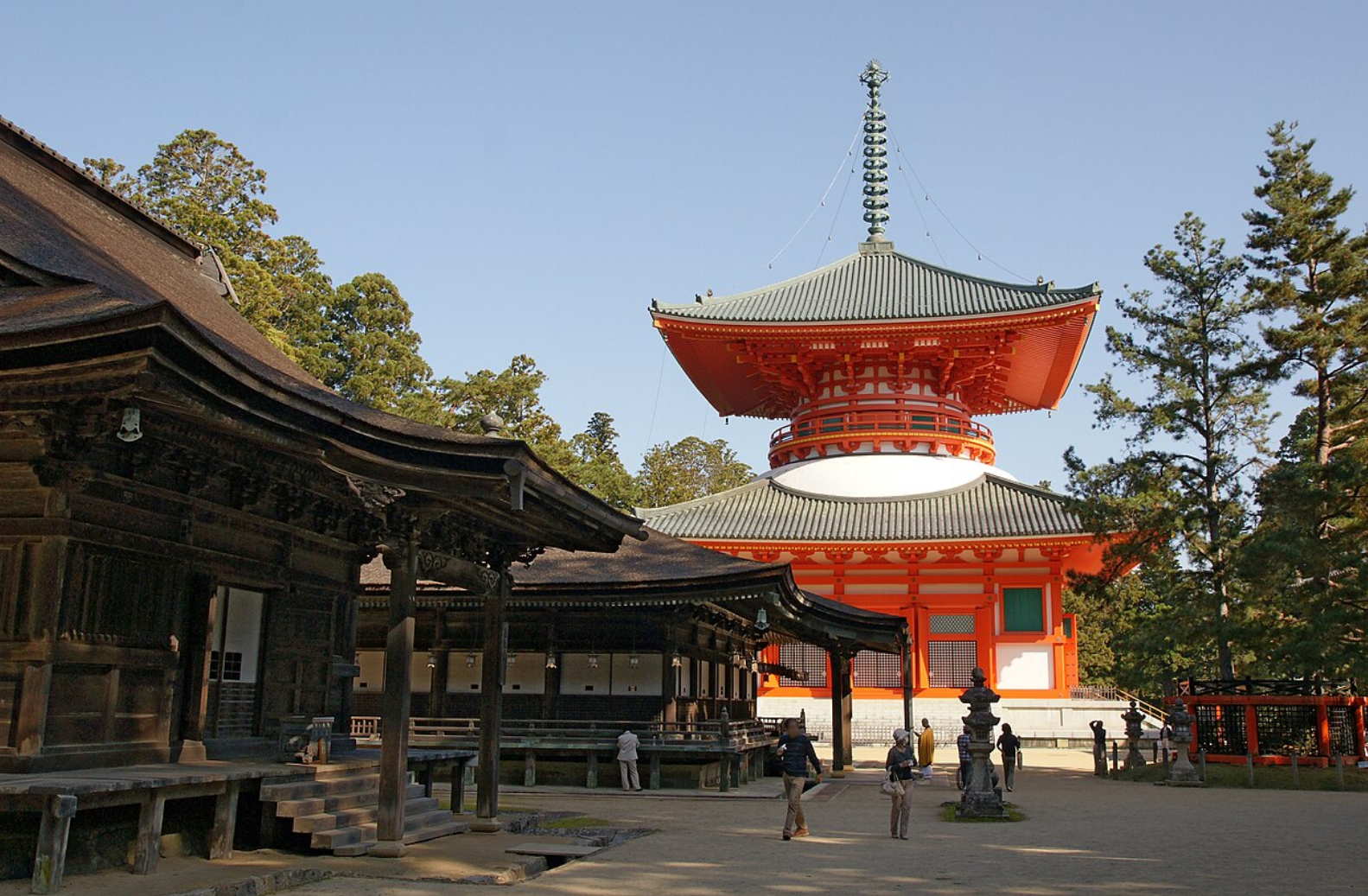
@ Sacred Sites and Pilgrimage Routes in the Kii Mountain Range
기이 산맥의 성지와 순례길은 일본 기이 반도에 위치한 유네스코 세계문화유산입니다.
Sacred Sites and Pilgrimage Routes in the Kii Mountain Range is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located on the Kii Peninsula in Japan.

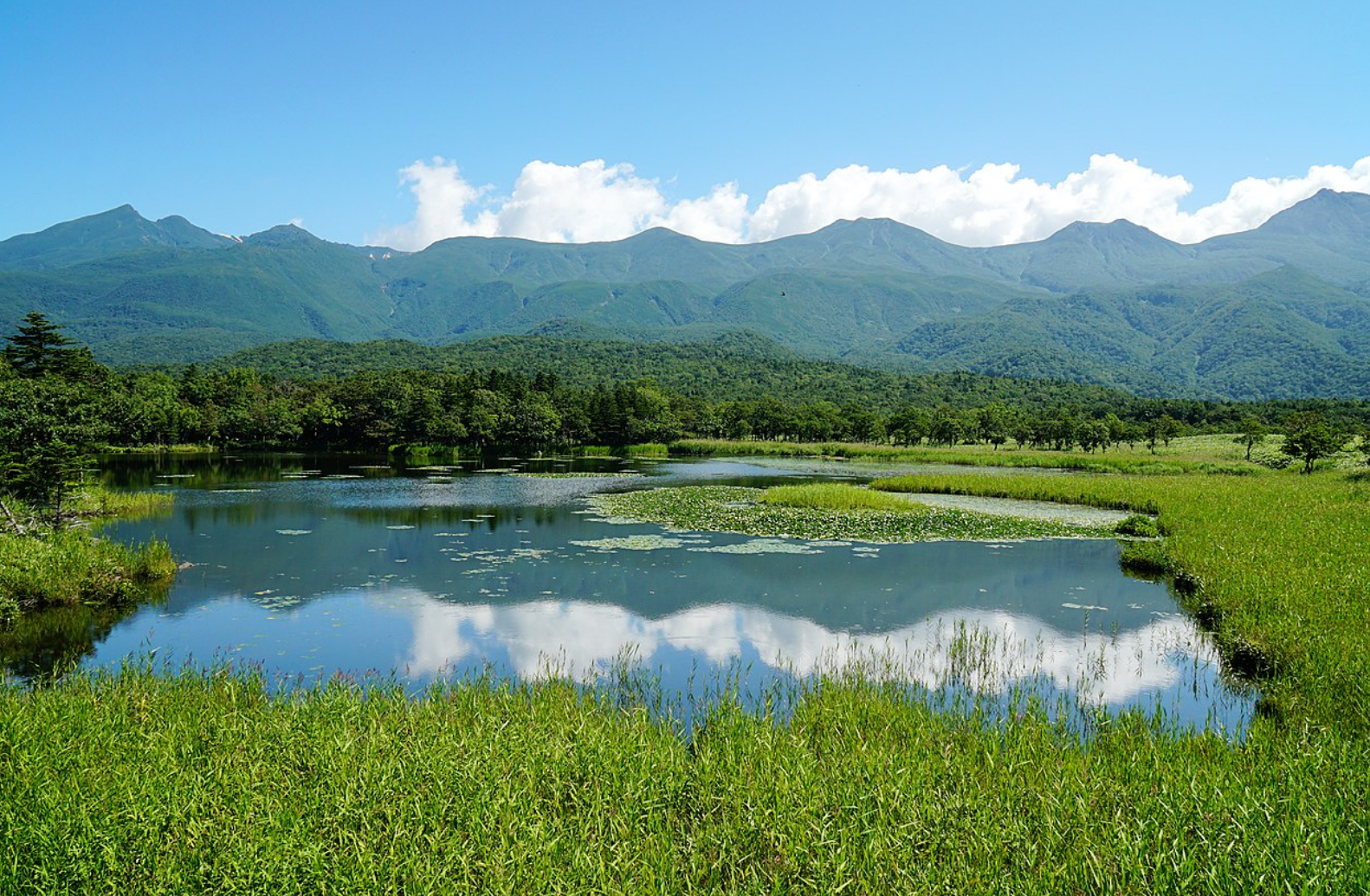
@ Shiretoko
시레토코 국립공원 (知床国立公園, 시레토코 코쿠리쓰 코엔)은 일본 홋카이도 섬의 북동쪽 끝에 있는 시레토코 반도의 대부분을 덮고 있습니다. "시레토코"라는 단어는 "지구가 튀어나온 곳"을 의미하는 아이누어 "시레토코"에서 유래되었습니다.
Shiretoko National Park (知床国立公園, Shiretoko Kokuritsu Kōen) covers most of the Shiretoko Peninsula at the northeastern tip of the island of Hokkaidō, Japan. The word "Shiretoko" is derived from an Ainu word "sir etok", meaning "the place where the earth protrudes".

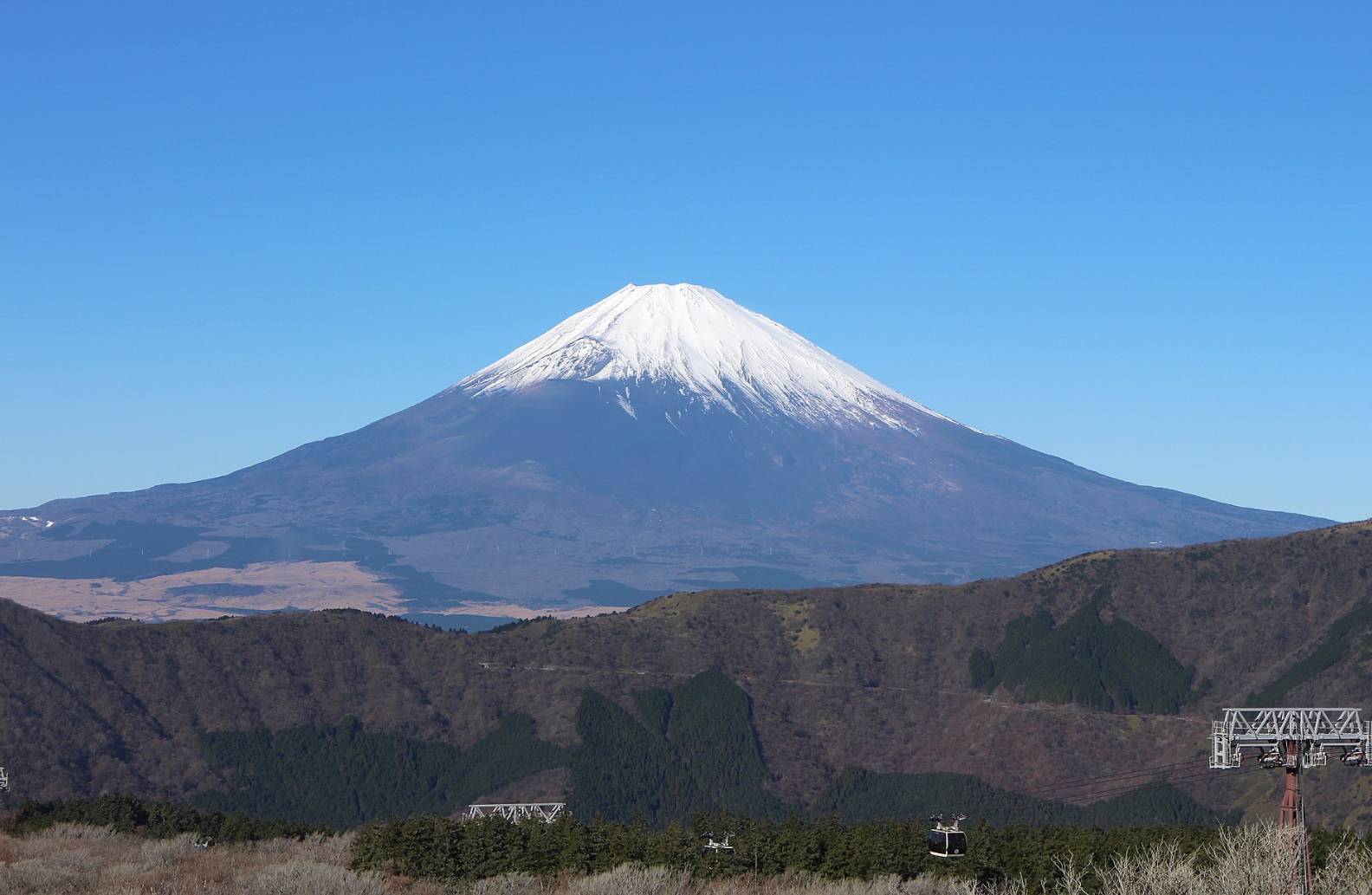
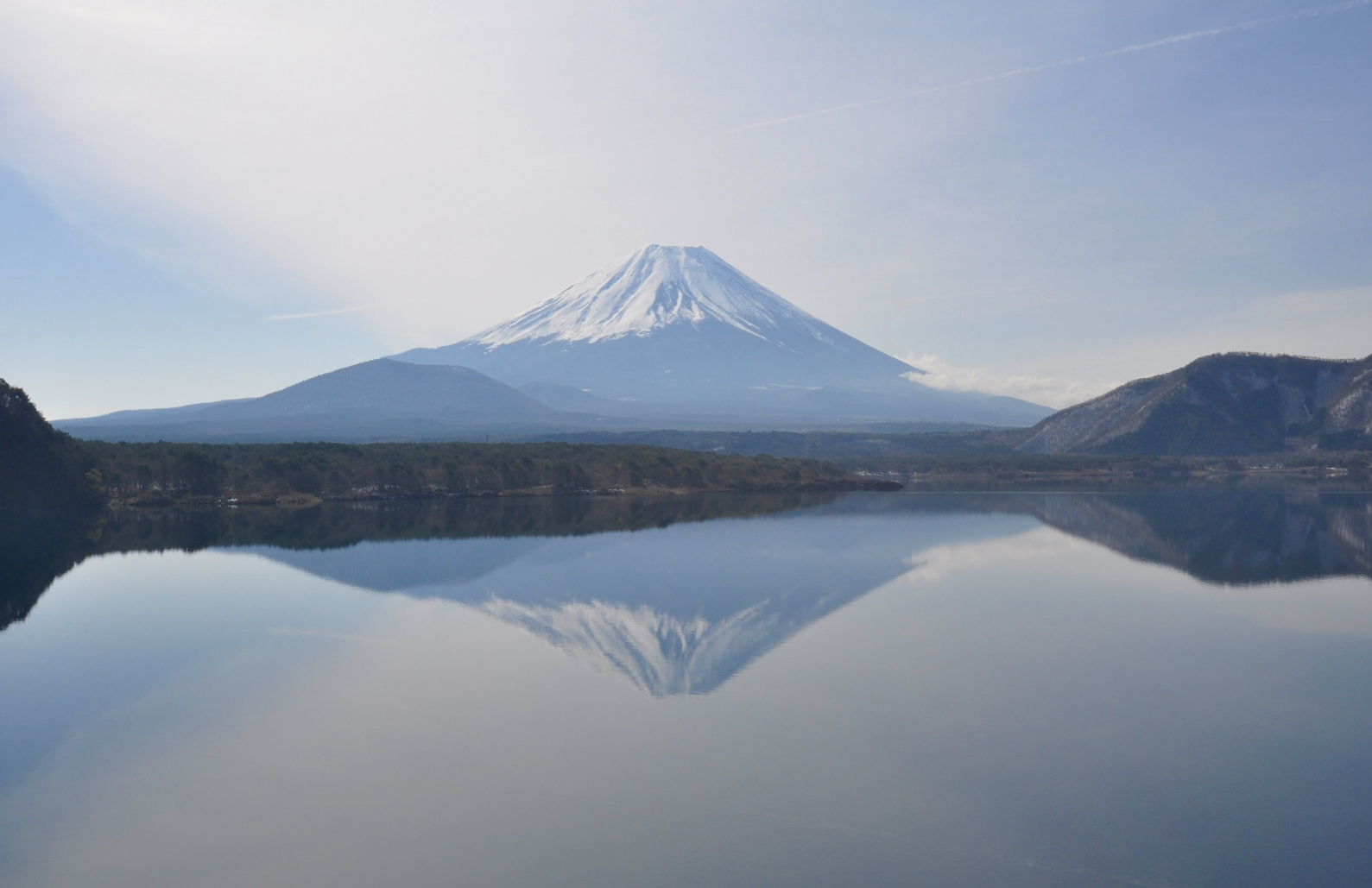
@ Fujisan, sacred place and source of artistic inspiration
후지산(富士山, 후지산)은 일본 혼슈 섬에 위치한 활동적인 성층 화산으로, 정상 고도는 3,776.24m (12,389피트 3인치)입니다. 일본에서 가장 높은 산이며, 아시아에서 두 번째로 높은 화산이며, 지구상에서 일곱 번째로 높은 섬의 봉우리입니다. [1] 후지산은 1707년부터 1708.[4] 마지막으로 분화하여 맑은 날에 일본 수도에서 볼 수 있습니다. 1년 중 약 5개월 동안 눈으로 덮인 후지산의 유난히 대칭적인 원뿔은 일본의 문화 아이콘으로 흔히 사용되며 예술과 사진뿐만 아니라 관광객, 등산객, 등산객이 방문합니다.
Mount Fuji (富士山, Fujisan) is an active stratovolcano located on the Japanese island of Honshu, with a summit elevation of 3,776.24 m (12,389 ft 3 in). It is the tallest mountain in Japan, the second-highest volcano located on an island in Asia (after Mount Kerinci on the Indonesian island of Sumatra), and seventh-highest peak of an island on Earth. Mount Fuji last erupted from 1707 to 1708. The mountain is located about 100 km (62 mi) southwest of Tokyo and is visible from the Japanese capital on clear days. Mount Fuji's exceptionally symmetrical cone, which is covered in snow for about five months of the year, is commonly used as a cultural icon of Japan and is frequently depicted in art and photography, as well as visited by sightseers, hikers and mountain climbers.


@ Hidden Christian Sites in the Nagasaki Region
나가사키 지역의 숨겨진 기독교 유적지(일본어: 長崎と天草地方の潜伏キリシタン関連遺産)는 일본의 기독교 역사와 관련된 나가사키현과 구마모토현에 있는 12곳의 유적지 그룹입니다. 나가사키 교회는 각각 오랜 공식적인 탄압 후 기독교의 부활에 대한 이야기를 담고 있다는 점에서 독특합니다.
Hidden Christian Sites in the Nagasaki Region (Japanese: 長崎と天草地方の潜伏キリシタン関連遺産) is a group of twelve sites in Nagasaki Prefecture and Kumamoto Prefecture relating to the history of Christianity in Japan. The Nagasaki churches are unique in the sense that each tells a story about the revival of Christianity after a long period of official suppression
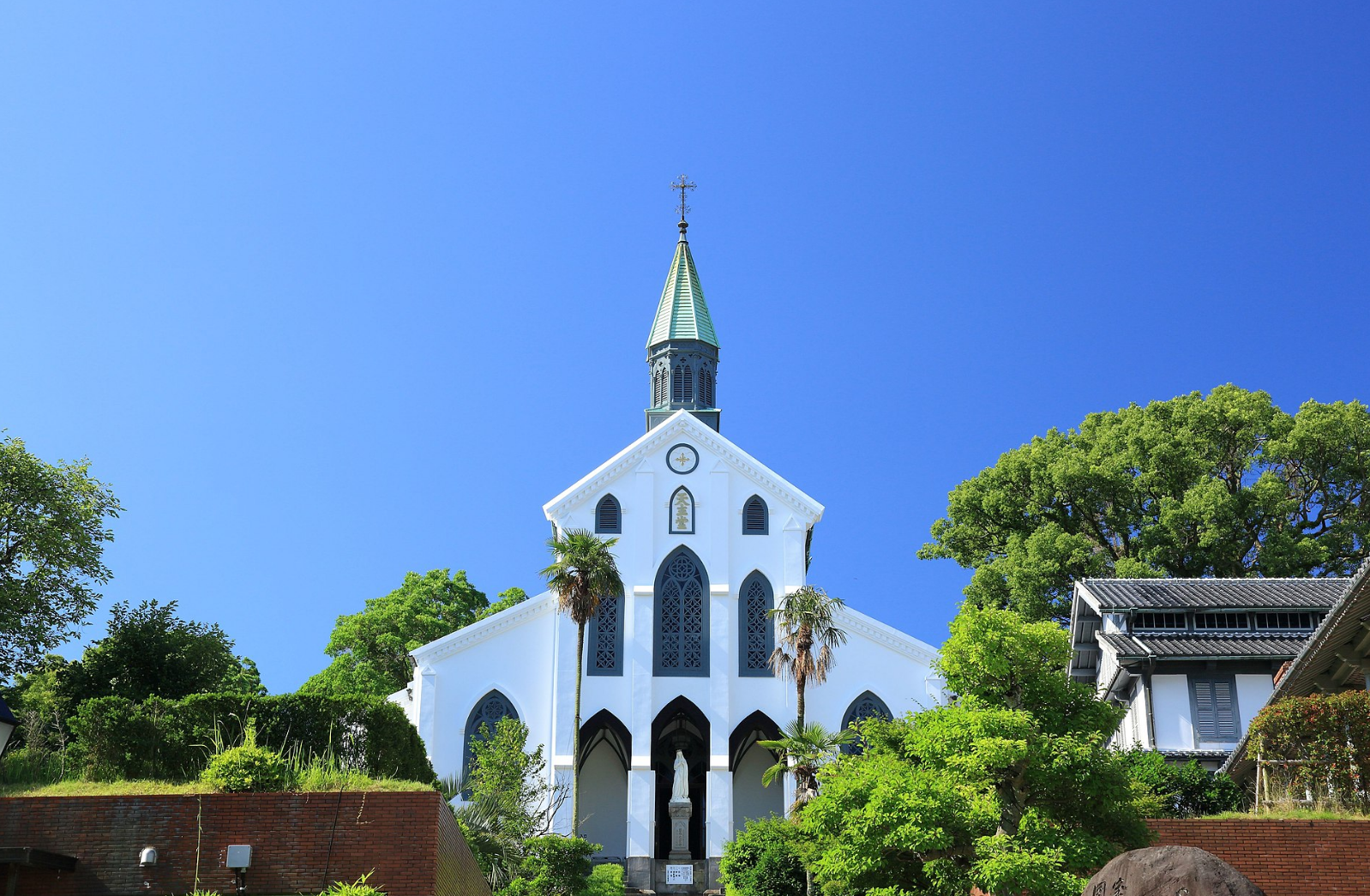
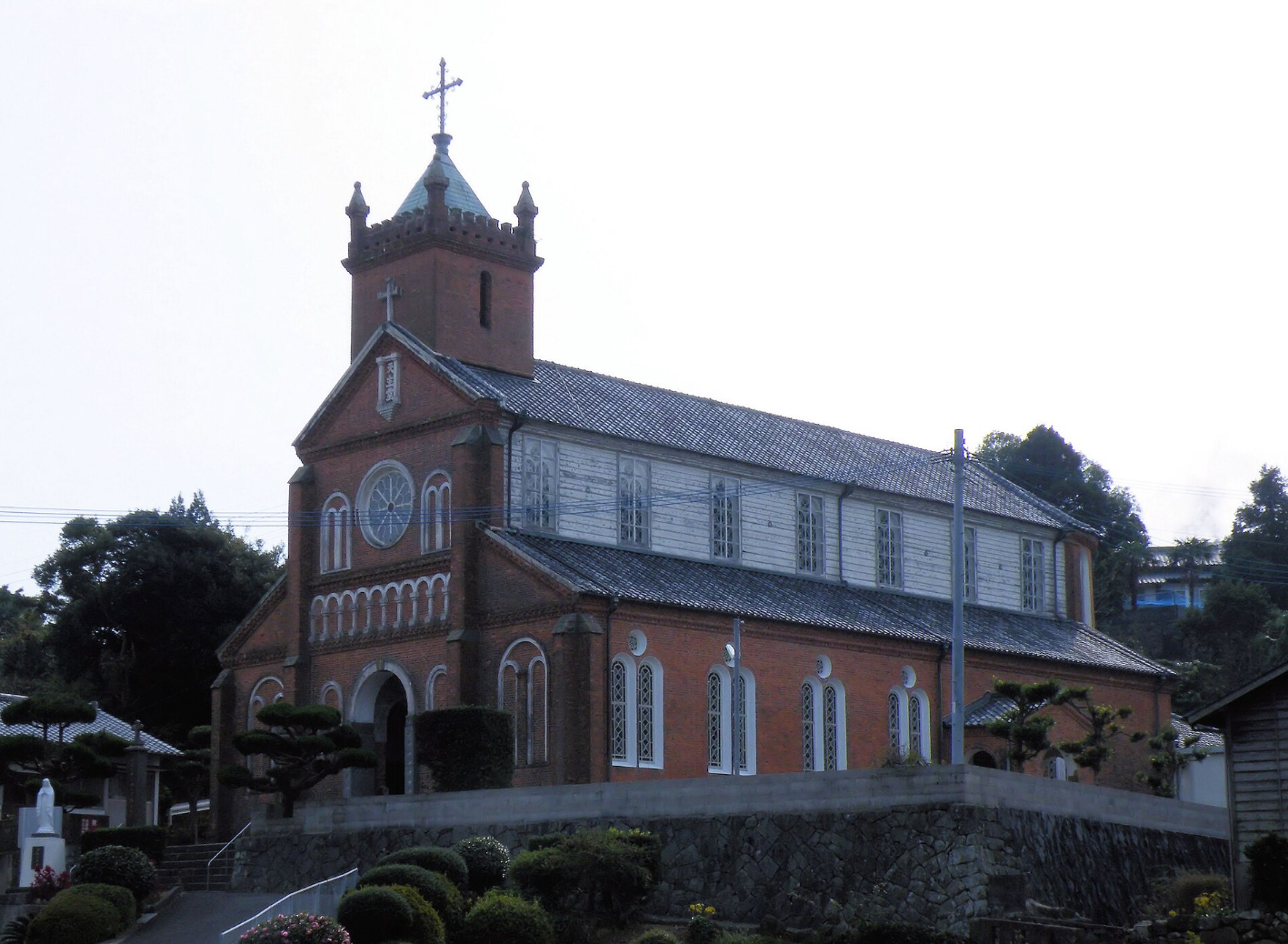


.
@ Mozu-Furuichi Kofungun, Ancient Tumulus Clusters
고펀(古墳, 중-일 "고분"에서 유래)은 북동 아시아에 있는 거석 무덤 또는 고분입니다. 고펀은 주로 3세기 중반에서 7세기 초 사이에 일본 열도에서 건설되었습니다.
Kofun (古墳, from Sino-Japanese "ancient grave") are megalithic tombs or tumuli in Northeast Asia. Kofun were mainly constructed in the Japanese archipelago between the middle of the 3rd century to the early 7th century CE.
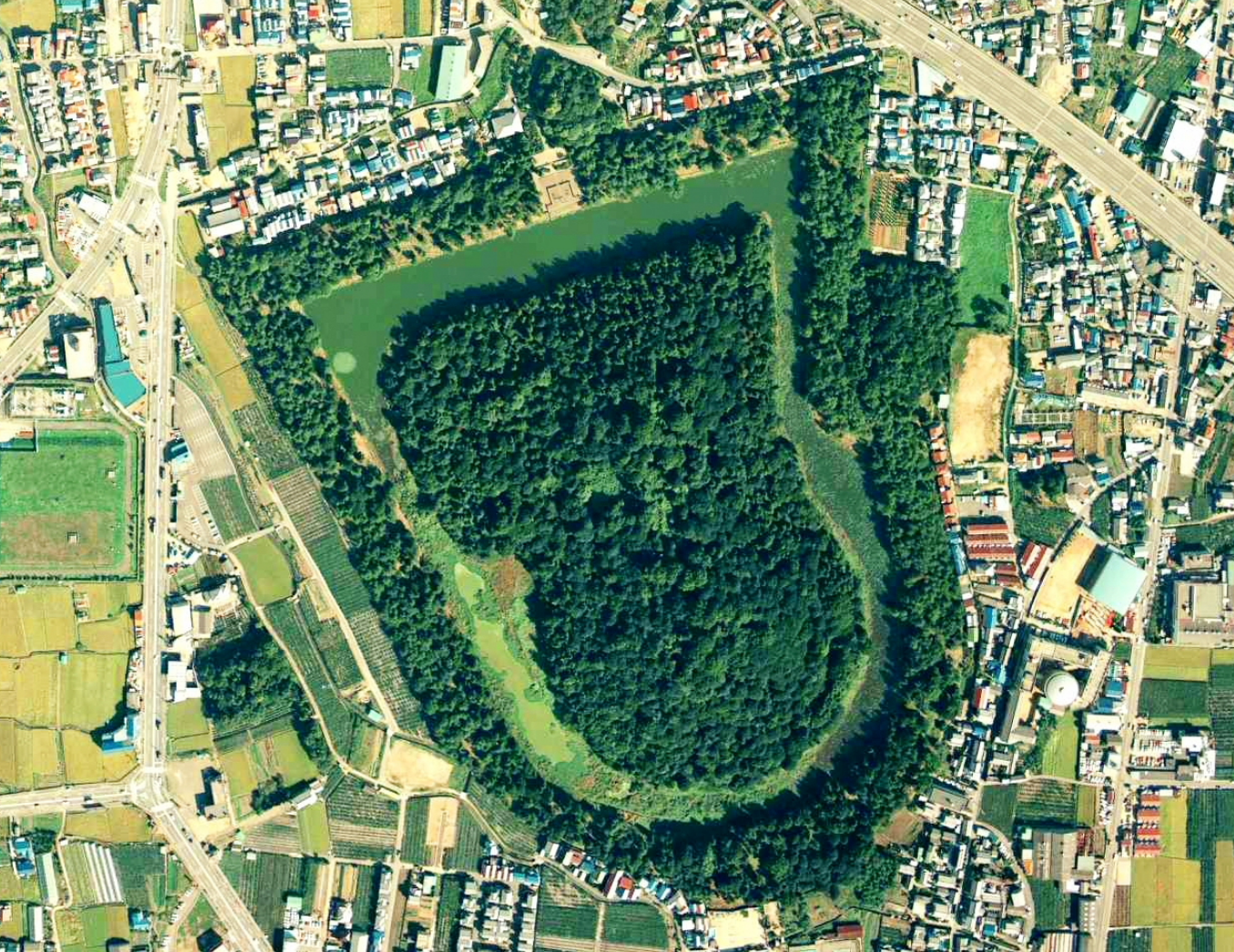

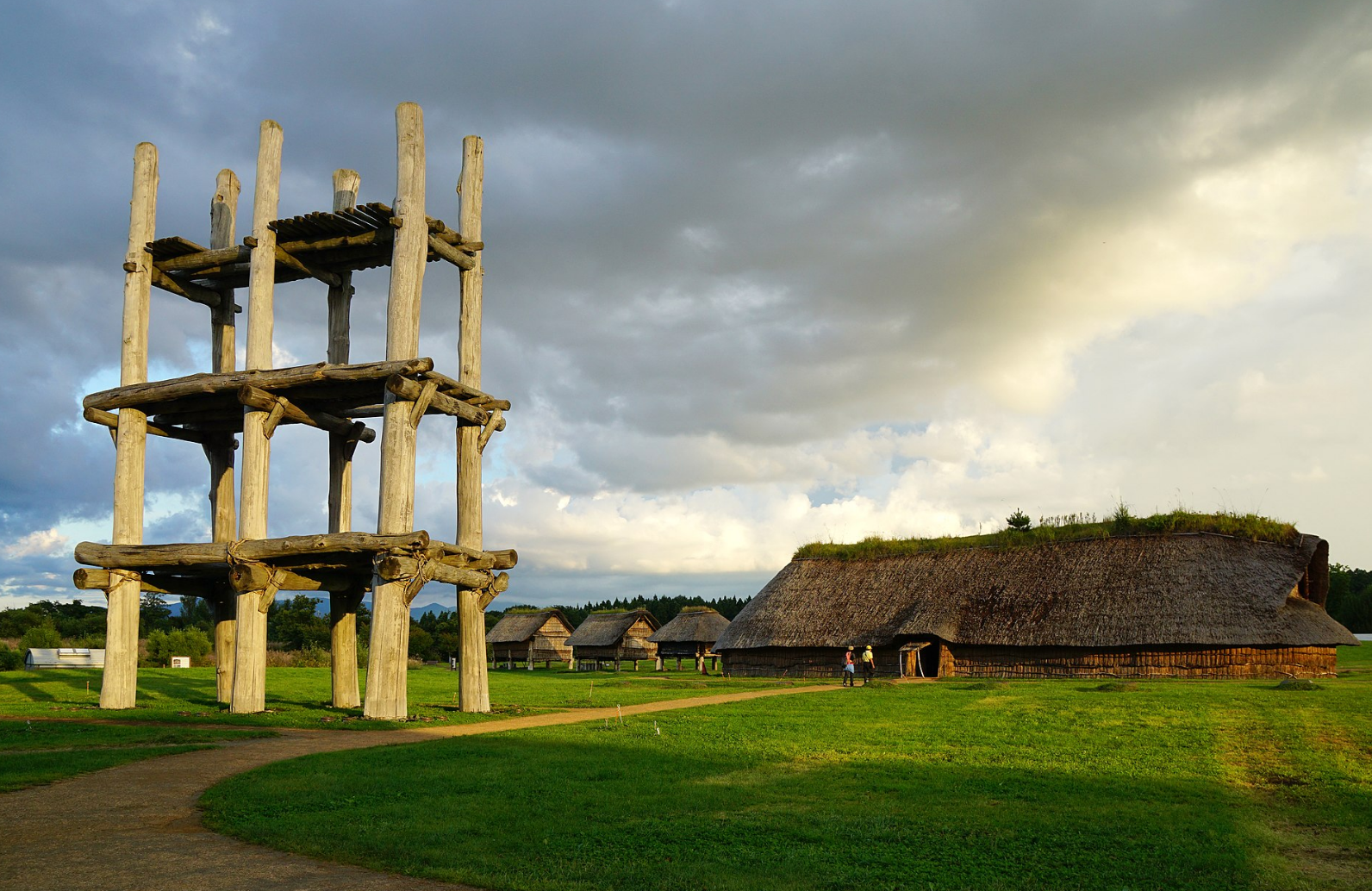
@ Jōmon Prehistoric Sites in Northern Japan
일본 북부의 조몬 선사시대 유적지 (北海道, 北東北の縄文遺跡群)는 일본 홋카이도와 도호쿠 북부에 있는 17개의 조몬 시대 고고학 유적지로 구성된 유네스코의 연속 세계 문화유산입니다. 조몬 시대는 10,000년 이상 지속되었으며, 이는 "선사시대 사람들의 정주적인 농업 이전 생활 방식과 복잡한 정신 문화"를 나타냅니다.
Jōmon Prehistoric Sites in Northern Japan (北海道・北東北の縄文遺跡群) is a serial UNESCO World Heritage Site consisting of 17 Jōmon-period archaeological sites in Hokkaidō and northern Tōhoku, Japan. The Jōmon period lasted more than 10,000 years, representing "sedentary pre-agricultural lifeways and a complex spiritual culture of prehistoric people".

@ Itsukushima Shrine
이쓰쿠시마 신사(厳島神社(嚴島神社)), 이쓰쿠시마 진자)는 일본 히로시마현 하쓰카이치시에 있는 신도 신사로, 떠다니는 도리이로 가장 잘 알려져 있습니다. 미야지마구치 역에서 페리로 본토에서 접근할 수 있습니다. 이 신사 단지는 유네스코 세계 문화 유산으로 등재되어 있고, 일본 정부는 여러 건물과 소유물을 국보로 지정했습니다.
Itsukushima Shrine (厳島神社 (嚴島神社), Itsukushima-jinja) is a Shinto shrine on the island of Itsukushima (popularly known as Miyajima), best known for its "floating" torii.[1] It is in the city of Hatsukaichi, in Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan, accessible from the mainland by ferry at Miyajimaguchi Station. The shrine complex is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and the Japanese government has designated several buildings and possessions as National Treasures.
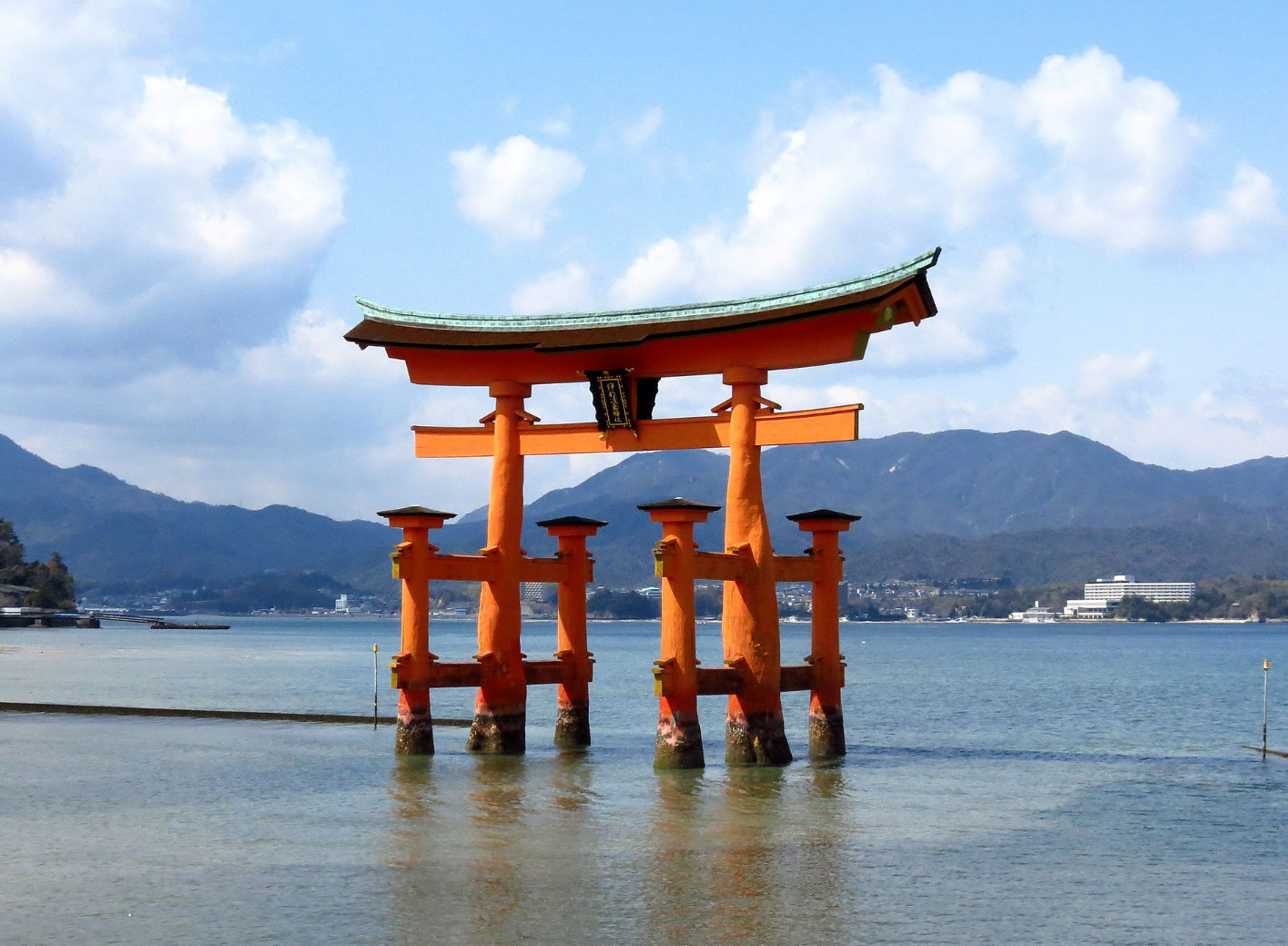
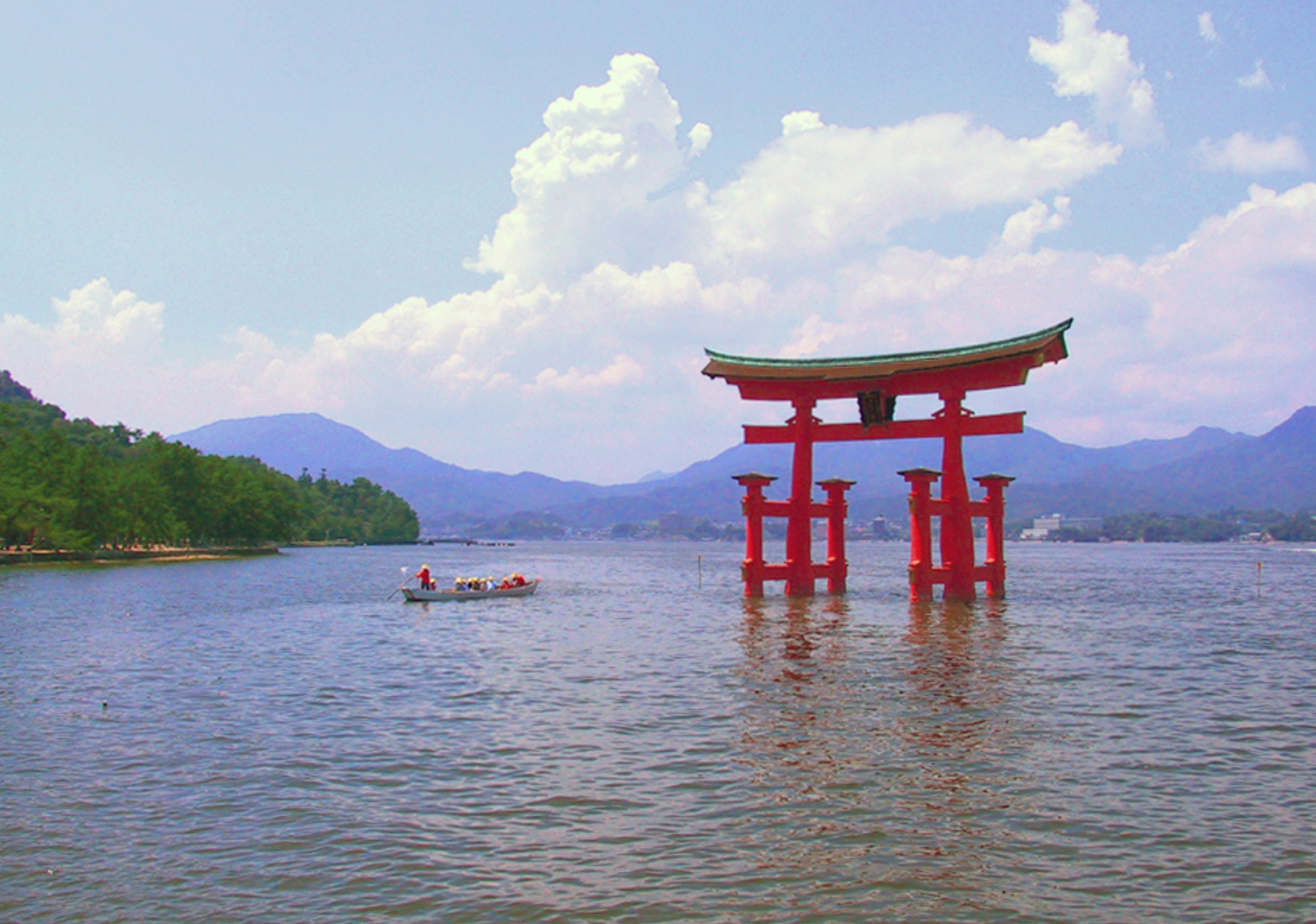


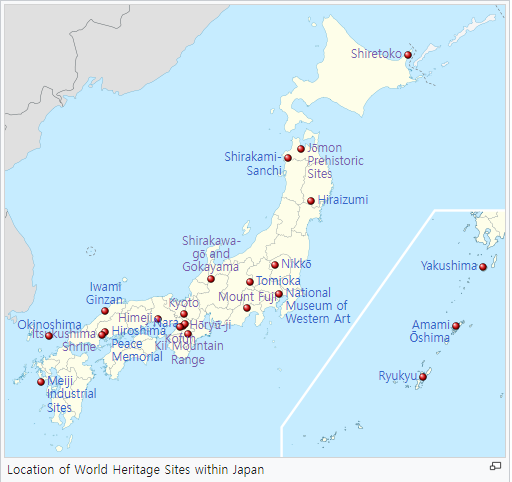
@ 2023년 현재 유네스코에 등재된 일본 25개의 유적지 (25 sites in Japan listed on UNESCO as of 2023)
출처: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_World_Heritage_Sites_in_Japan
'여행' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 유네스코 세계 문화유산 브라질 (UNESCO in Brazil) (0) | 2024.05.16 |
|---|---|
| 유네스코 세계 문화유산 미국 (UNESCO in UnitedStates) (0) | 2024.04.24 |
| 유네스코 세계 문화유산 이란 (UNESCO in Iran) (6) | 2024.04.01 |
| 유네스코 세계 문화유산 러시아 (UNESCO in Russia) (2) | 2024.03.23 |
| 유네스코 세계문화유산 영국 (UNESCO in United Kingdom) (6) | 2024.03.14 |



