
유네스코 세계문화유산 인도 (UNESCO in India)
유엔교육과학문화기구(UNESCO)는 1972년에 설립된 유네스코 세계유산협약에 서명한 국가들에 의해 지명된 문화유산 또는 자연유산에 대해 탁월한 보편적 가치가 있는 세계유산을 지정합니다. 문화유산은 기념물(건축 작품, 기념비적인 조각 또는 비문과 같은), 건물 그룹, 유적지(고고학적 유적지 포함)로 구성됩니다. 자연적인 특징(물리적 및 생물학적인 형성으로 구성됨), 지질학적인 형성(위협을 받는 동식물 종의 서식지를 포함함), 그리고 과학, 보존 또는 자연미의 관점에서 중요한 자연 유적지는 자연유산으로 정의됩니다. 인도는 1977년 11월 14일 협약을 수락하여 해당 유적지를 목록에 포함할 수 있는 자격을 얻었습니다.
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) designates World Heritage Sites of outstanding universal value to cultural or natural heritage which have been nominated by countries which are signatories to the UNESCO World Heritage Convention, established in 1972. Cultural heritage consists of monuments (such as architectural works, monumental sculptures, or inscriptions), groups of buildings, and sites (including archaeological sites). Natural features (consisting of physical and biological formations), geological and physiographical formations (including habitats of threatened species of animals and plants), and natural sites which are important from the point of view of science, conservation or natural beauty, are defined as natural heritage. India accepted the convention on 14 November 1977, making its sites eligible for inclusion on the list.
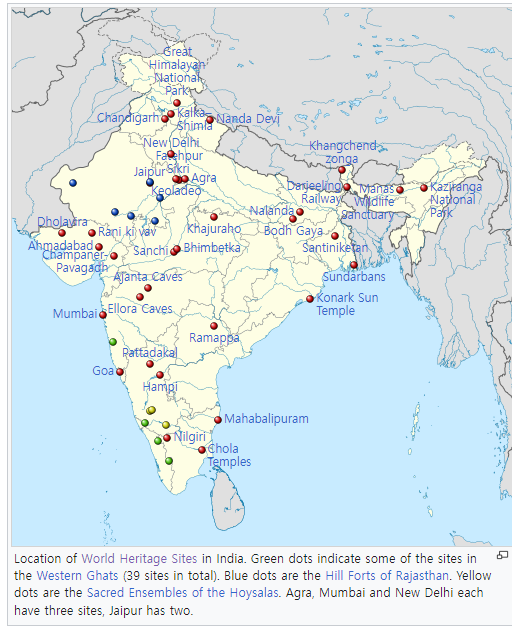
인도에는 42개의 세계문화유산이 있습니다. 이들 중, 34개는 문화유산이고, 7개는 자연유산이며, 한 곳인 Kangchendzonga 국립공원은 혼합형입니다. 인도는 세계적으로 여섯 번째로 많은 유적지를 가지고 있습니다. 첫 번째로 등재된 유적지는 아잔타 동굴, 엘로라 동굴, 아그라 요새, 타지마할로, 모두 세계문화유산위원회의 1983년 회기에 등재되었습니다. 가장 최근에 등재된 유적지는 2023년에 산티니케탄과 호이살라 사원입니다. 다른 시기에, 두 곳이 멸종위기에 처한 곳으로 등재되었습니다: 마나스 야생동물 보호구역은 밀렵과 보도 민병대의 활동으로 인해 1992년에서 2011년 사이에, 함피의 기념물은 교통량 증가와 주변 신축으로 인한 위험으로 인해 1999년에서 2006년 사이에 등재되었습니다. 한 곳은 초국가적입니다. 르 코르뷔지에 건축 작업은 다른 6개국과 공유됩니다. 게다가, 인도는 잠정 목록에 50개의 유적지가 있습니다.
There are 42 World Heritage Sites in India. Out of these, 34 are cultural, seven are natural, and one, Khangchendzonga National Park, is of mixed type. India has the sixth-most sites worldwide. The first sites to be listed were the Ajanta Caves, Ellora Caves, Agra Fort, and Taj Mahal, all of which were inscribed in the 1983 session of the World Heritage Committee. The most recent sites listed were Santiniketan and the Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysalas, in 2023. At different times, two sites were listed as endangered: the Manas Wildlife Sanctuary was listed between 1992 and 2011 due to poaching and the activities of Bodo militias, and the monuments at Hampi were listed between 1999 and 2006 due to risks from increased traffic and new constructions in surroundings. One site is transnational: The Architectural Work of Le Corbusier is shared with six other countries. In addition, India has 50 sites on its tentative list.
@ Ajanta Caves
아잔타에 있는 동굴들은 두 시대의 불교 예술의 집합체를 나타냅니다. 최초의 기념물들은 기원전 2세기와 1세기로 거슬러 올라가고, 테라바다 불교의 추종자들에 의해 만들어졌습니다. 더 많은 기념물들은 대승불교의 추종자들에 의해 바카타카 왕조 동안인 서기 5세기와 6세기에 추가되었습니다. 그 기념물들은 불교 예술의 걸작들이고 인도와 더 넓은 지역, 특히 자바에서 강력한 예술적인 영향력을 행사했습니다.
The caves at Ajanta represent a collection of Buddhist art from two periods. The first monuments date to the 2nd and 1st centuries BCE and were created by the followers of Theravada Buddhism. Further monuments were added in the 5th and 6th centuries CE, during the Vakataka dynasty, by the followers of Mahayana Buddhism. The monuments are masterpieces of Buddhist art and exerted strong artistic influence in India and the broader region, especially in Java.

@ Ellora Caves
엘로라 동굴은 7세기에서 11세기 사이에 2킬로미터(1.2마일) 길이의 현무암 절벽으로 깎인 34개의 사원과 수도원으로 구성되어 있습니다. 불교, 힌두교, 자이나교를 믿는 사람들에 의해 지어진 것이기 때문에, 그것들은 건설 당시의 종교적 관용을 보여줍니다. 가장 큰 사원은 조각과 그림으로 정교하게 장식된 카일라사 사원(사진)입니다.
The Ellora Caves comprise 34 temples and monasteries that were cut into a 2 km (1.2 mi) long basalt cliff between the 7th and 11th centuries. As they were built by followers of Buddhism, Hinduism, and Jainism, they illustrate the religious tolerance of the period when they were constructed. The largest temple is the Kailasa Temple (pictured), which is elaborately decorated with sculptures and paintings.

@ Taj Mahal
타지마할은 인도-이슬람 건축의 가장 훌륭한 예로 여겨집니다. 그것은 1631년과 1648년 사이에 무굴 황제 샤 자한의 페르시아인 아내 뭄타즈 마할의 묘로서 야무나 강둑의 아그라에 지어졌습니다. 그것은 우스타드 아흐마드 라호리에 의해 설계되었고 귀하고 반귀한 돌들로 상감된 하얀 대리석으로 지어졌습니다. 그 무덤은 4개의 독립된 작은 건물들에 의해 둘러싸여 있습니다. 그 단지는 정문, 모스크, 게스트 하우스, 그리고 주변의 정원들도 포함합니다.
The Taj Mahal is considered the finest example of Indo-Islamic architecture. It was built in Agra on the bank of the Yamuna river as a mausoleum of Mumtaz Mahal, the Persian wife of the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan, between 1631 and 1648. It was designed by Ustad Ahmad Lahori and built in white marble inlaid with precious and semi-precious stones. The tomb is surrounded by four free-standing minarets. The complex also includes the main gate, a mosque, a guesthouse, and surrounding gardens.

@ Sun Temple, Konârak
이 힌두교 사원은 13세기에 지어졌고 칼링가 건축의 가장 좋은 예들 중 하나입니다. 그것은 태양신 수리야의 전차를 나타냅니다: 외면에는 돌로 조각된 24개의 바퀴가 있고 여섯 마리의 말이 끄는 풍부하게 장식되어 있습니다. 다른 장식적인 모티브는 사자, 음악가, 무용가, 그리고 에로틱 장면을 포함합니다.
This Hindu temple was built in the 13th century and is one of the finest examples of Kalinga architecture. It represents the chariot of the solar deity Surya: on the outer sides, it has 24 wheels carved of stone and richly decorated, being pulled by six horses. Other decorative motifs include lions, musicians, dancers, and erotic scenes.

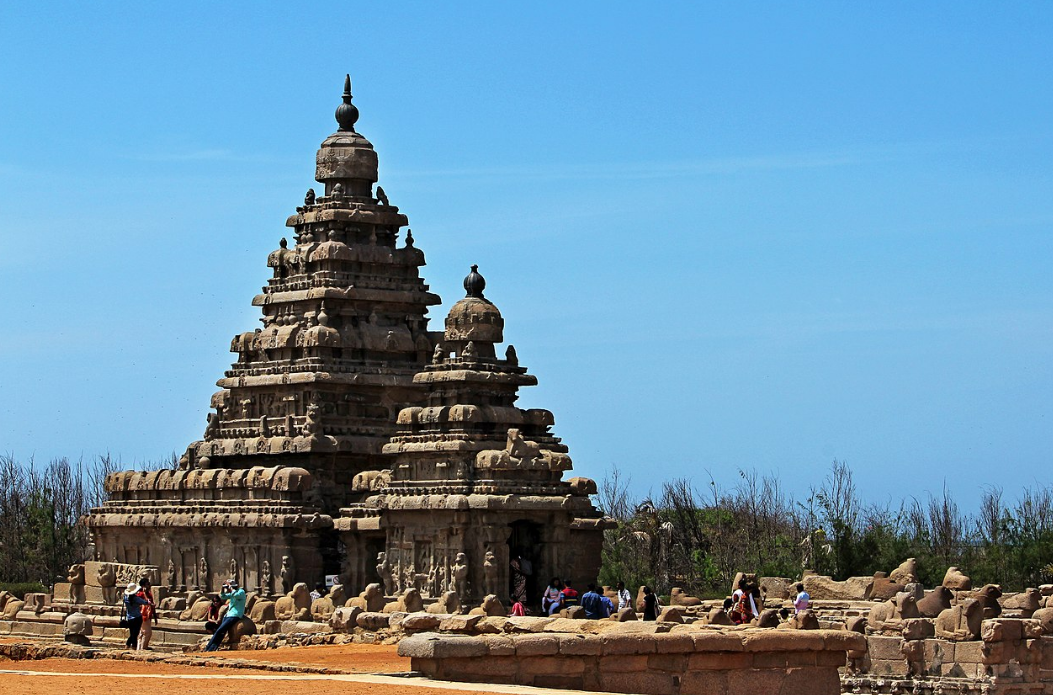
@ Group of Monuments at Mahabalipuram
마말라푸람 마을 주변의 기념물들은 팔라바 왕조 아래 7세기와 8세기에 지어졌습니다. 다른 종류의 기념물들이 있습니다: 전차 모양의 사원들인 라타스 (Dharmaraja Ratha); 만다파스 (암석을 깎아 만든 사원); 거대한 갠지스 강의 하강을 포함한 바위 부조; 해안 사원 (사진) 그리고 다른 사원들과 고고학적 유적들. 기념물들의 예술적인 표현은 캄보디아, 베트남, 그리고 자바를 포함한 더 넓은 지역에서 영향을 미쳤습니다.
The monuments around the town of Mamallapuram were built in the 7th and 8th centuries, under the Pallava dynasty. There are different types of monuments: the rathas, which are chariot-shaped temples (Dharmaraja Ratha); the mandapas (rock-cut temples); rock reliefs, including the giant Descent of the Ganges; Shore Temple (pictured) and other temples and archaeological remains. The artistic expression of the monuments was influential in the broader region, including Cambodia, Vietnam, and Java.

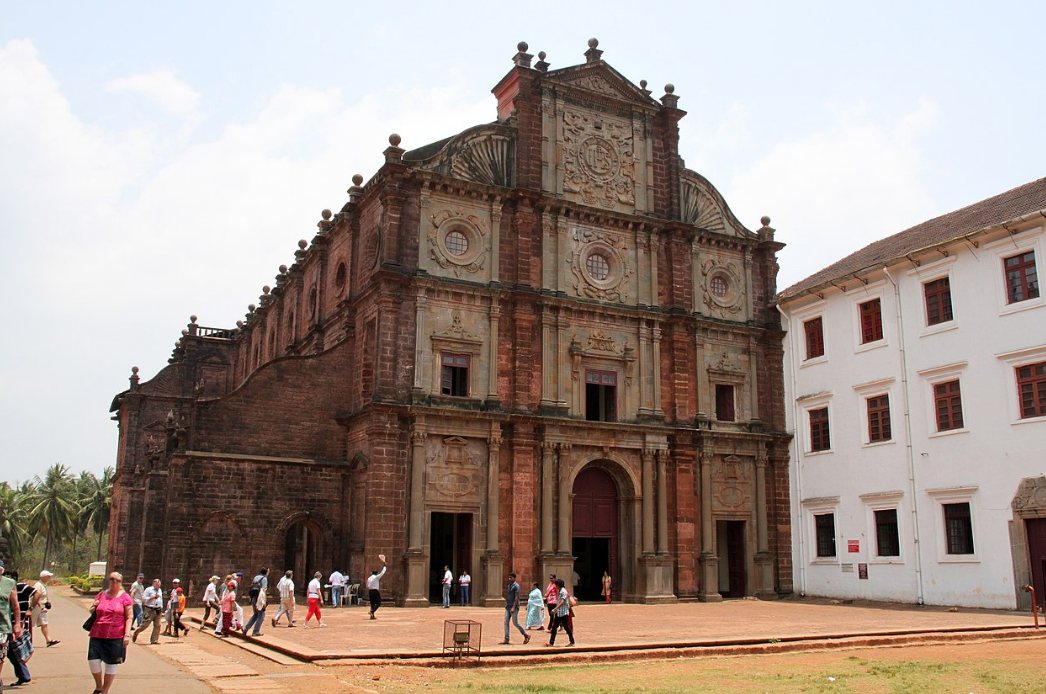
@ Churches and Convents of Goa
올드 고아는 1961년까지 450년 동안 지속된 식민지인 포르투갈 인도의 수도였습니다. 그 장소는 고딕, 마누엘린, 매너리즘, 바로크 양식으로 16세기와 17세기에 지어졌지만 지역 기술과 자원에 맞게 개조된 7개의 교회와 컨벤션으로 구성되어 있습니다. 그들은 가톨릭 선교회가 설립된 아시아 국가들에 건축적인 영향을 퍼뜨렸습니다. 성 프란치스코 자비에가 묻힌 봄 예수 대성당이 사진에 찍혔습니다.
Old Goa was the capital of Portuguese India, a colony that lasted for 450 years until 1961. The site comprises seven churches and convents that were built in the 16th and 17th centuries in the Gothic, Manueline, Mannerist, and Baroque styles, but which were also adapted to suit local techniques and resources. They spread architectural influences to Asian countries where Catholic missions were established. The Basilica of Bom Jesus, where Saint Francis Xavier is buried, is pictured.

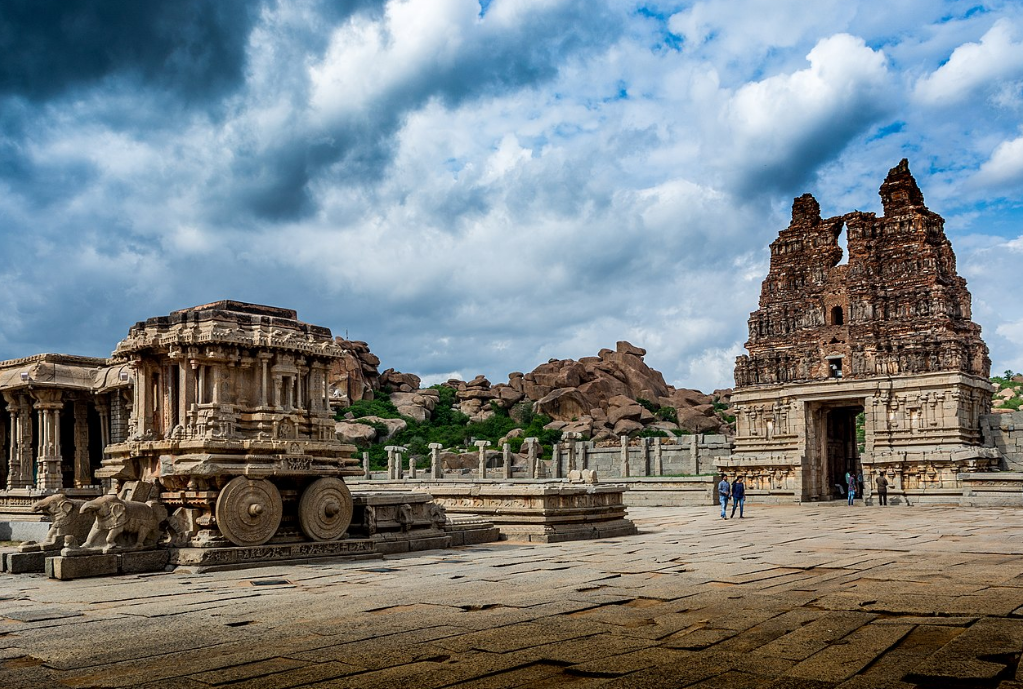
@ Group of Monuments at Hampi
함피는 1565년 데칸 술탄에 의한 약탈과 약탈 이후 포기하기 전까지 비자야나가라 제국의 수도였습니다. 약 200년 동안, 그곳은 드라비다 양식뿐만 아니라 인도-이슬람 양식의 여러 기념물을 남긴 번창한 다문화 도시였습니다. 남아 있는 것은 종교적이고 세속적인 건물들과 방어 구조물들입니다. 비탈라 사원이 사진에 찍혔습니다. 그 장소의 약간의 경계 수정이 2012년에 일어났습니다. 1999년과 2006년 사이에, 그 장소는 교통량 증가와 새로운 건설로 인한 위험 때문에 위험에 처한 곳으로 목록에 올랐습니다.
Hampi was the capital of the Vijayanagara Empire until its abandonment after its sacking and pillaging by the Deccan sultanates in 1565. For about 200 years, it was a prosperous multi-cultural city that left several monuments in the Dravidian style as well as the Indo-Islamic style. The remains include religious and secular buildings and defensive structures. The Vitthala Temple is pictured. A minor boundary modification of the site took place in 2012. Between 1999 and 2006, the site was listed as endangered due to risks posed by increased traffic and new constructions.

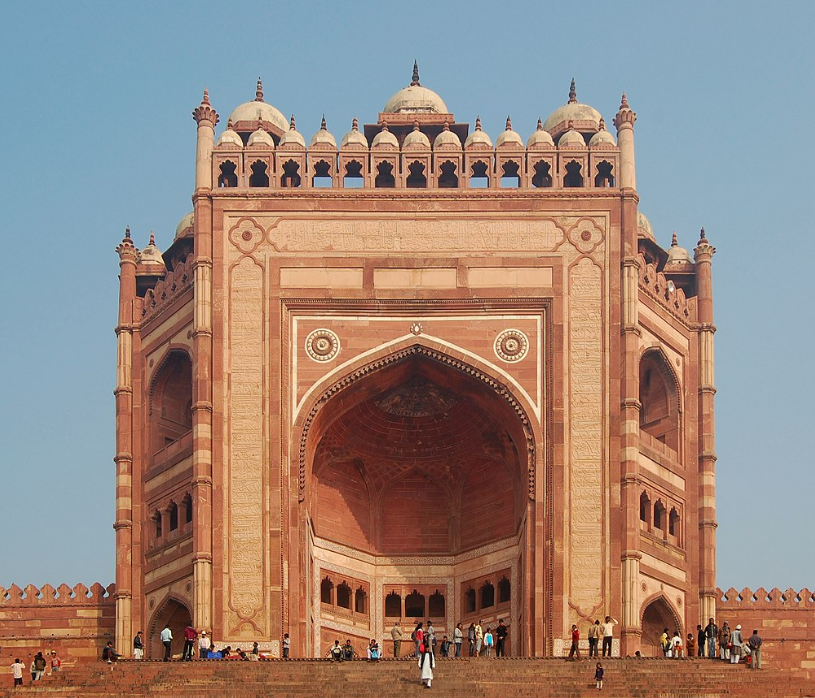
@ Fatehpur Sikri
16세기 후반 약 10년 동안 파테푸르 시크리는 1585년에 수도가 라호르로 이전되고 도시가 대부분 버려지기 전까지 아크바르 황제의 통치하에 무굴 제국의 수도였습니다. 이 유적지는 자마 마스지드(이슬람 사원의 문, 그림의 불란드 다르와자), 판흐 마할 궁전, 살림 치슈티 무덤과 같은 무굴 양식의 많은 기념물과 사원들로 구성되어 있습니다.
For about a decade in the second half of the 16th century, Fatehpur Sikri was the capital of the Mughal Empire under Emperor Akbar, until the capital was moved to Lahore in 1585 and the city was mostly abandoned. The site comprises a large collection of monuments and temples in the Mughal style, such as the Jama Masjid (the gate to the mosque, the Buland Darwaza, pictured), the Panch Mahal palace, and the Tomb of Salim Chishti.

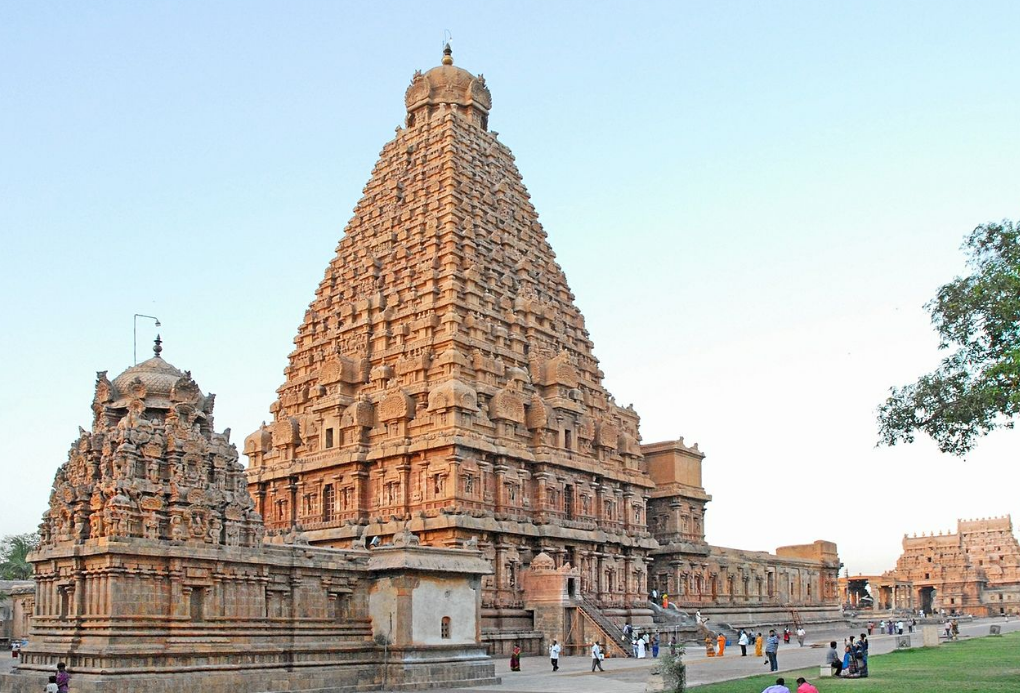
@ Great Living Chola Temples
이 장소는 촐라 왕조 아래 11세기와 12세기에 지어진 세 개의 힌두교 사원으로 구성되어 있습니다. 그것들은 촐라 시대의 드라비다 건축의 가장 좋은 예들 중 일부를 나타냅니다. 그것들은 돌로 만들어지고 돌과 청동 조각으로 장식됩니다. 처음에, 브리하디스바라 사원 (사진)만이 세계 문화 유산으로 등재되었습니다; 브리하디스바라 사원과 에어라바타바라 사원, 두 개의 다른 사원들이 2004년에 추가되었고, 그 후에 그 장소는 현재의 이름으로 바뀌었습니다.
This site comprises three Hindu temples built in the 11th and 12th centuries under the Chola dynasty. They represent some of the best examples of Dravidian architecture of the Chola period. They are made of stone and decorated with stone and bronze sculptures. Initially, only the Brihadisvara Temple (pictured) was listed as a World Heritage Site; two other temples, the Brihadisvara Temple and the Airavatesvara Temple were added in 2004, after which the site was renamed to its current name.

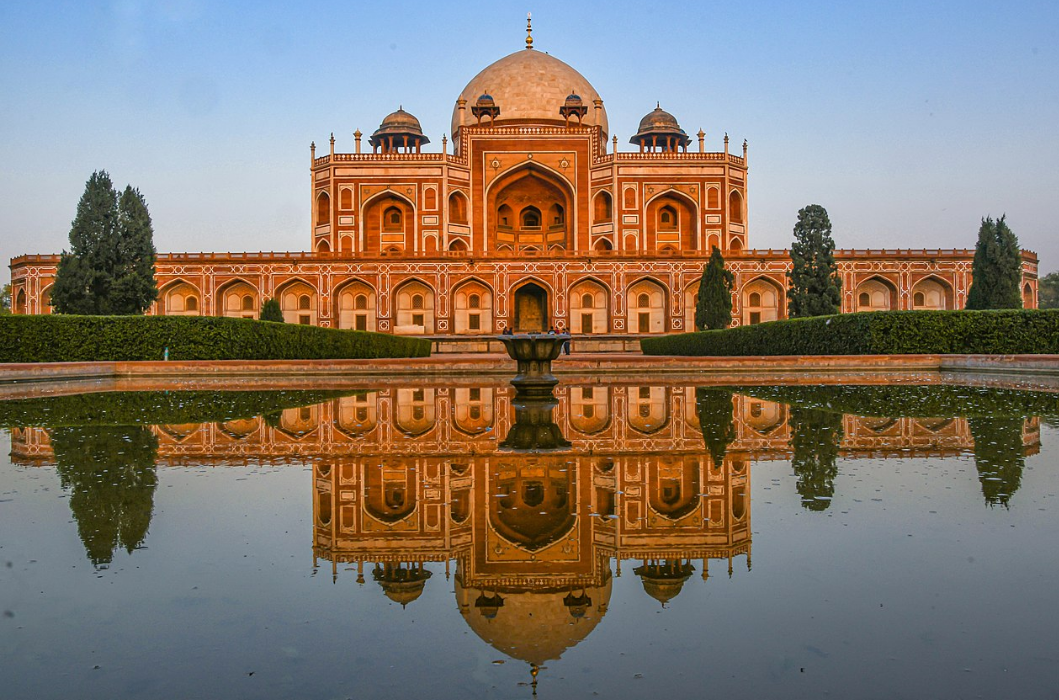
@ Humayun's Tomb, Delhi
무굴 황제 후마윤의 무덤은 1560년대에 지어졌으며 페르시아 정원의 요소를 소개하는 인도 아대륙의 정원 무덤의 첫 번째 예를 나타냅니다. 기념비적인 이중 돔 묘는 무굴 건축의 도약을 나타내며 타지마할의 건축적인 전신입니다. 그 단지는 그 시기의 몇 개의 더 작은 무덤을 포함합니다. 2016년에 약간의 경계 수정이 있었습니다.
The tomb of the Mughal emperor Humayun was constructed in the 1560s and represents the first example of a garden tomb on the Indian subcontinent, introducing the elements of Persian gardens. The monumental double-domed mausoleum represents a leap in Mughal architecture and is an architectural predecessor of the Taj Mahal. The complex includes several smaller tombs from the period. A minor boundary modification took place in 2016.

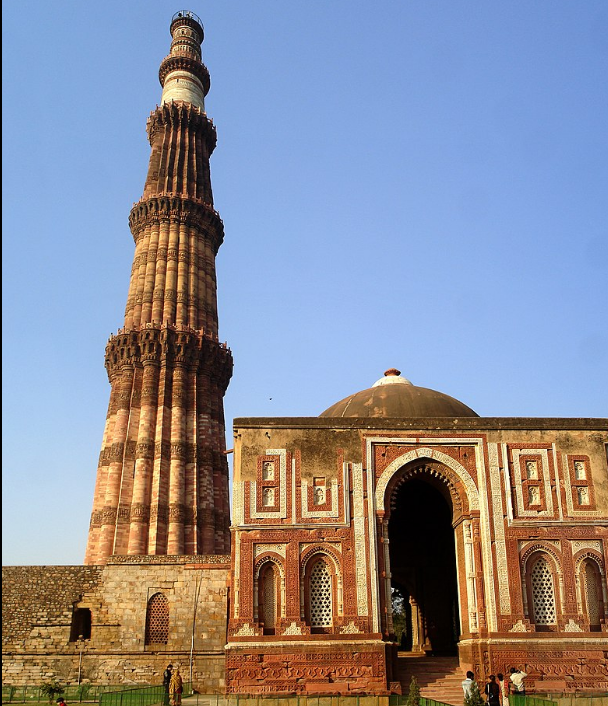
@ Qutb Minar and its Monuments, Delhi
이 단지는 델리 술탄국이 그곳에서 권력을 세웠던 13세기와 14세기의 초기 이슬람 인도 기념물들로 구성되어 있습니다. 그것들은 쿠트브 미나르, 72.5m (238피트) 높이의 미나렛 (사진), 알라이 다르와자 문, 이전 힌두 사원의 여러 돌기둥이 용도가 변경된 쿠왓울 이슬람 사원, 철 기둥, 그리고 여러 무덤과 다른 기념물들을 포함합니다.
The complex comprises several early Islamic India monuments from the 13th and 14th centuries when the Delhi Sultanate established power there. They include the Qutb Minar, a 72.5 m (238 ft)-high minaret (pictured), the Alai Darwaza gateway, the Quwwat-ul-Islam Mosque where several stone pillars from previous Hindu temples were repurposed, the Iron pillar, and several tombs and other monuments.

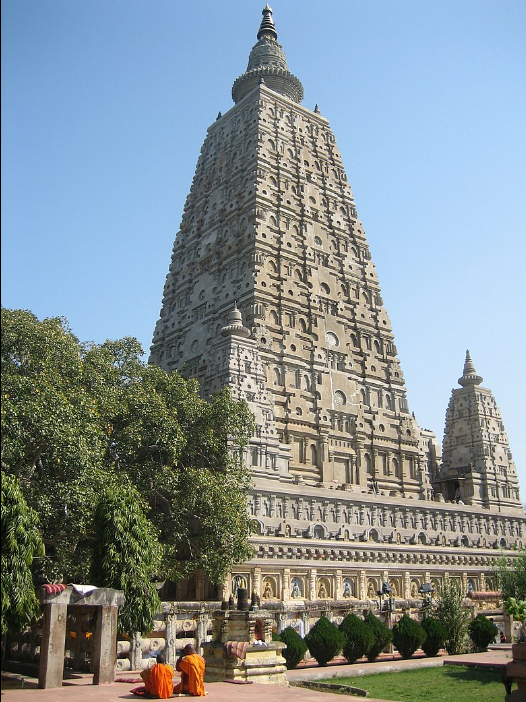
@ Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodh Gaya
그 불교 사원은 부처님이 보리수 아래에서 깨달음을 얻었다고 말하는 장소를 표시하고 있습니다. 현재의 사원은 서기 5세기와 6세기로 거슬러 올라가고, 기원전 3세기에 아쇼카 황제에 의해 의뢰된 이전의 건축물 위에 지어졌습니다. 그 사원은 높이가 50m (160피트)이고 벽돌로 만들어졌습니다. 그것은 그 후 몇 세기 동안 건축의 발전에 상당한 영향을 미쳤습니다. 수 세기 동안 버려지고 방치된 후, 그 사원은 19세기에 광범위하게 복구되었습니다.
The Buddhist temple complex marks the site where Buddha is said to have attained enlightenment under the Bodhi Tree. The present temple dates to the 5th and 6th centuries CE (during the Gupta period) and was built upon a previous structure commissioned by Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE. The temple is 50 m (160 ft) high and made of brick. It had a substantial influence on the development of architecture in the following centuries. After centuries of abandonment and neglect, the temple was extensively restored in the 19th century.

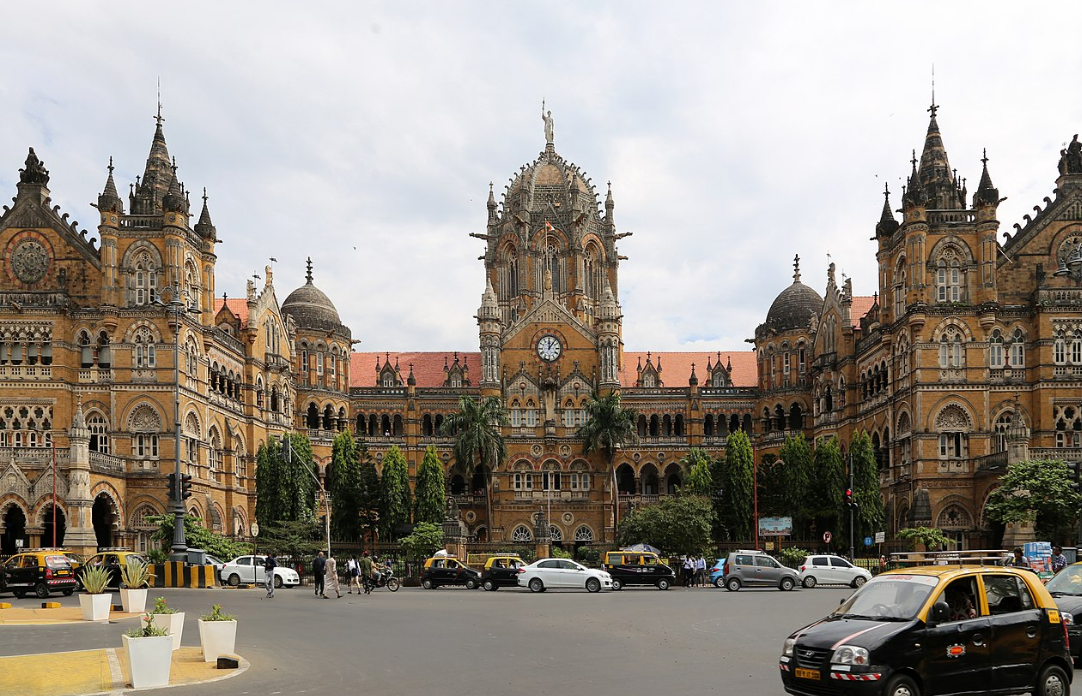
@ Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus (formerly Victoria Terminus)
뭄바이의 역사적인 터미널 기차역은 19세기 후반에 지어졌습니다. 프레드릭 윌리엄 스티븐스(Frederick William Stevens)가 빅토리아 고딕 스타일로 디자인하여 이탈리아 고딕 건축의 영향을 받고 인도 전통 건물의 영향과 결합했습니다. 이는 영국 연방 내의 주요 상업 항구로서 뭄바이의 부를 상징했습니다.
The historic terminal train station in Mumbai was built in the late 19th century. It was designed by Frederick William Stevens in the Victorian Gothic style, drawing influences from Italian Gothic architecture and combining them with influences from Indian traditional buildings. It symbolized the wealth of Mumbai as a major commercial port within the British Commonwealth.

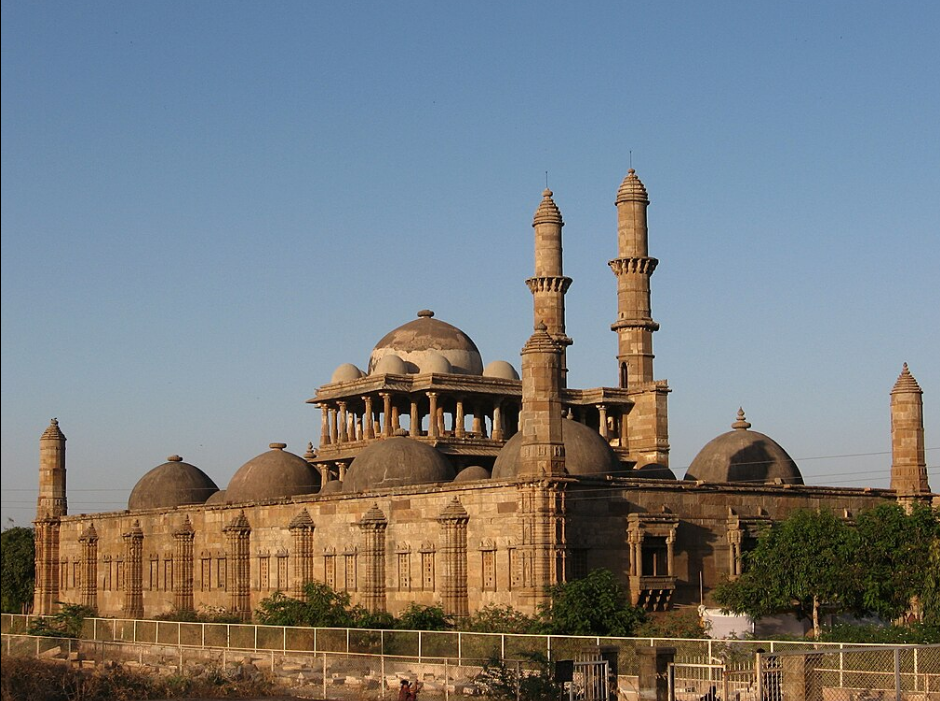
@ Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park
이 유적지는 찰콜리스틱에서부터 16세기 구자라트 술탄국의 단명한 수도인 샹파네르의 유적까지 여러 시대의 유적을 포함하고 있습니다. 중요한 건물로는 힌두교와 이슬람교의 건축 요소가 모두 특징인 힌두교 사원 칼리카 마타(Kalika Mata), 자인 사원(Jain Temple), 자마 모스크(Jama Mosque, 사진)와 물을 관리하는 시스템, 요새, 14세기 사원의 유적이 있습니다.
The site contains remains from several periods, from the Chalcolithic to the remains of Champaner, a short-lived capital of the Gujarat Sultanate in the 16th century. Important buildings include the Hindu temple Kalika Mata, Jain temples, and Jama Mosque (pictured) which features both Hindu and Muslim architectural elements, and the remains of water-managing systems, fortifications, and 14th-century temples.

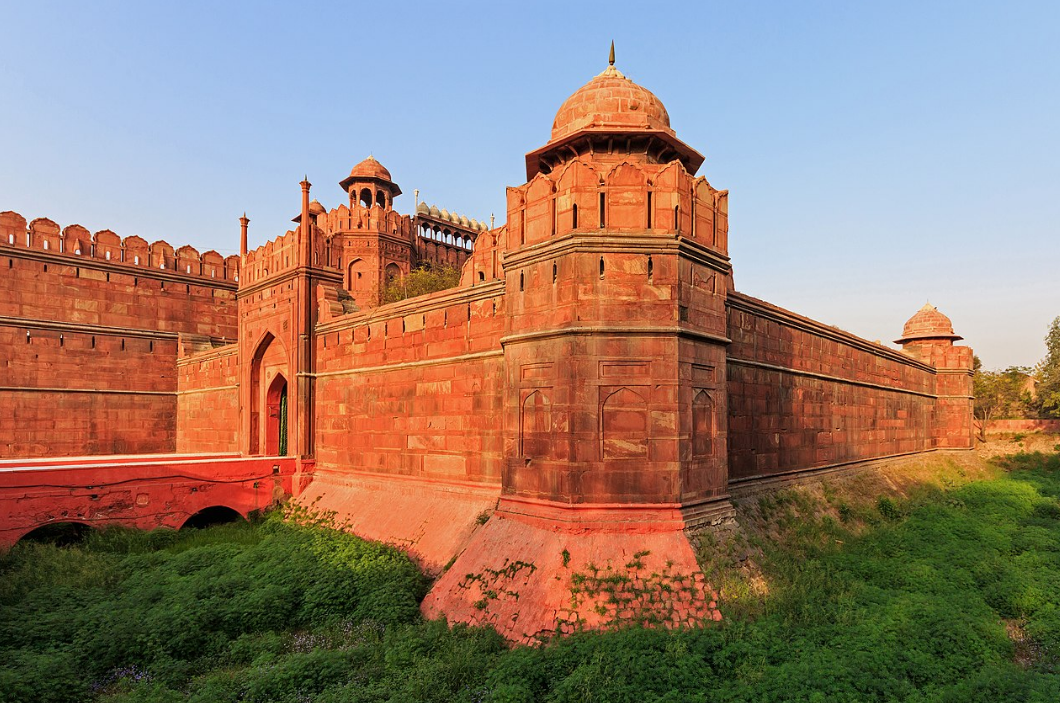
@ Red Fort Complex
붉은 요새는 17세기 중반에 무굴 황제 샤 자한 아래 지어졌습니다. 그것은 인도-페르시아 문화의 요소와 티무리드의 요소를 혼합한 무굴 건축의 절정을 나타냅니다. 그것의 건축은 그 지역의 나중의 궁전과 정원에 강한 영향을 미쳤습니다. 붉은 요새는 또한 역사적인 사건의 배경이기도 합니다; 그것은 영국에 의해 약탈되고 부분적으로 용도가 변경되었으며, 그것은 인도의 독립을 처음 기념했던 장소입니다. 델리 문이 사진에 나와 있습니다.
The Red Fort was built under Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in the mid-17th century. It represents the zenith of Mughal architecture, blending the elements of Indo-Persian culture with Timurid elements. Its architecture had a strong influence on later palaces and gardens in the region. The Red Fort was also the setting of historical events; it was sacked and partially repurposed by the British, and it was the site where the independence of India was first celebrated. The Delhi Gate is pictured.

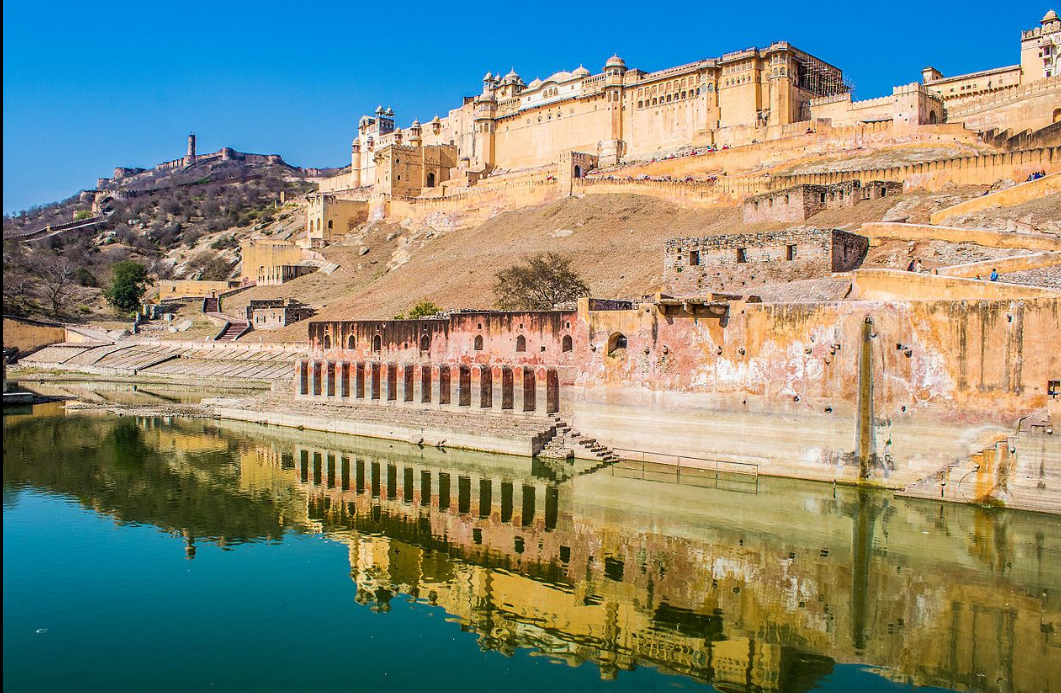
@ Hill Forts of Rajasthan
이 지역은 6개의 요새로 구성되어 있습니다: 8세기에서 18세기 사이에 라즈푸트 왕국에 의해 건설된 치토르 요새, 쿰발가르 요새, 란탐보레 요새, 가그론 요새, 앰버 요새 (사진), 자이살머 요새입니다. 그들은 술탄국과 무굴 건축의 요소가 있는 절충적인 양식을 가지고 있으며 마라타 제국의 후기 양식에 영향을 미쳤습니다. 예를 들어, 란탐보레는 숲에 있고 자이살머는 사막에 있는 등 다양한 환경에 위치하고 있습니다.
This site comprises six forts: the Chittor Fort, Kumbhalgarh Fort, Ranthambore Fort, Gagron Fort, Amber Fort (pictured), and Jaisalmer Fort, which were constructed between the 8th and 18th centuries by Rajput kingdoms. They are eclectic in style, with elements of Sultanate and Mughal architecture, and were influential on the later styles of the Maratha Empire. They are situated in different settings; for example, Ranthambore is in a forest, and Jaisalmer is in a desert.

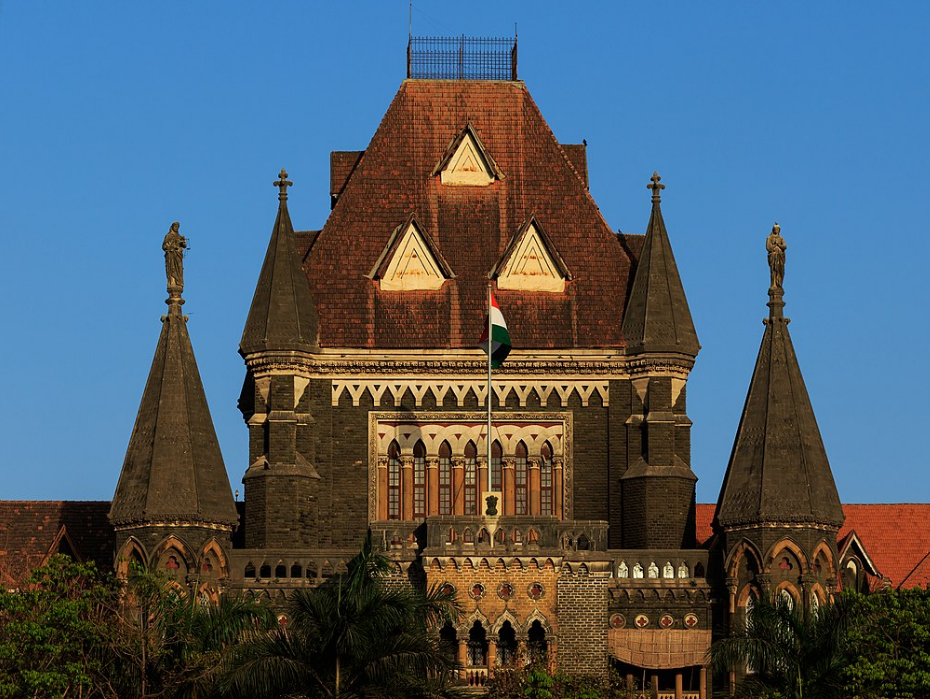
@ Victorian Gothic and Art Deco Ensembles of Mumbai
이 장소는 대영제국 시대의 뭄바이에 있는 두 개의 건물 집합체로 구성되어 있습니다. 19세기 후반의 빅토리아 고딕 스타일의 공공 건물은 발코니와 베란다와 같은 특징을 도입하여 인도 기후에 고딕 부흥 요소를 적용했습니다. 봄베이 고등법원 건물이 사진에 표시되어 있습니다. 아르데코 건물은 20세기 초까지 거슬러 올라가며 영화관과 아파트 건물을 포함합니다. 뭄바이의 아르데코도 살펴보세요.
This site comprises two assemblies of buildings in Mumbai from the British Empire era. Public buildings in the Victorian Gothic style from the second half of the 19th century adapted Gothic Revival elements for the Indian climate, introducing features such as balconies and verandas. The Bombay High Court building is pictured. The Art Deco buildings date to the early 20th century and include cinema halls and apartment buildings. See also Art Deco in Mumbai.

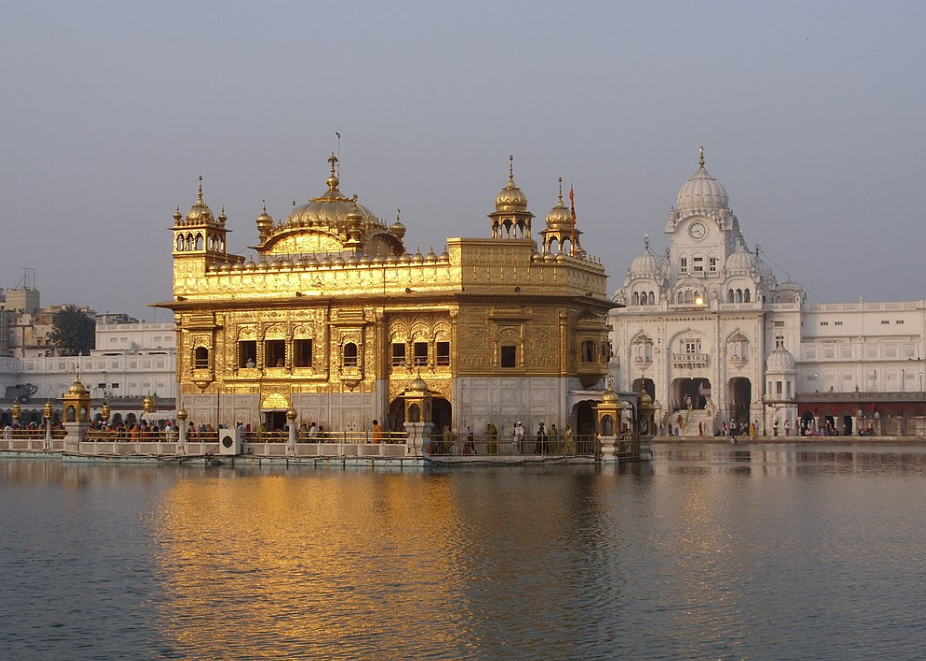
@ Sri Harimandir Sahib, Amritsar, Punjab
황금 사원으로도 알려진 스리 하리만디르 사히브는 시크교의 정신적인 중심지입니다. 그 사원 단지는 여러 번 재건축되었습니다. 그 단지의 건축 배치는 종교의 정신적인 개념을 반영합니다. 주요 사원 건물은 채색되거나 대리석 인레이로 장식된 꽃무늬로 풍부하게 장식되어 있습니다
Sri Harimandir Sahib, also known as the Golden Temple, is the spiritual centre of Sikhism. The temple complex was rebuilt several times. The architectural layout of the complex reflects the spiritual concepts of the religion. The main temple building is richly decorated with floral patterns, either painted or as marble inlay

@ 2023년 현재 유네스코에 등재된 인도 42개의 유적지 (42 sites in India listed on UNESCO as of 2023)
출처 : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_World_Heritage_Sites_in_India
'여행' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 유네스코 세계문화유산 영국 (UNESCO in United Kingdom) (6) | 2024.03.14 |
|---|---|
| 유네스코 세계문화유산 멕시코 (UNESCO in Mexico) (2) | 2024.03.07 |
| 유네스코 세계문화유산 스페인 (UNESCO in Spain) (4) | 2024.02.15 |
| 유네스코 세계문화유산 독일 (UNESCO in Germany) (0) | 2024.01.19 |
| 유네스코 세계문화유산 프랑스편 (UNESCO in France) (4) | 2024.01.11 |



