
유엔교육과학문화기구(UNESCO) 세계유산은 1972년에 설립된 유네스코 세계유산협약에 기술된 바와 같이 문화유산 또는 자연유산에 중요한 장소입니다. 문화유산은 기념물(건축 작품, 기념비적인 조각 또는 비문과 같은), 건물의 그룹, 유적(고고학 유적지 포함)으로 구성됩니다. 과학, 보존 또는 자연미의 관점에서 중요한 자연적 특징(물리적 및 생물학적 형성으로 구성됨), 지질학적 및 생리학적 형성(위협을 받는 동식물의 서식지 포함), 자연 유적지는 자연유산으로 정의됩니다. 스페인은 1982년 5월 4일 협약을 비준하여 역사적 유적지를 그 목록에 포함할 수 있는 자격을 얻었습니다.
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Heritage Sites are places of importance to cultural or natural heritage as described in the UNESCO World Heritage Convention, established in 1972. Cultural heritage consists of monuments (such as architectural works, monumental sculptures, or inscriptions), groups of buildings, and sites (including archaeological sites). Natural features (consisting of physical and biological formations), geological and physiographical formations (including habitats of threatened species of animals and plants), and natural sites which are important from the point of view of science, conservation or natural beauty, are defined as natural heritage. Spain ratified the convention on May 4, 1982, making its historical sites eligible for inclusion on the list.
스페인의 유적지들은 1984년 아르헨티나 부에노스 아이레스에서 열린 제8차 세계유산위원회 회의에서 처음으로 그 목록에 새겨졌습니다. 그 회의에서, 다섯 곳이 추가되었습니다: 가정의 여인 코르도바 대성당; 알함브라와 일반 생활, 그라나다; 부르고스 대성당; 마드리드 에스코리알의 수도원과 유적지; 그리고 바르셀로나의 파크 귈, 팔라우 귈, 카사 밀라입니다. 다섯 곳은 1985년에 추가되었고, 또 다른 네 곳은 1986년에 추가되었습니다. 1984년, 1985년, 그리고 1986년(스페인의 회원국 가입 첫 3년)을 제외하고, 2000년에 가장 많은 새로운 유적지가 그 해에 다섯 곳이 추가되었습니다. 2021년 현재, 스페인은 목록에 새겨진 총 49개의 유적지를 가지고 있는데, 이는 이탈리아(58개), 중국(56개), 독일(51개) 다음으로 국가당 네 번째로 많은 유적지인 프랑스와 같은 숫자입니다. 이 49개의 유적지 중, 43개는 문화적인 것이고, 4개는 자연적인 것이고, 2개는 혼합된 것(문화적인 그리고 자연적인 기준을 모두 충족하는 것), 이 기구의 선정 기준에 의해 결정됩니다.
Sites in Spain were first inscribed on the list at the 8th Session of the World Heritage Committee, held in Buenos Aires, Argentina in 1984. At that session, five sites were added: the Cathedral of Our Lady of the Assumption, Córdoba; The Alhambra and the Generalife, Granada; Burgos Cathedral; Monastery and Site of the Escorial, Madrid; and Park Güell, Palau Güell and Casa Milà, in Barcelona. Five sites were added in 1985, and another four in 1986. Apart from 1984, 1985, and 1986 (Spain's first three years as a member), 2000 saw the most new sites inscribed, with five that year. As of 2021, Spain has 49 total sites inscribed on the list, the same number as France, which is the fourth largest number of sites per country, only behind Italy (58), China (56), and Germany (51).Of these 49 sites, 43 are cultural, 4 are natural, and 2 are mixed (meeting both cultural and natural criteria), as determined by the organization's selection criteria.
세 곳은 발레아레스 제도에 위치해 있고 네 곳은 카나리아 제도에 있습니다. 네 곳은 초국가적입니다. 피리네오스 – 몬테 페르디도 세계 문화 유산은 프랑스와 공유되고, 코트 계곡과 시에가 베르데 지역의 선사시대 암석 문화 유산은 포르투갈과 공유됩니다. 알마덴은 슬로베니아의 이드리자 (Idrija) 옆에 새겨져 있습니다. 유럽의 카르파티아와 다른 지역의 고대 및 원시 너도밤나무 숲은 17 개의 다른 유럽 국가들과 공유됩니다.
Three sites are located in the Balearic Islands and four are in the Canary Islands. Four sites are transnational. The Pirineos – Monte Perdido World Heritage Site is shared with France, while the Prehistoric Rock-Art Sites in the Côa Valley and Siega Verde site is shared with Portugal. Almadén is inscribed alongside Idrija in Slovenia. The Ancient and Primeval Beech Forests of the Carpathians and Other Regions of Europe are shared with 17 other European countries.
게다가, 스페인은 유네스코와 스페인 신탁 기금이라고 알려진 협약을 맺었습니다. 이 협약은 2002년 4월 18일 유네스코의 스페인 대사이자 상임 대표인 프란시스코 비야르와 유네스코 사무총장인 고이치로 마츠우라 사이에 서명되었습니다. 그 기금은 선택된 프로그램에 매년 60만 유로를 제공합니다. 그 프로그램은 특히 라틴 아메리카의 다른 회원국들에게 추천 절차와 잠정적인 장소 평가와 같은 프로젝트를 돕는 것을 포함합니다. 스페인은 2008년과 2009년에 세계 유산 위원회의 의장으로 일했고, 2009년에는 안달루시아의 세비야에서 제33차 위원회를 개최했습니다.
Additionally, Spain has established an agreement with UNESCO known as the Spanish Funds-in-Trust. The agreement was signed on April 18, 2002, between Francisco Villar, Spanish Ambassador and Permanent Delegate to UNESCO, and the Director-General of UNESCO, Kōichirō Matsuura. The fund provides €600,000 annually to a chosen program. Programs include helping other member states, particularly in Latin America, with projects such as nominations processes and assessing tentative sites. Spain served as the chair of the World Heritage Committee in 2008 and 2009, and in 2009 hosted the 33rd Session of the Committee in Seville, Andalusia.
@ Old Town of Segovia and its Aqueduct
서기 50년경에 지어진 것으로 추정되는 세고비아의 로마 수도교는 현저하게 잘 보존되어 있습니다. 두 개의 아치가 있는 이 인상적인 건축물은 세고비아의 장엄한 역사적인 도시의 배경의 일부를 형성합니다. 다른 중요한 기념물로는 약 11세기에 시작된 알카자르 성당과 16세기 고딕 양식의 대성당이 있습니다.
The Roman aqueduct of Segovia, probably built c. A.D. 50, is remarkably well preserved. This impressive construction, with its two tiers of arches, forms part of the setting of the magnificent historic city of Segovia. Other important monuments include the Alcázar, begun around the 11th century, and the 16th-century Gothic cathedral.

@ Historic Centre of Córdoba
원래의 목록은 8세기에 모스크로 개조된 7세기 가톨릭 교회인 코르도바의 위대한 모스크였습니다. 13세기에 페르디난트 3세에 의해 로마 가톨릭 대성당으로 복원되었습니다. 무어인들이 이 지역을 통치했던 전성기 기간 동안, 코르도바는 콘스탄티노플, 다마스쿠스, 바그다드와 비교할 때 300개 이상의 모스크와 건축물을 가지고 있었습니다.
The original listing was the Great Mosque of Córdoba, a 7th-century Catholic Church converted to a mosque in the 8th century; restored to a Roman Catholic cathedral in the 13th century by Ferdinand III. During the high period of the Moorish rule of the region, Córdoba had over 300 mosques and architecture that compared to that of Constantinople, Damascus, and Baghdad.

@ Burgos Cathedral
부르고스의 여인은 일드 프랑스의 대성당들과 같은 시기인 13세기에 시작되었고 15세기와 16세기에 완성되었습니다. 고딕 예술의 전체 역사는 그것의 뛰어난 건축과 회화, 합창단 좌판, 레레도, 무덤과 스테인드글라스 창문을 포함한 독특한 예술 작품들의 컬렉션으로 요약됩니다.
Our Lady of Burgos was begun in the 13th century at the same time as the great cathedrals of the Ile-de-France and was completed in the 15th and 16th centuries. The entire history of Gothic art is summed up in its superb architecture and its unique collection of works of art, including paintings, choir stalls, reredos, tombs and stained-glass windows.
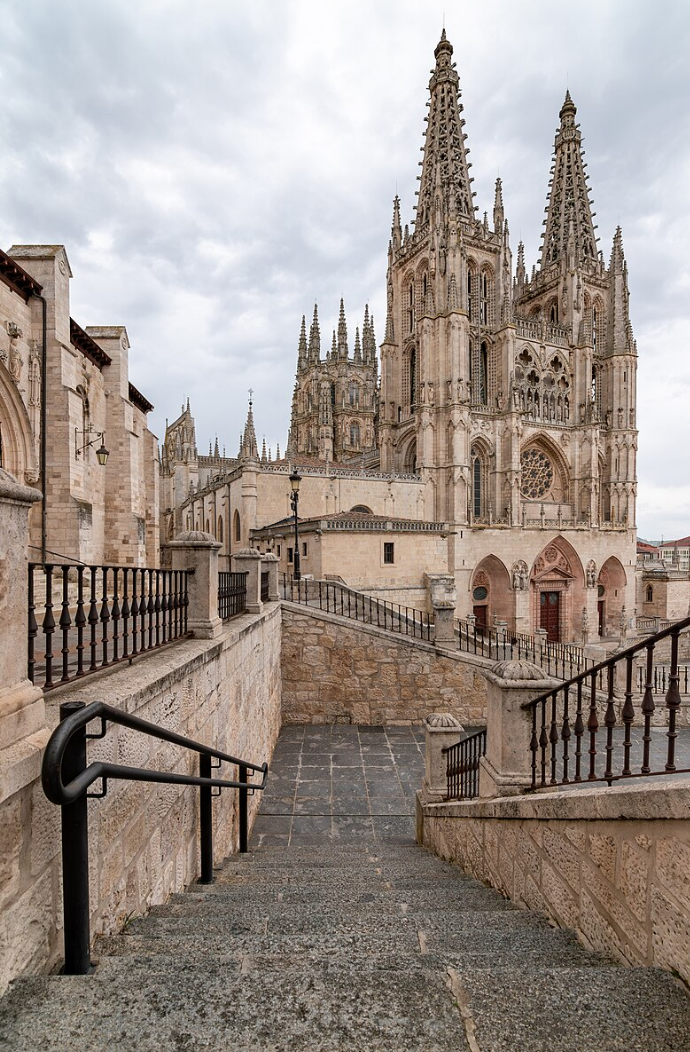

@ Monastery and Site of the Escorial
엘 에스코리알(El Escorial)은 왕실의 거주지로서의 역사로 인해 여러 스페인 왕실 유적지 중 하나입니다. 이 궁전은 필립 2세와 건축가 후안 바우티스타 데 톨레도(Juan Bautista de Toledo)에 의해 기독교 세계에서 스페인의 중심 역할에 대한 기념물로 설계되었습니다
El Escorial is one of several Spanish royal sites due to its history as a residence of the royal family. The palace was designed by King Philip II and architect Juan Bautista de Toledo to serve as a monument to Spain's central role in the Christian world
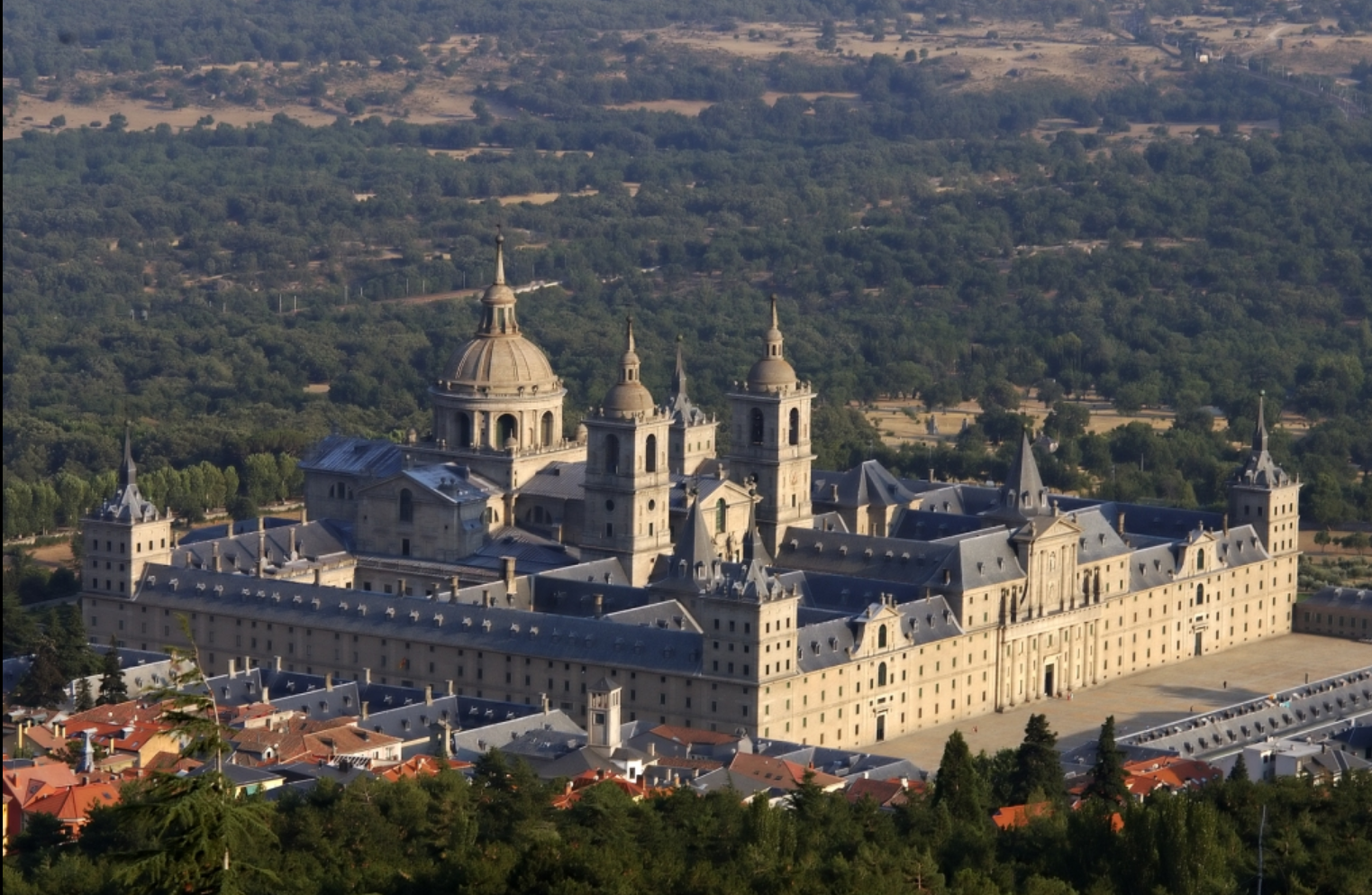

@ Works of Antoni Gaudí
안토니 가우디(Antoni Gaudí)의 건축물은 모더니즘 양식의 일부이지만, 그의 디자인은 매우 독특한 것으로 묘사됩니다. 원래 목록에는 구엘 공원(Park Güell), 팔라우 구엘(Palau Güell), 카사 밀라(Casa Mila)가 등장했습니다. 2005년 확장판에는 카사 비센(Casa Vicens), 사그라다 파밀리아(Sagrada Família)의 지하실 및 그리스도 성탄화 정면, 카사 바텔로(Casa Batllo), 콜 ò니아 구엘(Col agnia Güell)의 지하실이 추가되었습니다.
The architecture of Antoni Gaudí is part of the Modernist style, but his designs are described as highly unique. The original listing featured Park Güell, Palau Güell, and Casa Milà; the 2005 extension added Casa Vicens, the crypt and nativity façade of Sagrada Família, Casa Batlló, and the crypt at Colònia Güell.
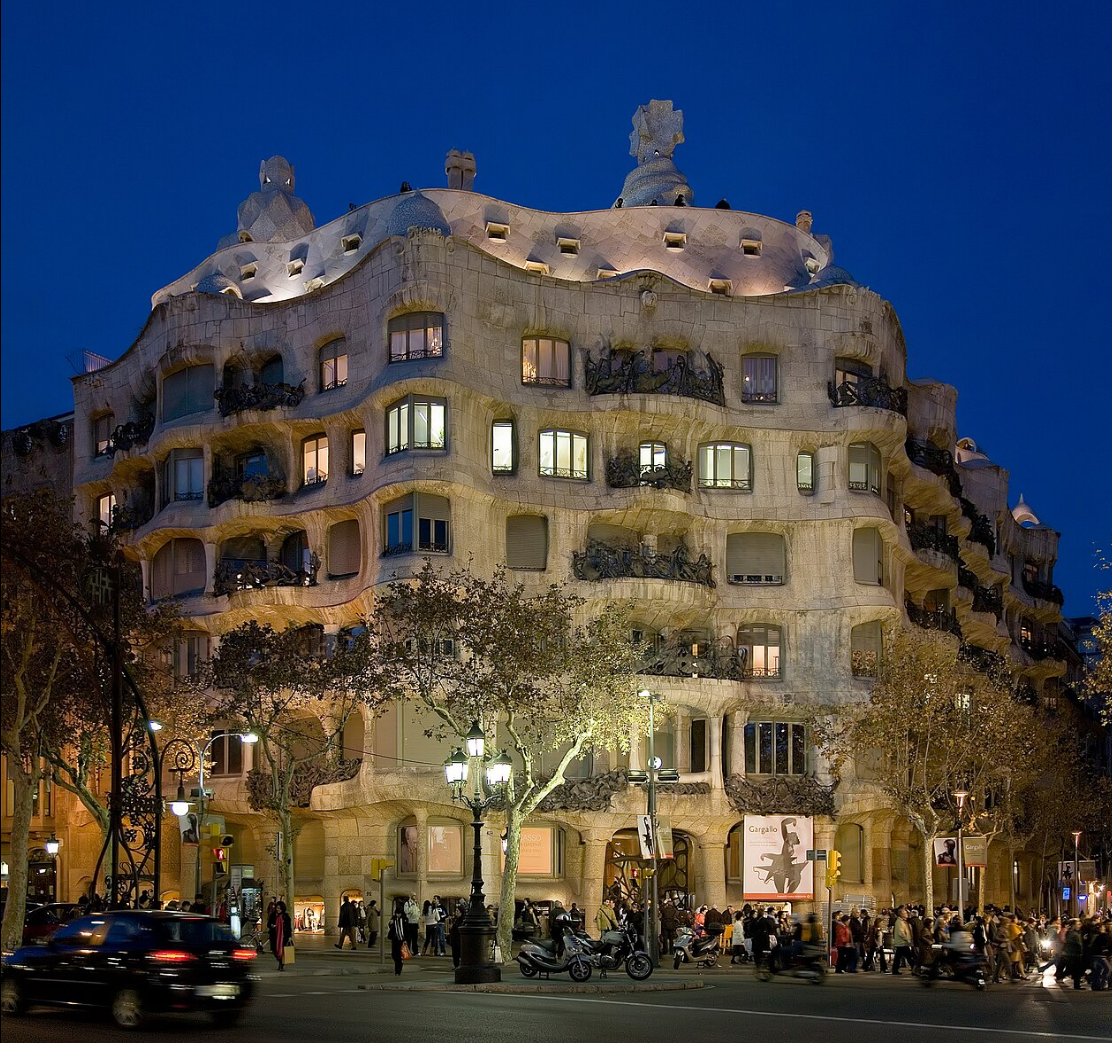

@ Santiago de Compostela (Old Town)
산티아고 데 콤포스텔라 대성당은 유명한 사도 야고보의 매장지이며, 스페인 북부를 가로지르는 순례길인 성 야고보의 종착역입니다. 그 마을은 10세기에 이슬람교도들에 의해 파괴되었고, 다음 세기에 재건되었습니다.
The Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela is the reputed burial-place of the apostle James, and is the terminus of the Way of St. James, a pilgrimage across northern Spain. The town was destroyed by Muslims in the 10th century and rebuilt during the following century.

@ Historic City of Toledo
톨레도는 로마인들에 의해 세워졌고, 서고트족 왕국의 수도 역할을 했고, 이슬람교도 스페인과 레콘키스타 시대에 중요했고, 잠시 스페인의 수도 역할을 했습니다. 그 도시는 기독교, 이슬람교도, 그리고 유대인의 영향을 결합하고 있습니다.
Toledo was founded by the Romans, served as the capital of the Visigothic Kingdom, was important in Muslim Spain and during the Reconquista, and briefly served as the capital of Spain. The city combines Christian, Muslim, and Jewish influences.

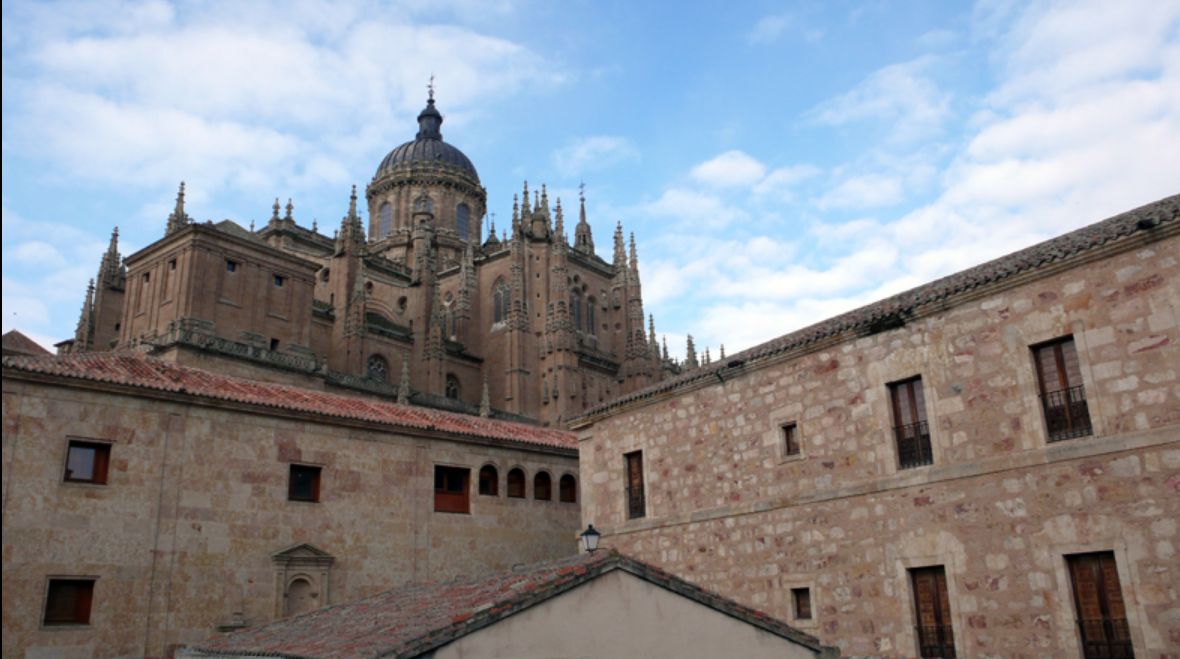
@ Old City of Salamanca
살라망카는 1218년에 설립된 살라망카 대학이 스페인에서 가장 오래된 대학이고 유럽에서 가장 오래된 대학 중 하나이기 때문에 대학 도시로서 중요합니다. 그 도시는 3세기에 카르타고에 의해 처음 정복되었고, 나중에 로마인과 무어인에 의해 지배되었습니다. 그 도시의 중심은 로마네스크, 고딕, 무어인, 르네상스, 바로크 건축을 나타냅니다.
Salamanca is important as a university city, as the University of Salamanca, founded in 1218, is the oldest in Spain and among the oldest in Europe. The city was first conquered by the Carthaginians in the 3rd century, and later ruled by the Romans and Moors. The city centre represents Romanesque, Gothic, Moorish, Renaissance, and Baroque architecture.

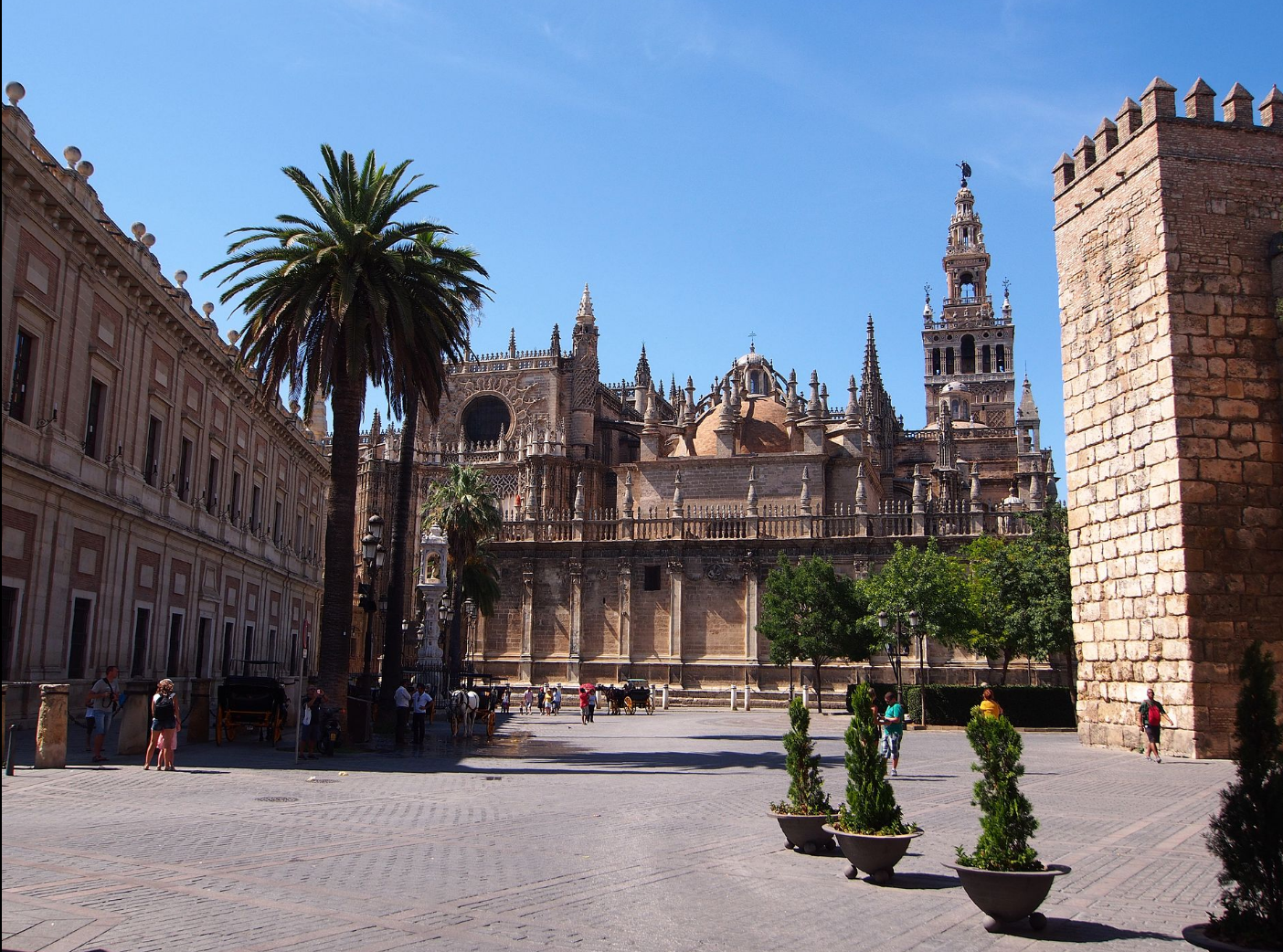
@ Cathedral, Alcázar and Archivo de Indias in Seville
알카자르는 레콘키스타까지 남부 스페인을 통치했던 알모하드 왕조 동안 지어졌습니다. 그 대성당은 15세기로 거슬러 올라가고 페르디난트 3세와 크리스토퍼 콜럼버스의 무덤이 있습니다. 그 기록 보관소는 아메리카 대륙의 식민지화에 관한 문서들을 보관하고 있습니다.
The Alcázar was built during the Almohad dynasty that ruled southern Spain until the Reconquista. The cathedral dates to the 15th century and holds the tombs of Ferdinand III and Christopher Columbus. The Archivo (Archive) houses documents relating to the colonization of the Americas.

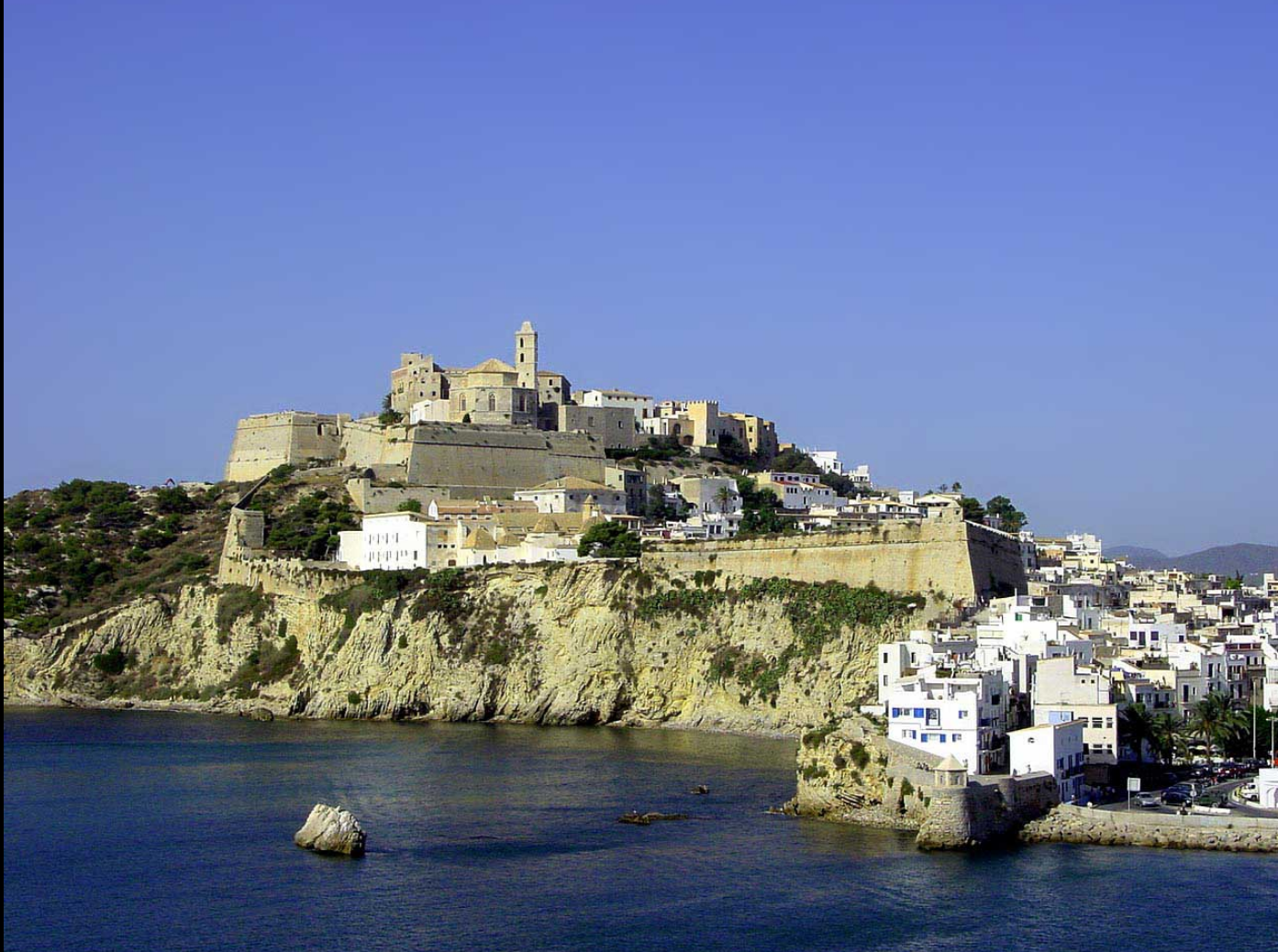
@ Ibiza, Biodiversity and Culture
이비자 해안은 다양한 해안 및 해양 생태계를 지원하는 지중해에서만 발견되는 해초인 포시도니아 오시아니카의 본거지입니다. 이 섬은 또한 많은 페니키아 유적을 포함하고 있으며, 도시의 요새화되고 벽으로 둘러싸인 오래된 부분은 16세기로 거슬러 올라갑니다.
The coast of Ibiza is home to posidonia oceanica, a seagrass only found in the Mediterranean that supports a diverse coastal and marine ecosystem. The island also contains numerous Phoenician ruins, and the fortified and walled older portions of the city date to the 16th century.

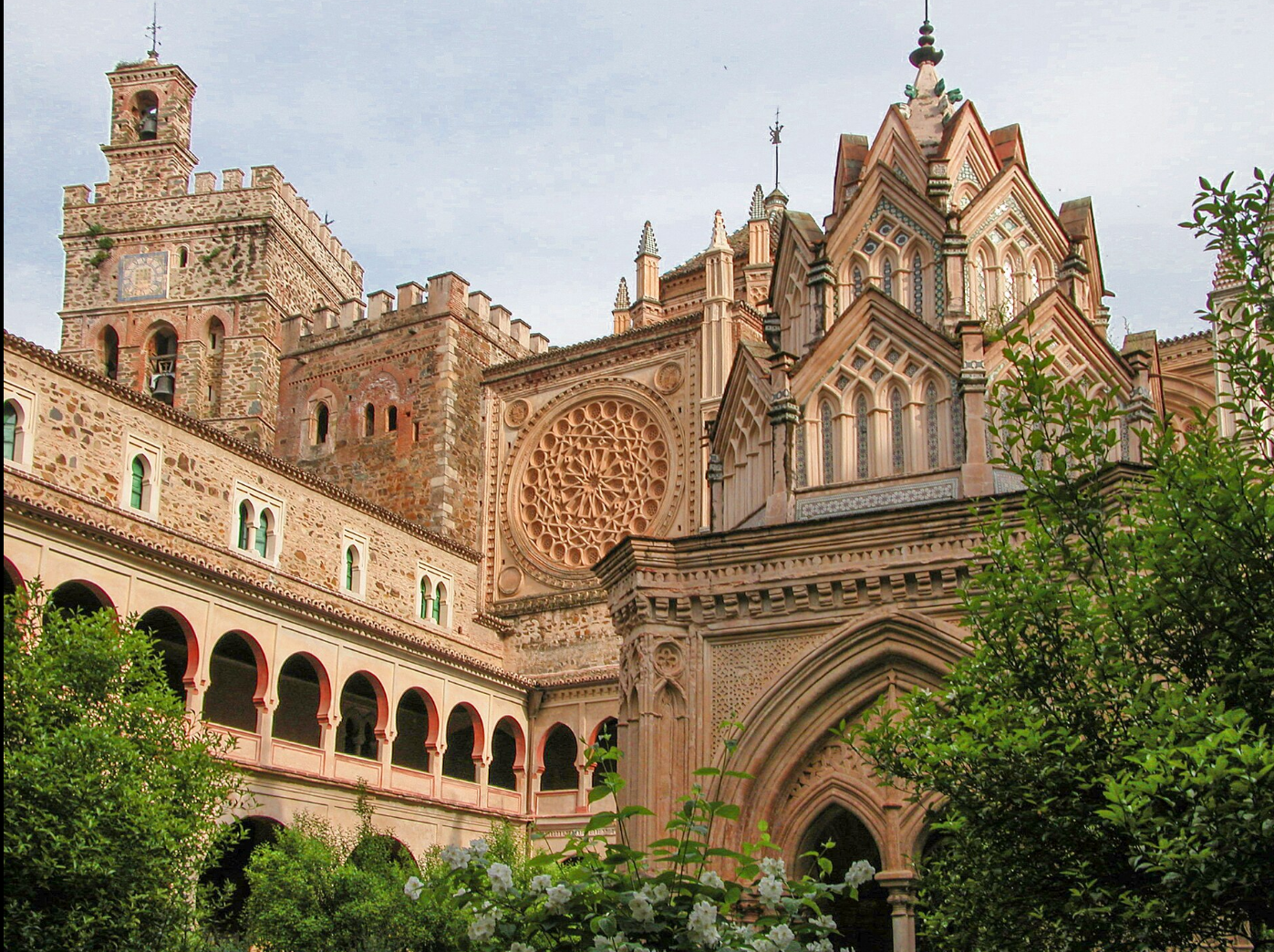
@ Royal Monastery of Santa María de Guadalupe
이 수도원은 714년 이슬람 침략자들로부터 묻힌 후 13세기에 발견된 마리아의 성지인 과달루페 성모 마리아의 본거지입니다. 과달루페의 성모와 수도원은 리콘키스타 기간 동안 중요한 상징물의 역할을 했고, 콜럼버스가 아메리카를 발견한 같은 해인 1492년에 절정에 이르렀습니다. 과달루페 성모는 아메리카의 복음화 기간 동안 중요한 상징물이 되었습니다.
The monastery is home of Our Lady of Guadalupe, a shrine to Mary found in the 13th century after being buried from Muslim invaders in 714. The Virgin of Guadalupe and the monastery served as important symbols during the Reconquista, culminating in 1492, the same year as Columbus' discovery of America. The Guadalupe Virgin became an important symbol during the evangelization of America.

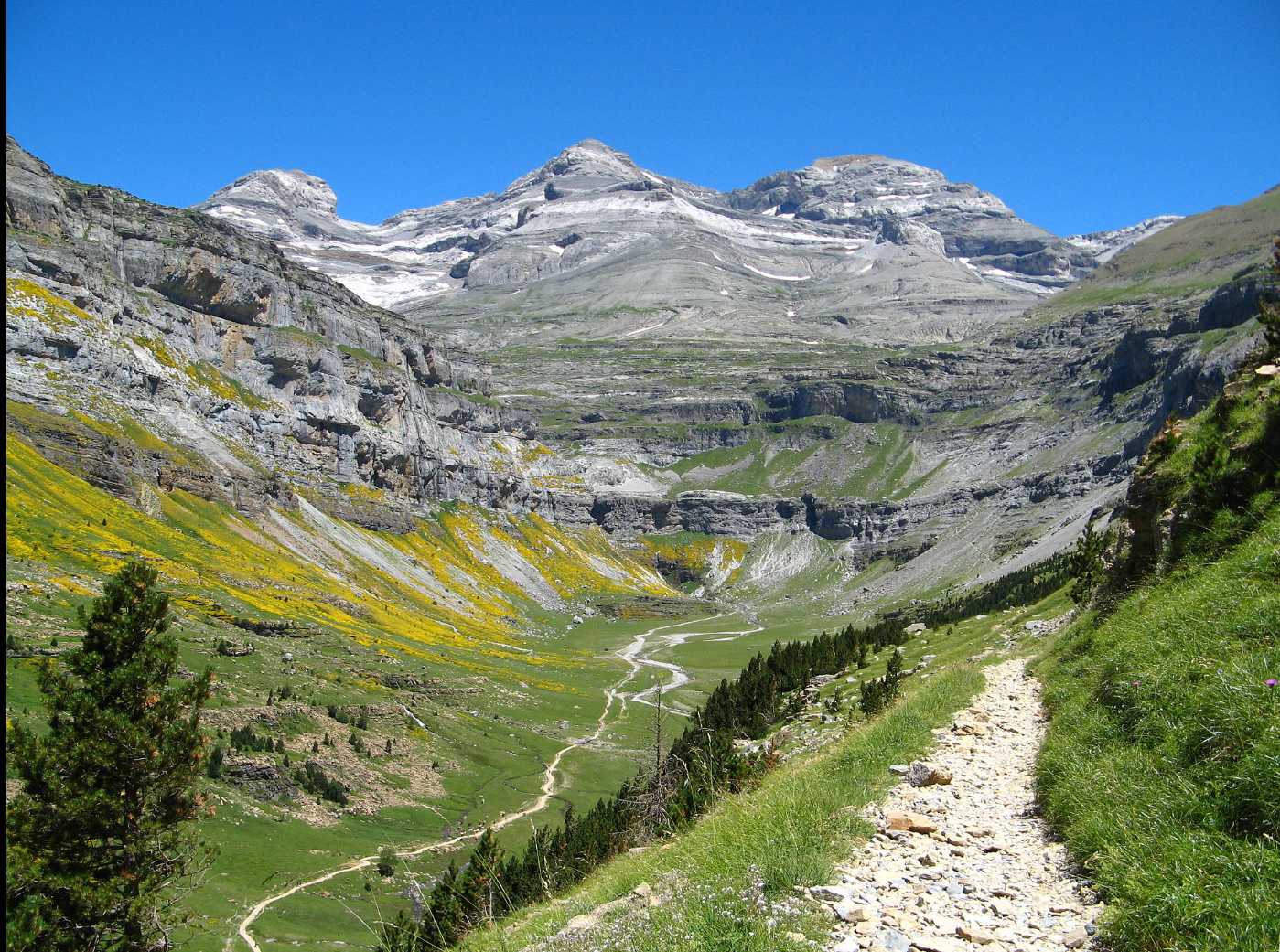
@ Pirineos – Monte Perdido
그 지역은 프랑스와 스페인 국경을 따라 피레네 산맥을 포함하고 있습니다. 스페인 부분은 유럽에서 가장 큰 협곡 두 개를 포함하고 있는 반면, 프랑스 쪽은 세 개의 큰 원형 벽을 포함하고 있습니다.
he site contains the Pyrenees mountain chain along the French-Spanish border. The Spanish portion contains two of the largest canyons in Europe, while the French side contains three large cirque walls.

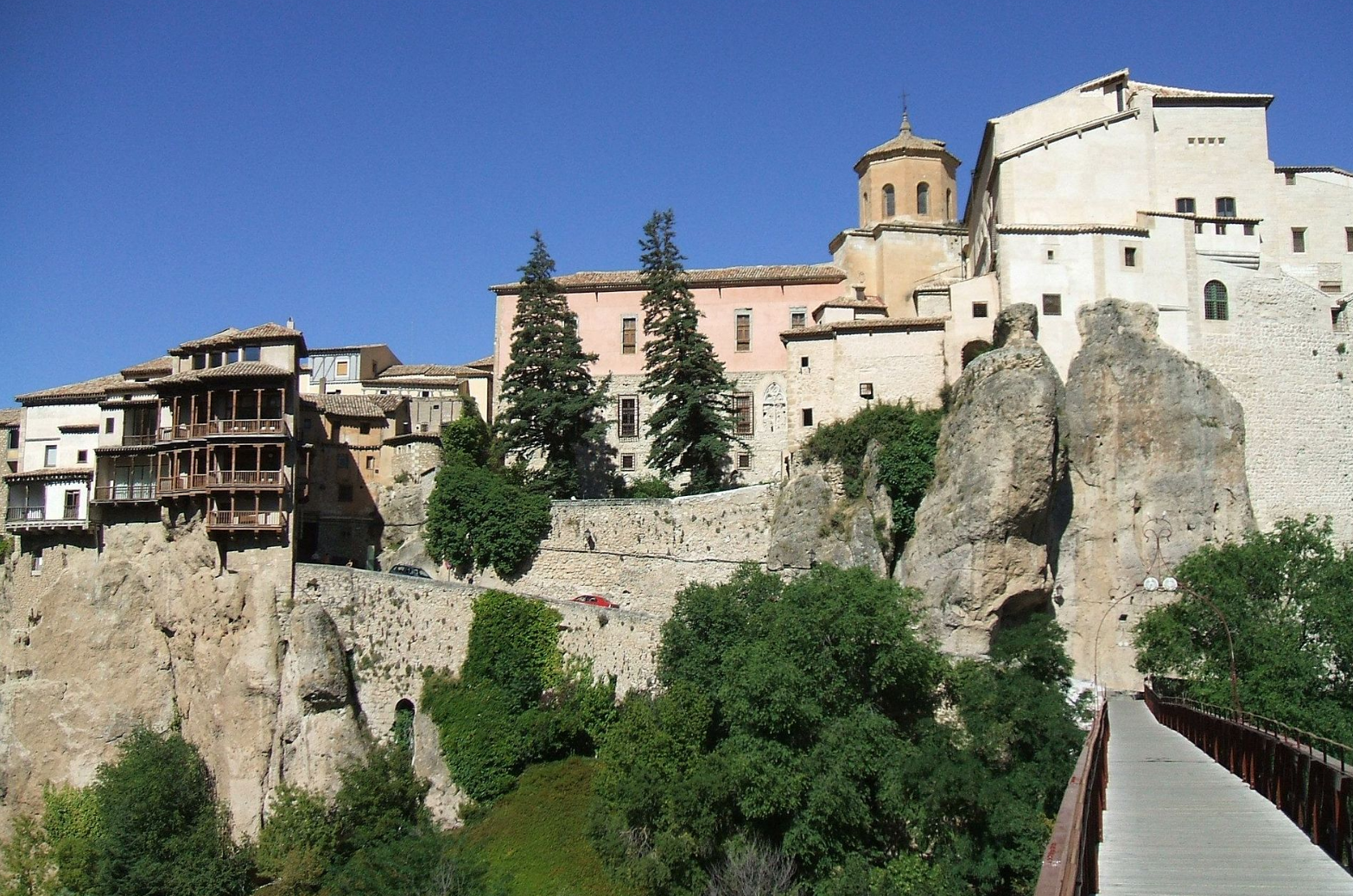
@ Historic Walled Town of Cuenca
무어인들은 8세기 초에 요새화된 도시를 지었고, 그것은 12세기에 기독교인들에게 사로잡혔습니다. 그 대성당은 스페인에서 첫 번째 고딕 양식의 본보기입니다. 그 마을은 또한 절벽 끝에 걸려 있는 집들인 카사스 콜가다로 유명합니다.
The Moors built the fortified city in the early 8th century, and it was captured by the Christians in the 12th century. The cathedral is the first Gothic example in Spain. The town is also famous for its casas colgadas, houses that hang over the edge of a cliff.

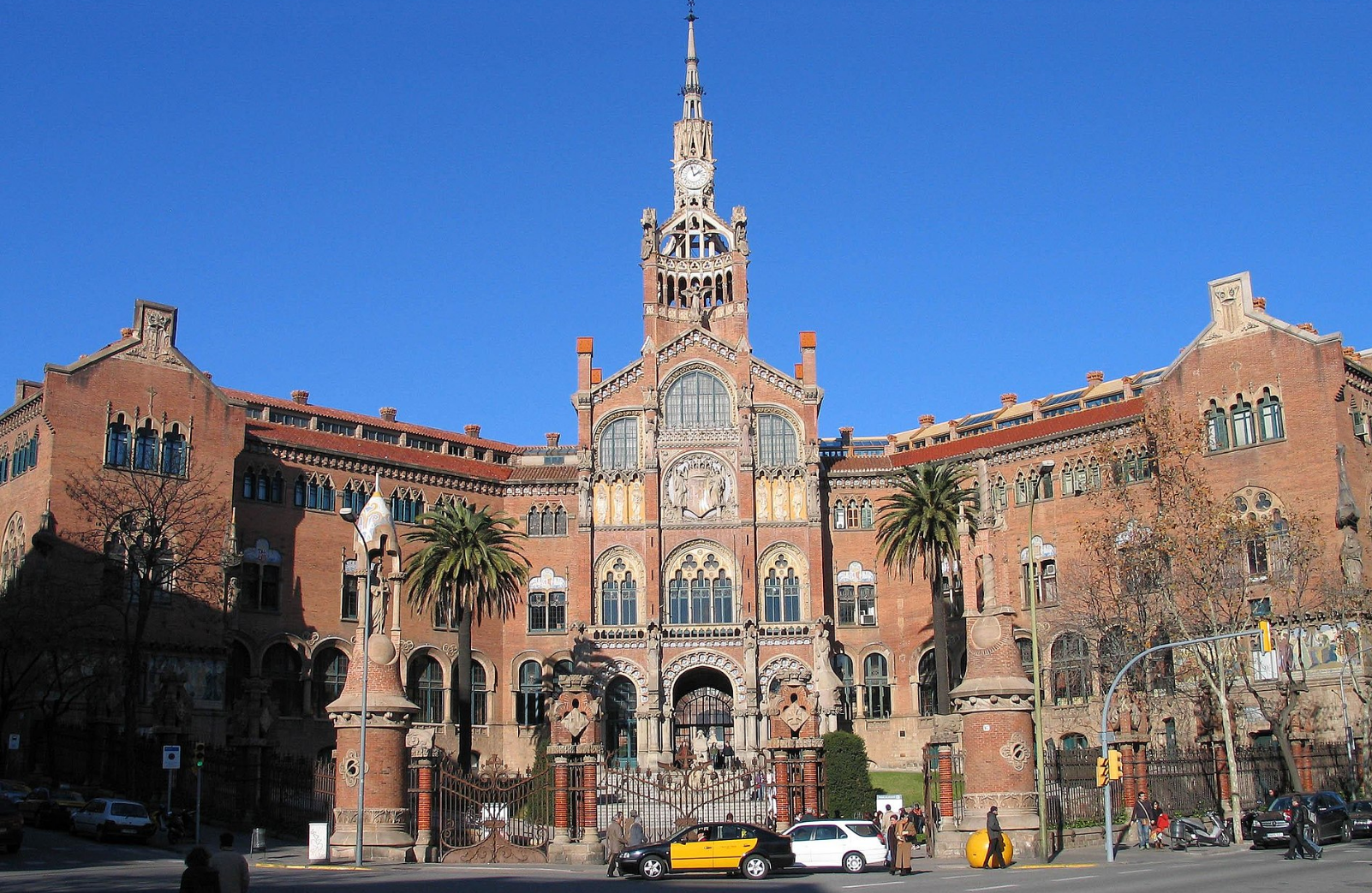
@ Palau de la Música Catalana and Hospital de Sant Pau, Barcelona
두 건물은 모두 20세기 초에 지어졌고 그 시기에 바르셀로나에서 매우 인기 있었던 모더니즘 아르누보 운동에서 Lluiis Domènechi Montaner에 의해 설계되었습니다. 두 건물은 Montaner의 가장 유명한 작품들입니다.
Both buildings were constructed in the early 20th century and designed by Lluís Domènech i Montaner in the modernist Art Nouveau movement that was very popular in Barcelona in that period. The two buildings are Montaner's most famous works.

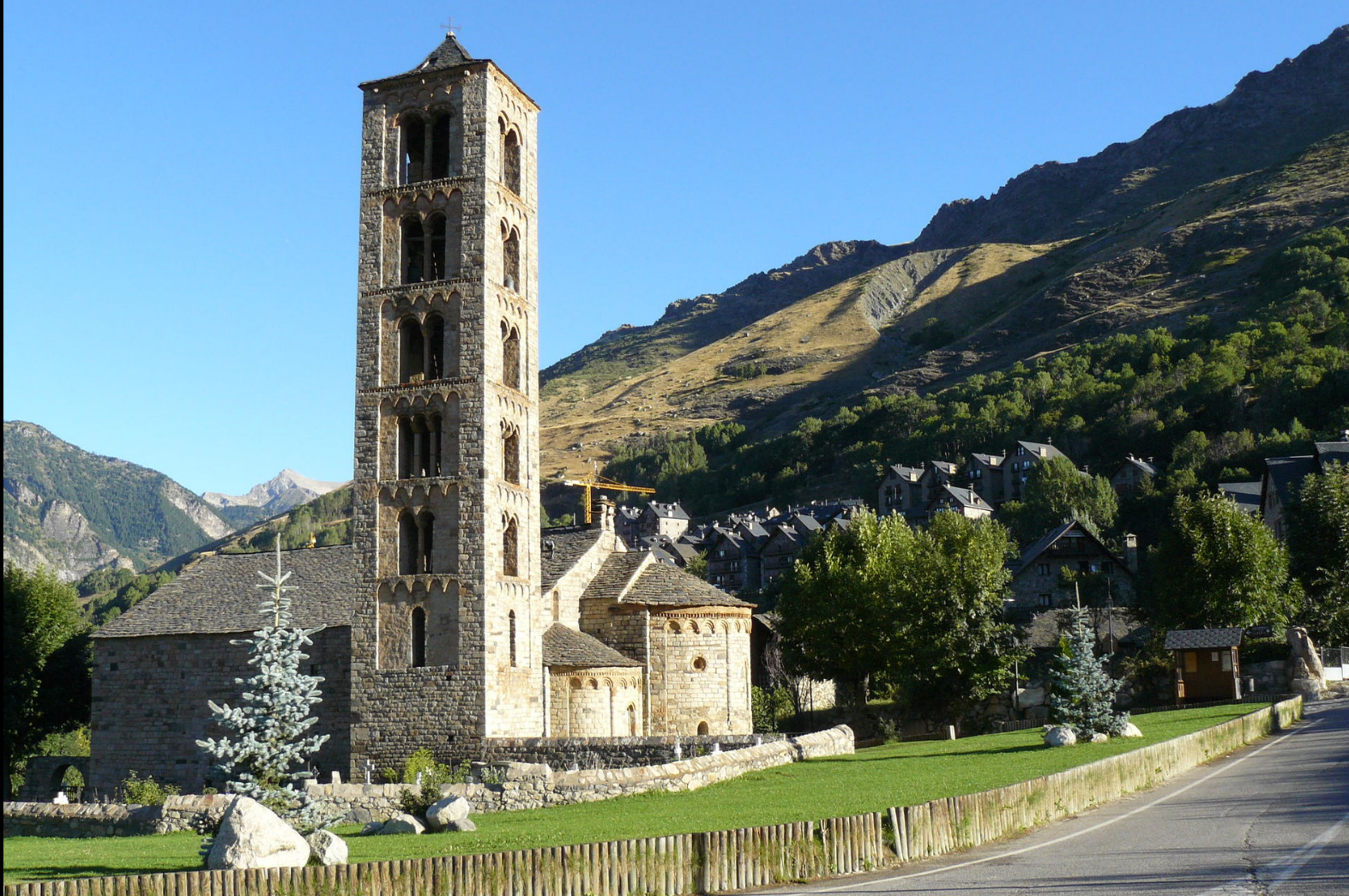
@ Catalan Romanesque Churches of the Vall de Boí
피레네 산맥 가장자리의 작은 계곡에는 로마네스크 양식의 교회들이 로마네스크 벽화, 조각상, 제단으로 장식되어 있습니다. 교회들은 높고 네모난 종탑으로 독특합니다.
The small valley at the edge of the Pyrenees contains churches in Romanesque style decorated with Romanesque murals, statues, and altars. The churches are unique for their tall, square bell towers.

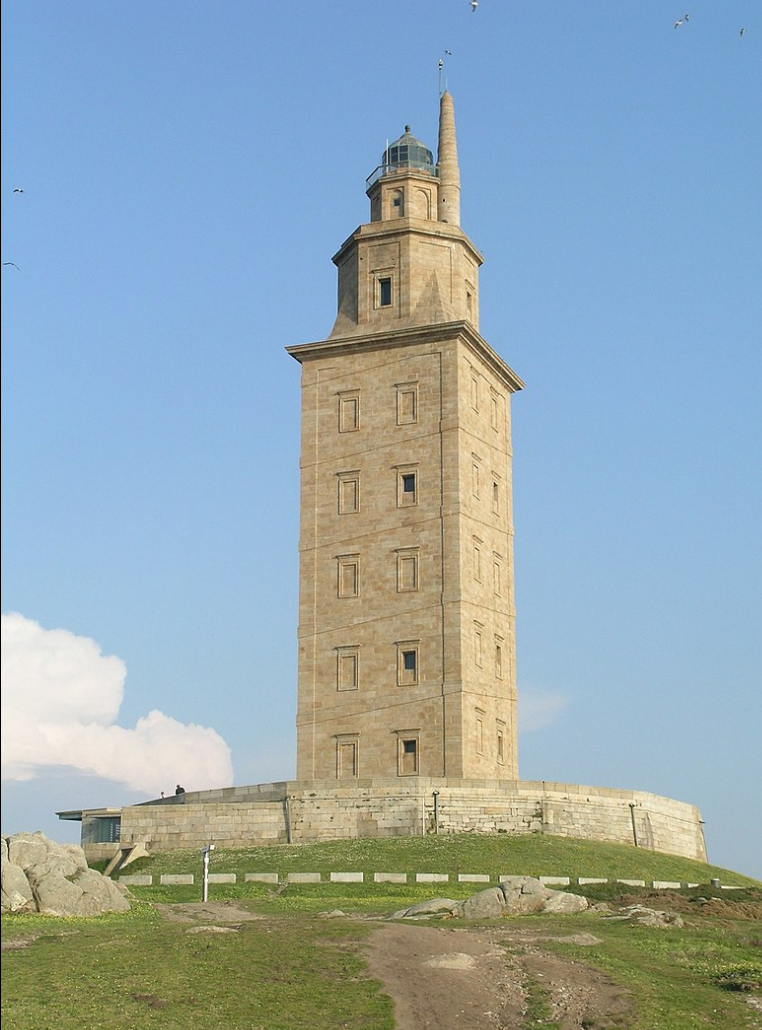
@ Tower of Hercules
로마인들은 A 코루냐 항구의 입구를 표시하기 위해 57미터(187피트) 바위에 55미터(180피트)의 등대를 지었습니다. 그것은 완전히 보존되고 작동하는 유일한 로마 등대입니다.
The Romans built this 55 metres (180 ft) lighthouse on a 57 metres (187 ft) rock to mark the entrance to the A Coruña harbor. It is the only fully preserved and functioning Roman lighthouse.

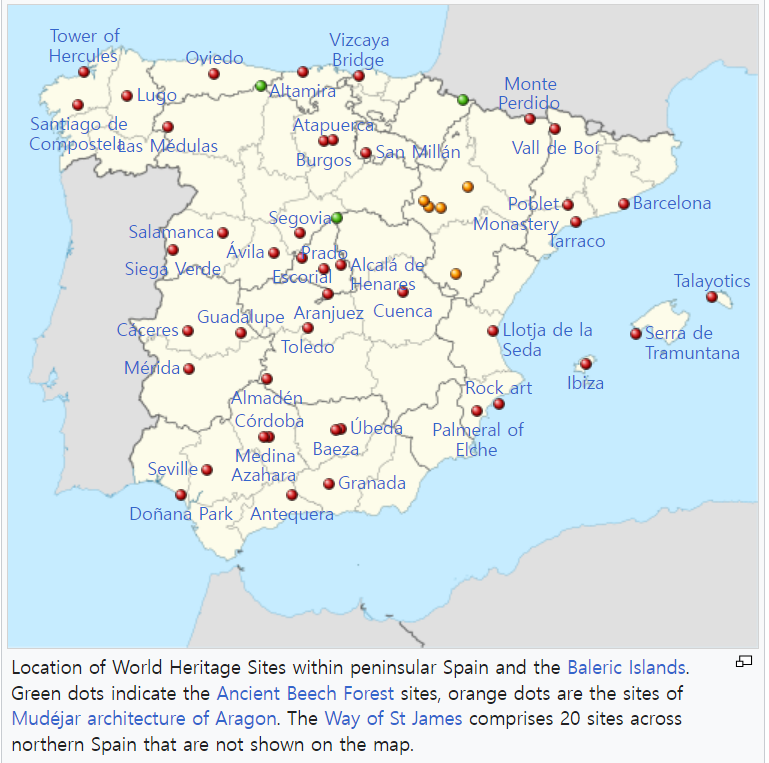
@ 2023년 현재 유네스코에 등재된 스페인 49개의 유적지 (49 sites in Spain listed on UNESCO as of 2023)
출처 : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_World_Heritage_Sites_in_Spain
'여행' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 유네스코 세계문화유산 멕시코 (UNESCO in Mexico) (2) | 2024.03.07 |
|---|---|
| 유네스코 세계문화유산 인도 (UNESCO in India) (4) | 2024.02.28 |
| 유네스코 세계문화유산 독일 (UNESCO in Germany) (0) | 2024.01.19 |
| 유네스코 세계문화유산 프랑스편 (UNESCO in France) (4) | 2024.01.11 |
| 유네스코 세계문화유산 중국편 (UNESCO in China) (2) | 2024.01.05 |



