
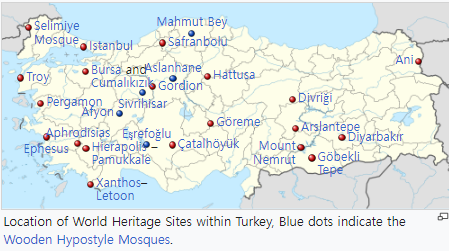
유엔교육과학문화기구(UNESCO) 세계유산은 1972년에 설립된 유네스코 세계유산협약에 기술된 바와 같이 문화 또는 자연유산에 중요한 장소입니다. 튀르키예는 1983년 3월 16일 협약을 수락하여 역사적인 장소를 목록에 포함할 수 있게 되었습니다. 2023년 현재 튀르키예에는 19개의 문화유적지와 2개의 혼합유적지를 포함하여 21개의 세계유산이 있습니다.
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Heritage Sites are places of importance to cultural or natural heritage as described in the UNESCO World Heritage Convention, established in 1972. Turkey accepted the convention on 16 March 1983, making its historical sites eligible for inclusion on the list. As of 2023, there are twenty-one World Heritage Sites in Turkey, including nineteen cultural sites and two mixed sites.
1985년 프랑스 파리에서 열린 세계문화유산위원회 제9차 회의에서 ğ의 첫 세 곳인 디브리 ğ의 위대한 모스크와 병원, 이스탄불의 역사적 지역과 괴렘 국립공원, 카파도키아의 바위 유적이 이 목록에 새겨져 있었습니다. 가장 최근의 비문인 중세 아나톨리아의 고르디온 모스크와 나무로 된 하이포스타일 모스크는 2023년에 이 목록에 추가되었습니다.
The first three sites in Turkey, Great Mosque and Hospital of Divriği, Historic Areas of Istanbul and Göreme National Park and the Rock Sites of Cappadocia, were inscribed on the list at the 9th Session of the World Heritage Committee, held in Paris, France in 1985. The latest inscriptions, Gordion and Wooden Hypostyle Mosques of Medieval Anatolia, were added to the list in 2023.
@ Aphrodisias
이 유적지는 아프로디시아스 자체(기원전 3세기경 아프로디테 신전의 모습)와 고대 그리스 도시에 부를 가져다 준 근처의 고대 대리석 채석장으로 구성되어 있습니다.
The site consists of Aphrodisias itself (featuring the 3rd-century BCE Temple of Aphrodite) and the ancient marble quarries nearby, which had brought wealth to the ancient Greek city.


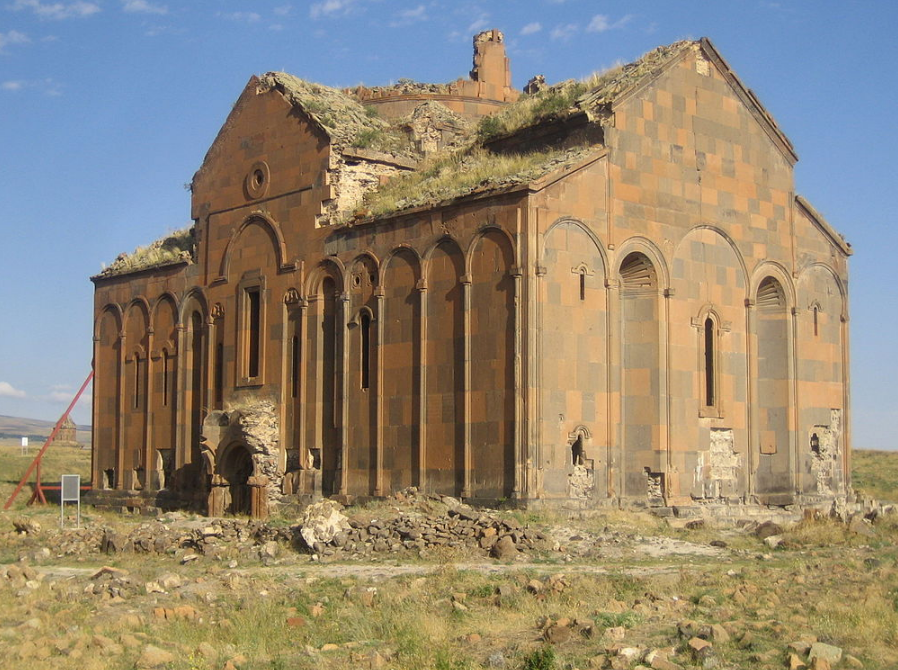
@ Archaeological Site of Ani
튀르키예와 아르메니아 국경에 가까운 곳에 위치한 중세 도시 아니는 바그라티드 아르메니아의 수도로서 10세기와 11세기에 황금기를 맞았고 몽골의 침공과 대지진 이후 14세기부터 쇠퇴했습니다.
Located close to the Turkey-Armenia border, the medieval city of Ani reached its golden age in the 10th and 11th centuries as the capital of Bagratid Armenia, before going into decline from the 14th century on following a Mongol invasion and a major earthquake.


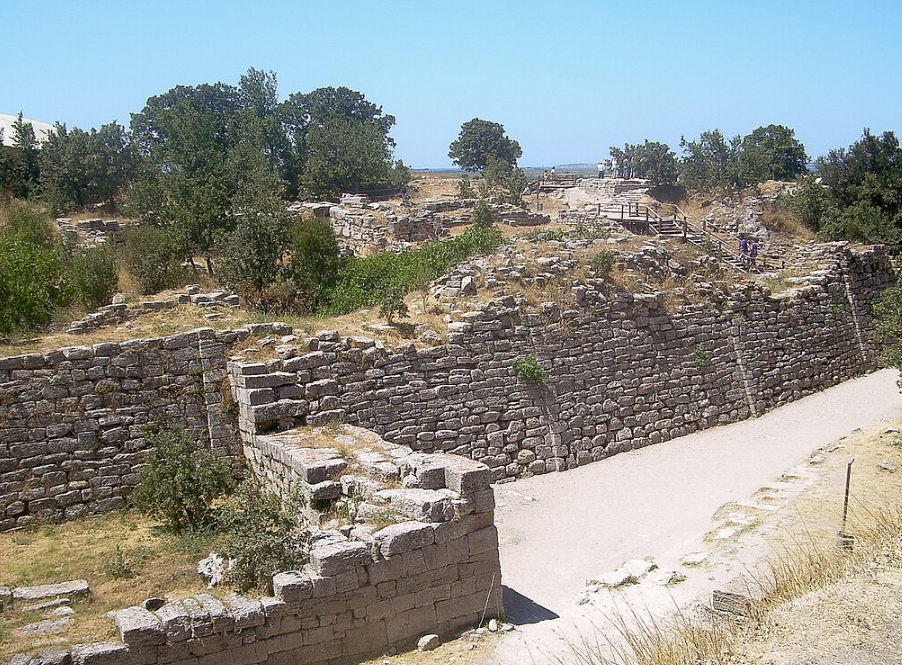
@ Archaeological Site of Troy
4천년 이상 전으로 거슬러 올라가 호메로스의 일리아드와 버질의 아이네이드에 핵심적인 영향을 미친 트로이는 19세기 후반 하인리히 슐리만에 의해 재발견되었고, 그 이후로 세계에서 가장 잘 알려진 고고학 유적지 중 하나가 되었습니다.
Dating back to more than four millennia ago and serving as a key influence on Homer's Iliad and Virgil's Aeneid, Troy was rediscovered by Heinrich Schliemann in the late 19th century, and has since become one of the most well-known archeological sites in the world.

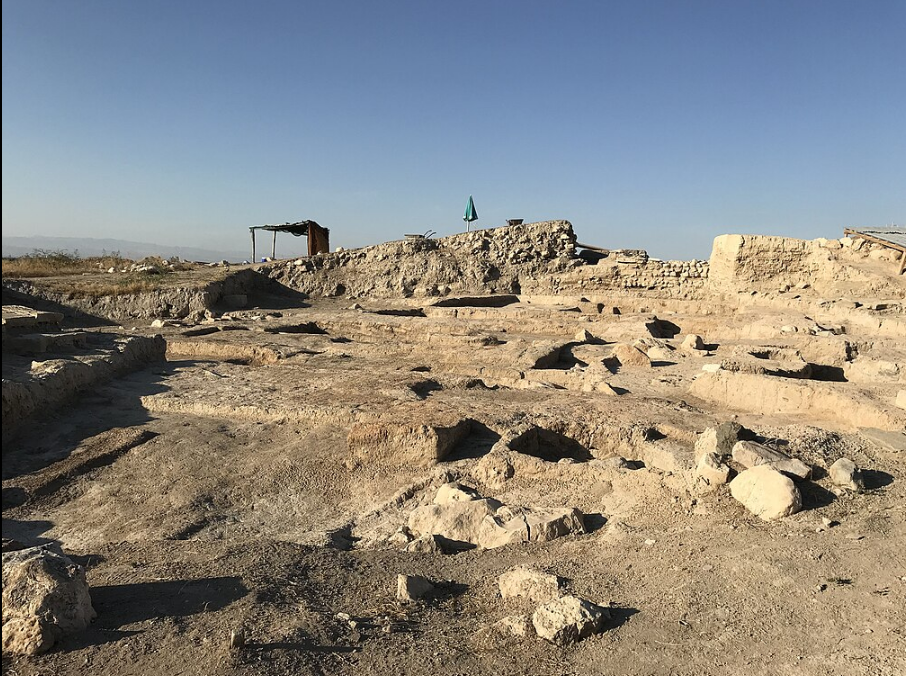
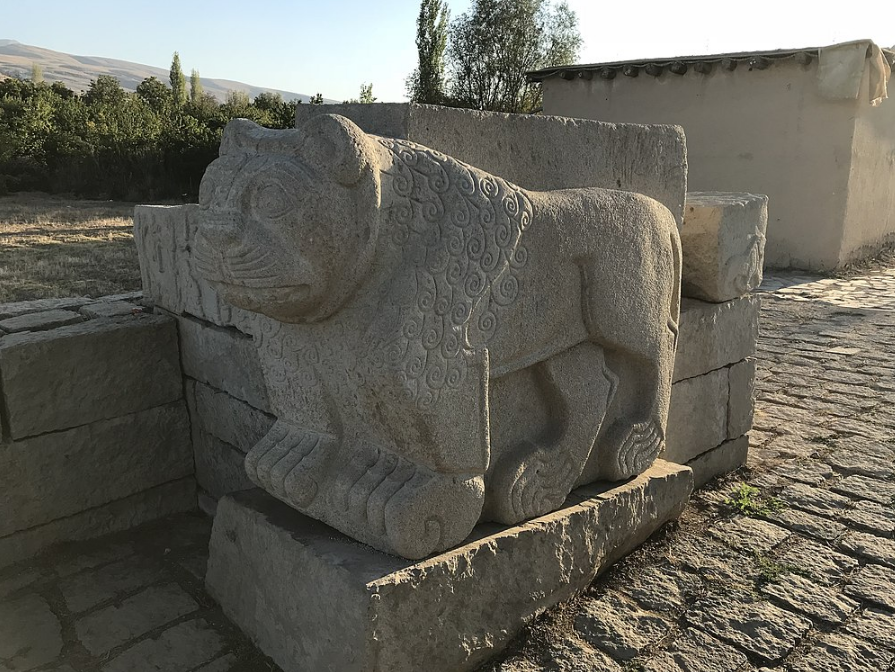
@ Arslantepe Mound
아르슬란테페는 타우루스 산맥에 솟아 있는 유프라테스 상류의 지류인 토흐마 강에 있는 고대 도시였습니다. 그것은 말라티아 근처의 아르슬란테페의 현대 고고학 장소와 동일시되었습니다. 초기 청동기 시대 (c. 33세기에서 31세기)에 알려진 첫 번째 칼은 로마 대학의 마르셀라 프란기판에 의해 아르슬란테페에서 발견된 것을 기반으로 합니다.
Arslantepe was an ancient city on the Tohma River, a tributary of the upper Euphrates rising in the Taurus Mountains. It has been identified with the modern archaeological site of Arslantepe near Malatya. The first swords known in the Early Bronze Age (c. 33rd to 31st centuries) are based on finds at Arslantepe by Marcella Frangipane of Rome University.


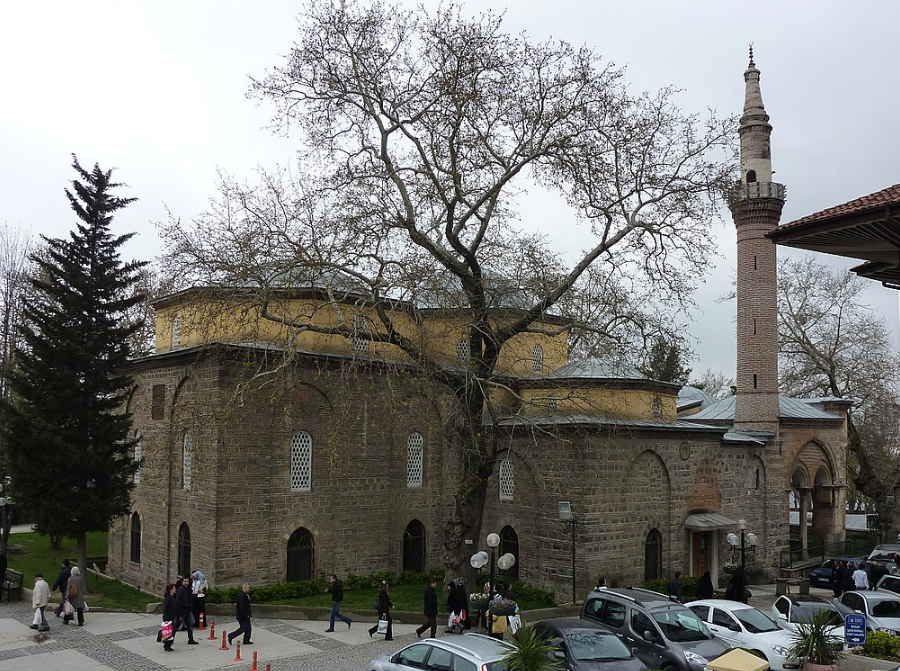
@ Bursa and Cumalıkızık: the Birth of the Ottoman Empire
14세기 오스만 제국의 첫 번째 수도였던 부르사는 혁신적인 도시 계획으로 미래 오스만 도시의 주요 참고 자료가 되었습니다. 인근 마을인 쿠말ı크 ı츠ı크는 바크 ı프 제도의 모범으로 수도 개발을 지원했습니다.
The first capital of the Ottoman Empire in the 14th century, Bursa, with its innovative urban planning, became a major source of reference for future Ottoman cities. The nearby village of Cumalıkızık, exemplar of the vakıf system, provided support for the development of the capital.
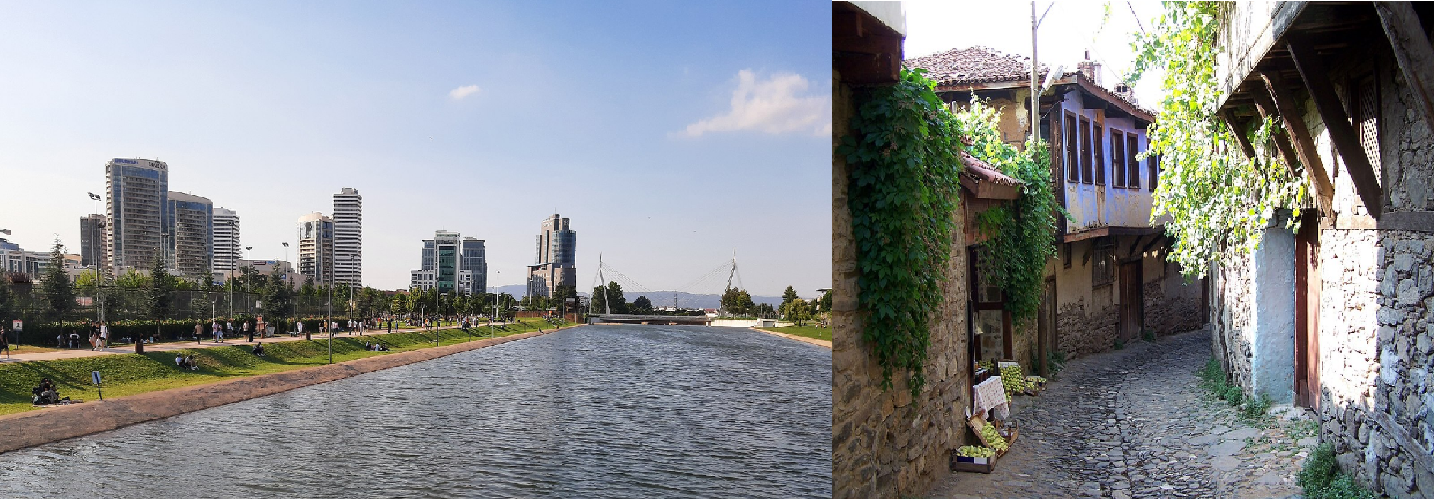


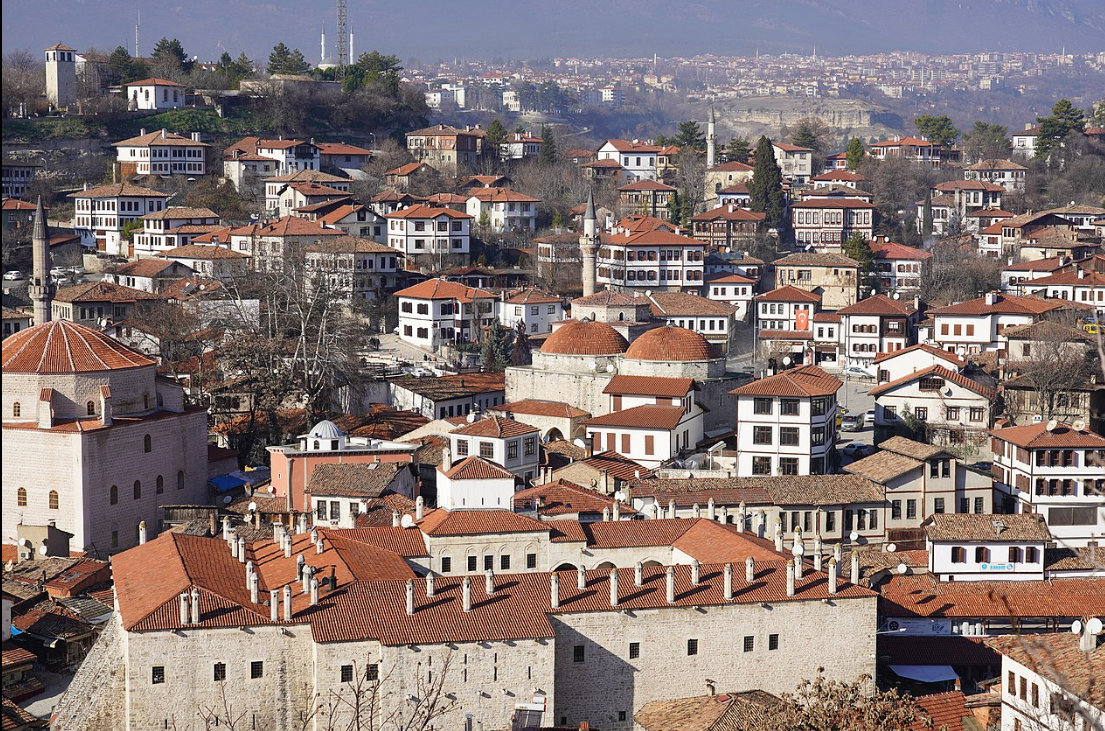
@ City of Safranbolu
카라반 무역의 교차로인 사프란볼루는 13세기부터 번성했습니다. 사프란볼루의 건축물은 오스만 제국 전체의 도시 개발에 주요한 영향을 미쳤습니다.
A crossroads of the caravan trade, Safranbolu flourished from the 13th century on. Its architecture became a major influence on urban development throughout the Ottoman Empire.

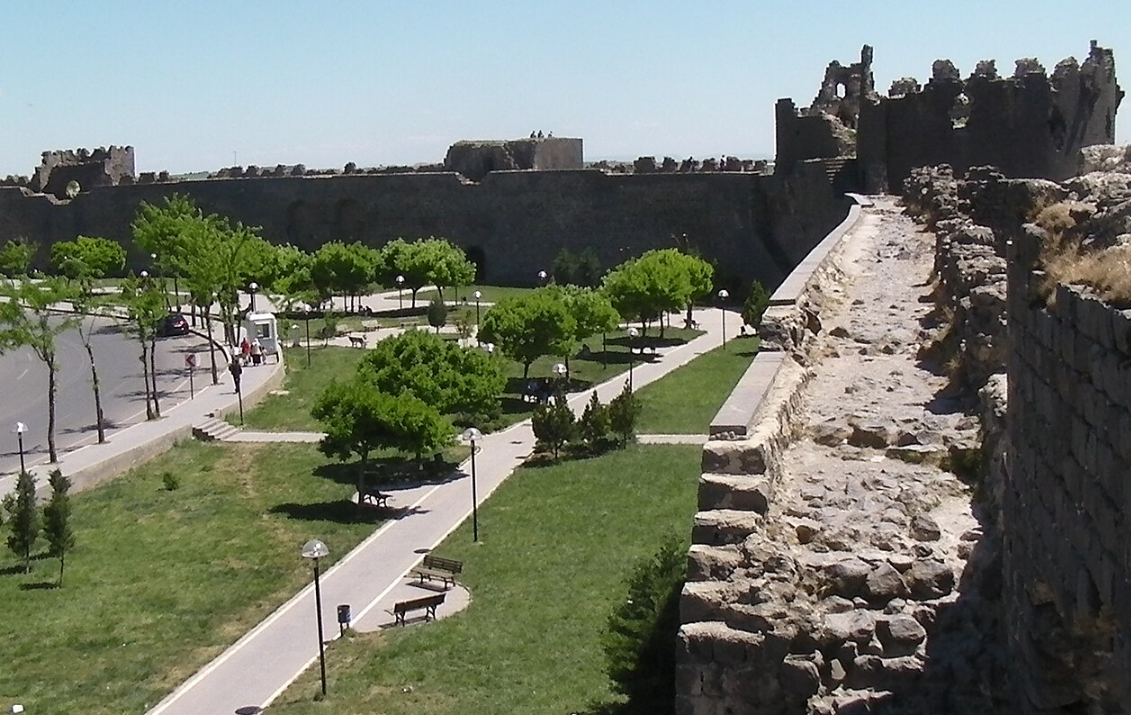
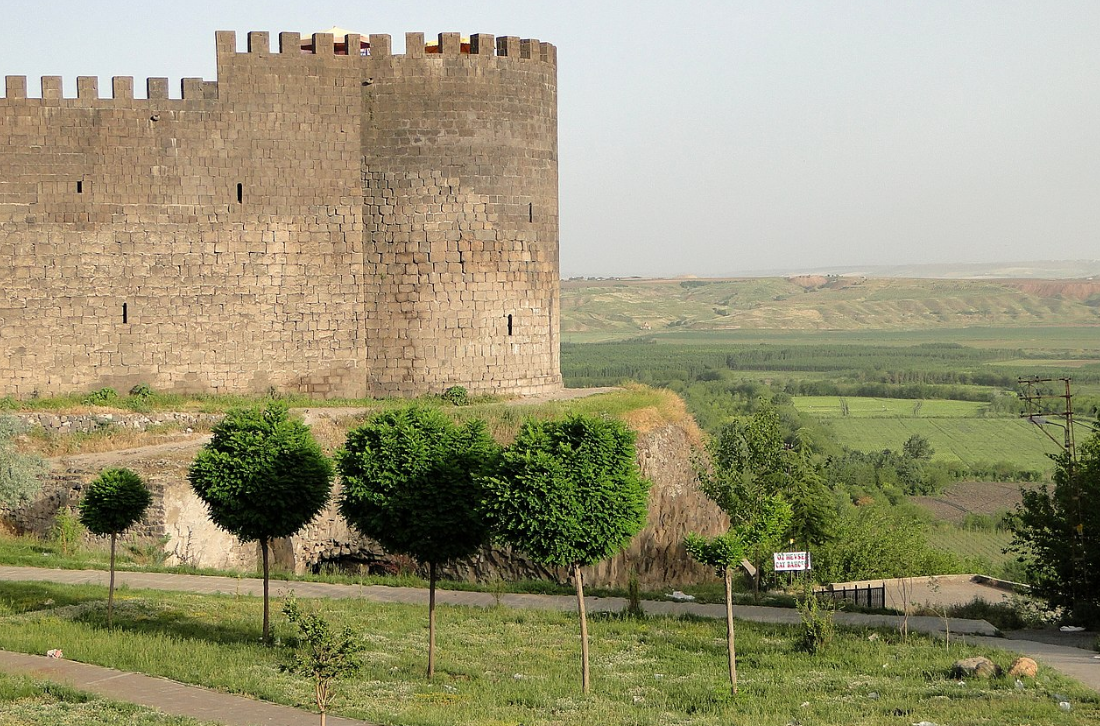
@ Diyarbakır Fortress and Hevsel Gardens Cultural Landscape
디야르바크르는 헬레니즘 시대부터 현재까지 매우 중요한 도시였습니다. 이 장소에는 디야르바크 ı르의 5.800km 길이의 성벽과 도시에 음식과 물을 공급했던 헤셀 가든이 있습니다.
Diyarbakır has been a city of great significance from the Hellenistic period until the present. The site contains Diyarbakır's 5.800km-long city walls, as well as the Hevsel Gardens, which provided food and water supply to the city.


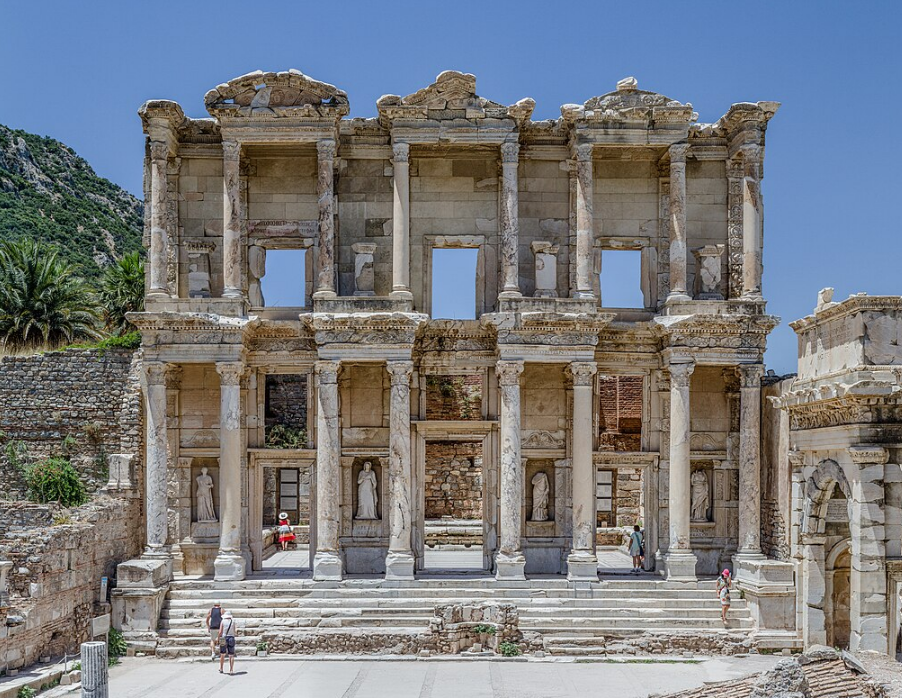
@ Ephesus
고대 그리스의 도시 에페소스는 고대 세계의 7대 불가사의 중 하나인 아르테미스 신전으로 유명했습니다. 기원전 2세기에 로마의 지배를 받은 후, 그 도시는 셀수스 도서관과 같은 기념비적인 건축물을 남기고 번성했습니다. 성모 마리아 집과 성 요한 대성당은 5세기부터 주요 기독교 순례지가 되었습니다.
The ancient Greek city of Ephesus was famed for one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, the Temple of Artemis, which now lies in ruins. After coming under Roman control in the 2nd century BCE, the city flourished, leaving behind monumental structures such as the Library of Celsus. The House of the Virgin Mary and the Basilica of St. John became major Christian pilgrimage sites from the 5th century on.

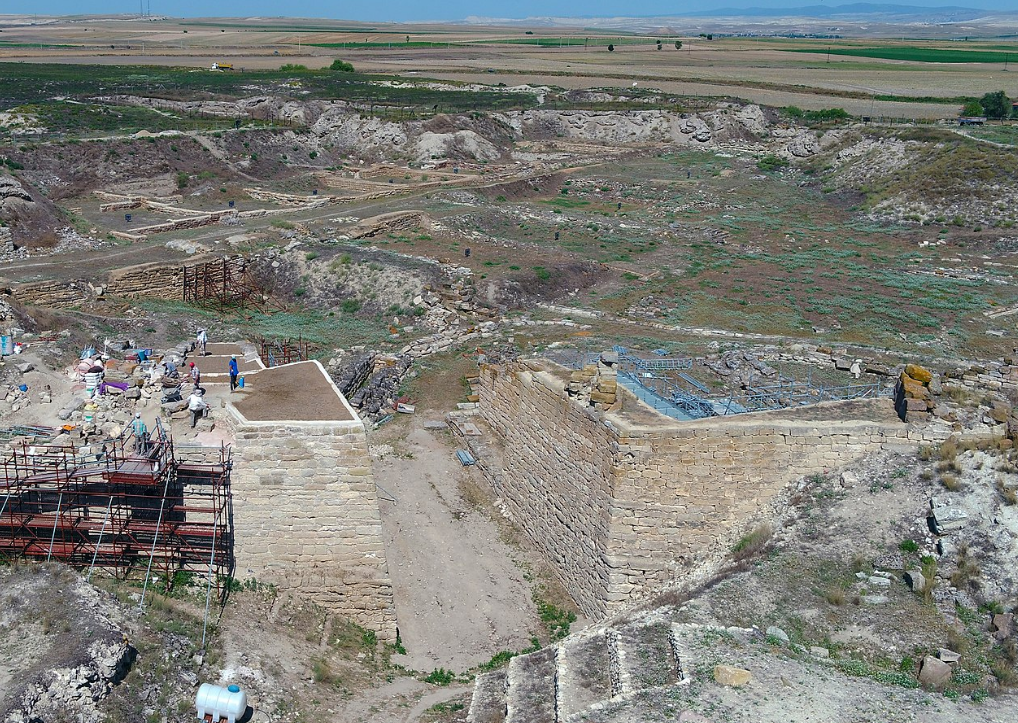
@ Gordion
고르디온은 고대 프리기아의 수도였습니다. 이 장소의 점령은 초기 청동기 시대 (c. 2300 BCE)부터 계속적으로 4세기까지 그리고 다시 13세기와 14세기에 증명됩니다.
Gordion was the capital city of ancient Phrygia. Occupation at the site is attested from the Early Bronze Age (c. 2300 BCE) continuously until the 4th century CE and again in the 13th and 14th centuries CE.

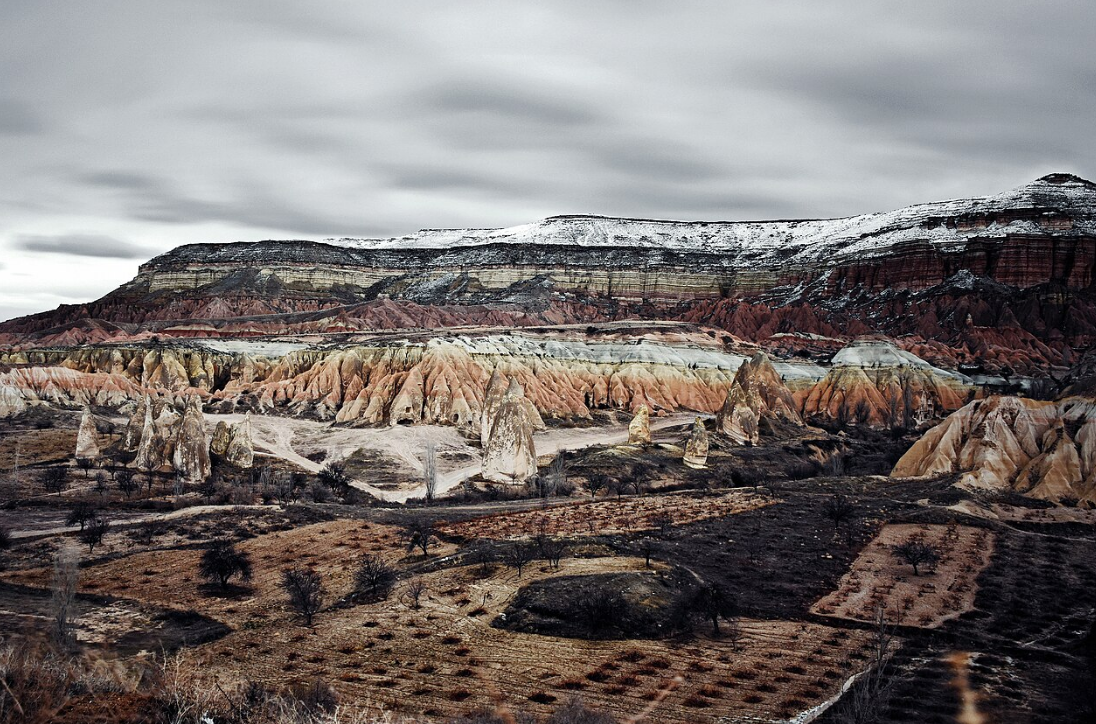
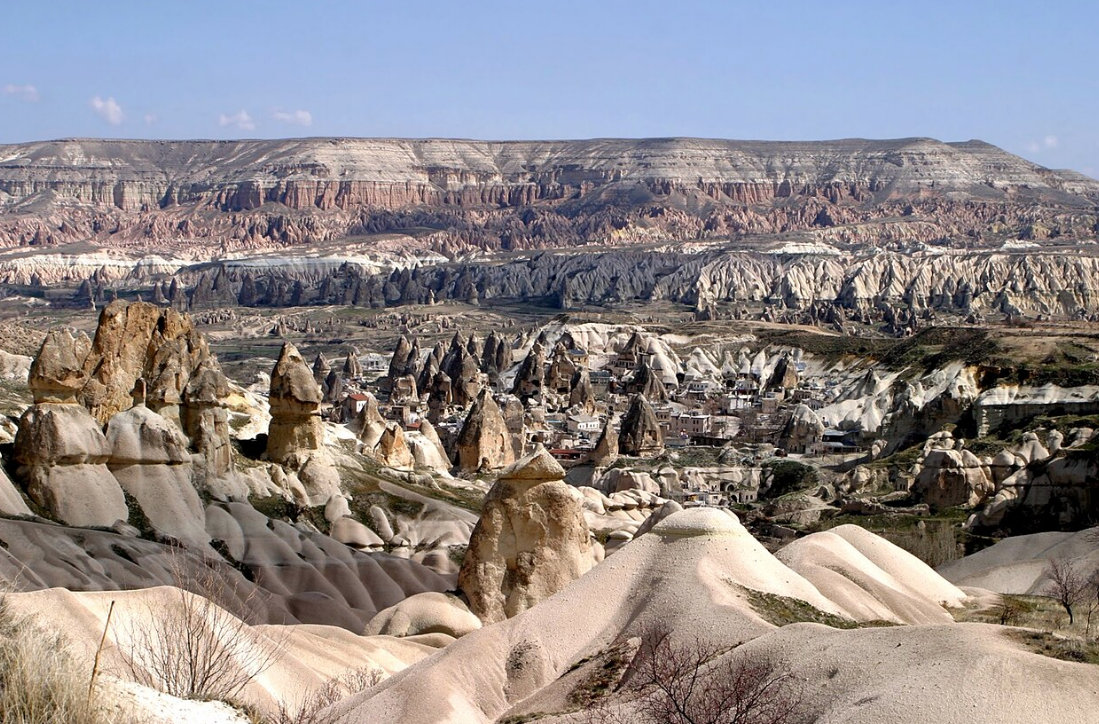
@ Göreme National Park and the Rock Sites of Cappadocia
괴레메 계곡 지역은 눈에 띄는 후두암질로 유명합니다. 카파도키아 지역은 또한 바위투성이의 주거지, 마을, 교회, 지하 도시 및 이코노클라스틱 비잔틴 예술의 훌륭한 예를 보여주는 갤러리를 특징으로 합니다.
The Göreme Valley area is famous for its striking hoodoo rock formations. The region of Cappadocia also features a gallery of rock-hewn dwellings, villages, churches, underground cities and great examples of post-Iconoclastic Byzantine art.


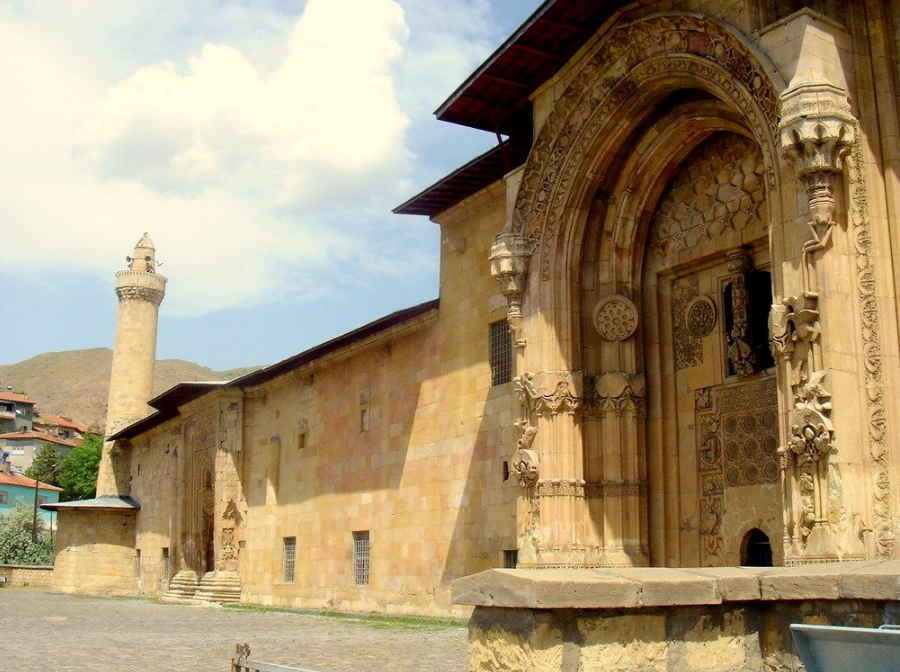
@ Great Mosque and Hospital of Divriği
13세기 초에 설립된 디브리 ğ의 모스크-병원 단지는 독특하고 때로는 대조적인 디자인이 혼합된 이슬람 건축의 독특하고 뛰어난 예입니다.
Founded in the early 13th century, the mosque-hospital complex at Divriği is a unique and outstanding example of Islamic architecture, blending distinct and sometimes contrasting designs.

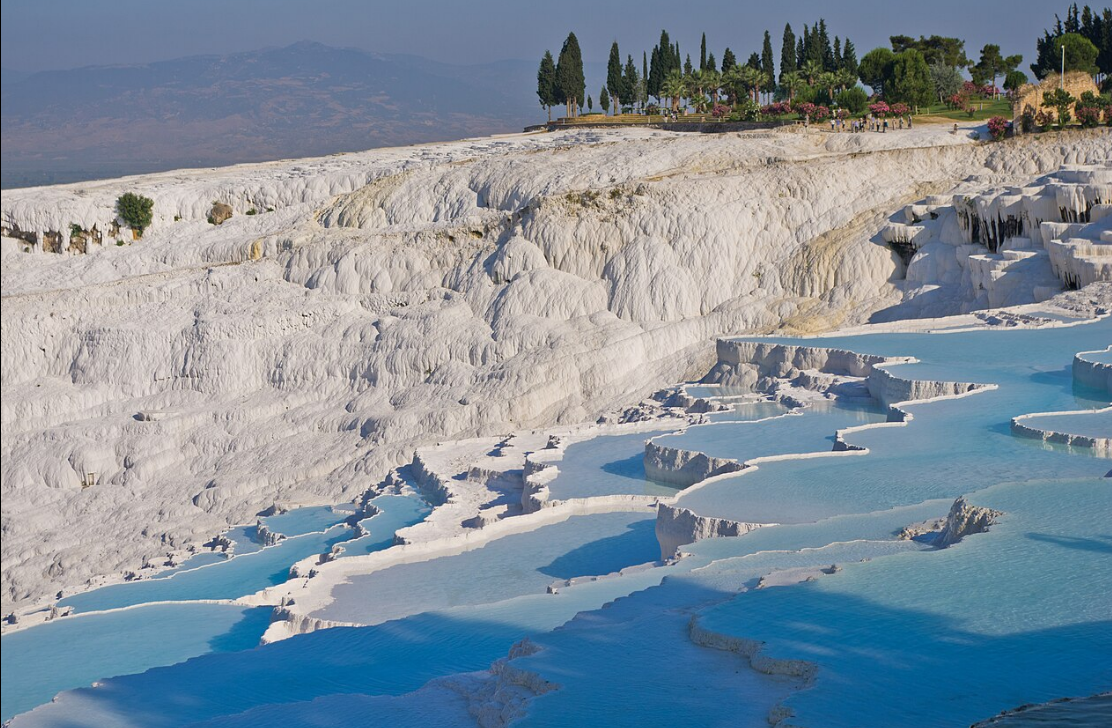
@ Hierapolis-Pamukkale
파묵칼레의 자연적인 장소는 석화된 폭포, 종유석과 테라스로 구성된 시각적으로 눈에 띄는 풍경으로 유명합니다. 기원전 2세기 말에 설립된 인근의 히에라폴리스 마을은 초기 기독교 건축의 예뿐만 아니라 사원, 목욕탕, 네크로폴리스를 포함한 다양한 그레코로만형 건축물을 보유하고 있습니다.
The natural site of Pamukkale is famous for its visually striking landscape, consisting of petrified waterfalls, stalactites and terraces. The nearby town of Hierapolis, founded at the end of the 2nd century BCE, hosts various Greco-Roman structures including temples, baths, a necropolis, as well as examples of Early Christian architecture.

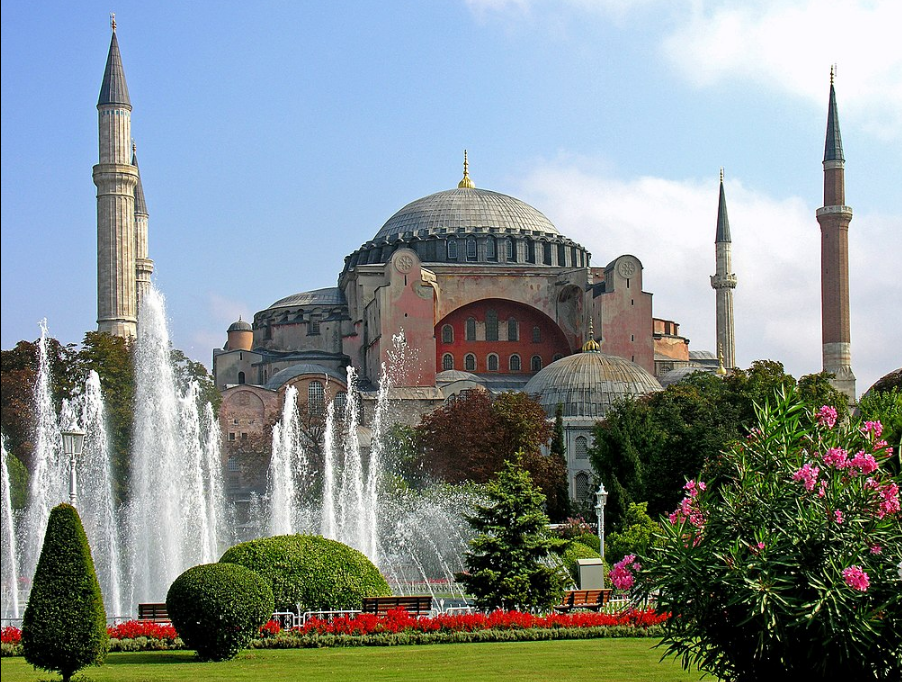
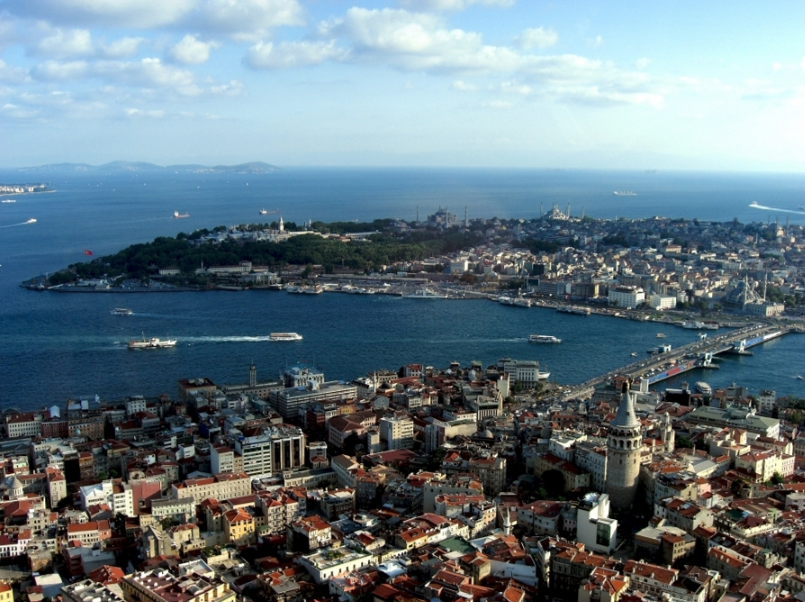
@ Historic Areas of Istanbul
비잔틴 제국과 오스만 제국의 제국 수도인 이스탄불은 2천년 이상 동안 주요한 정치, 종교, 문화의 중심지였습니다. 콘스탄티노플의 히프롬, 소피아 성당, 쉴레이마니예 모스크와 탑카프 ı 궁전과 같은 걸작들을 포함하는 스카이라인은 시대를 관통하는 건축가들의 위대한 천재성을 증언합니다.
The imperial capital of the Byzantine and Ottoman empires, Istanbul has been a major political, religious and cultural centre for more than two millennia. Its skyline, which includes masterpieces such as the Hippodrome of Constantinople, Hagia Sophia, the Süleymaniye Mosque and the Topkapı Palace, testifies to the great geniuses of architects through the ages.


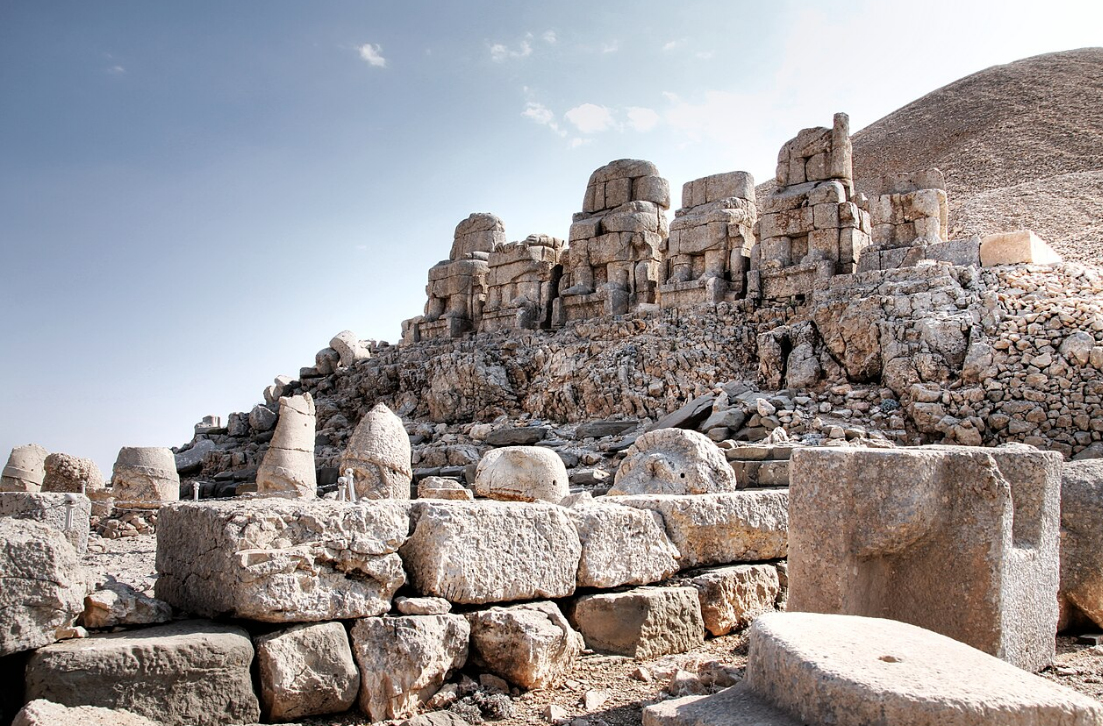
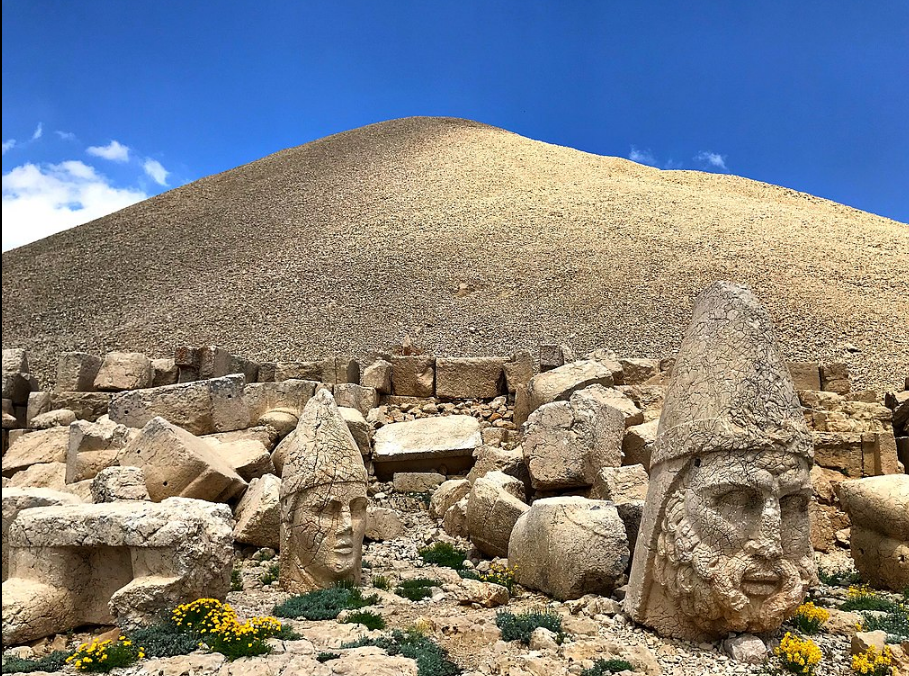
@ Nemrut Dağ
네므루트 다그는 코마게네의 안티오코스 1세 (기원전 69–34)가 헬레니즘 시대의 가장 야심찬 건축 사업 중 하나로 거대한 조각상과 석축으로 둘러싸인 자신의 사원 무덤을 건설한 곳입니다.
Nemrut Dağ is the location where King Antiochus I (69–34 B.C.) of Commagene constructed his own temple-tomb, surrounded by colossal statues and stelae, in one of the most ambitious architectural undertakings of the Hellenistic period.


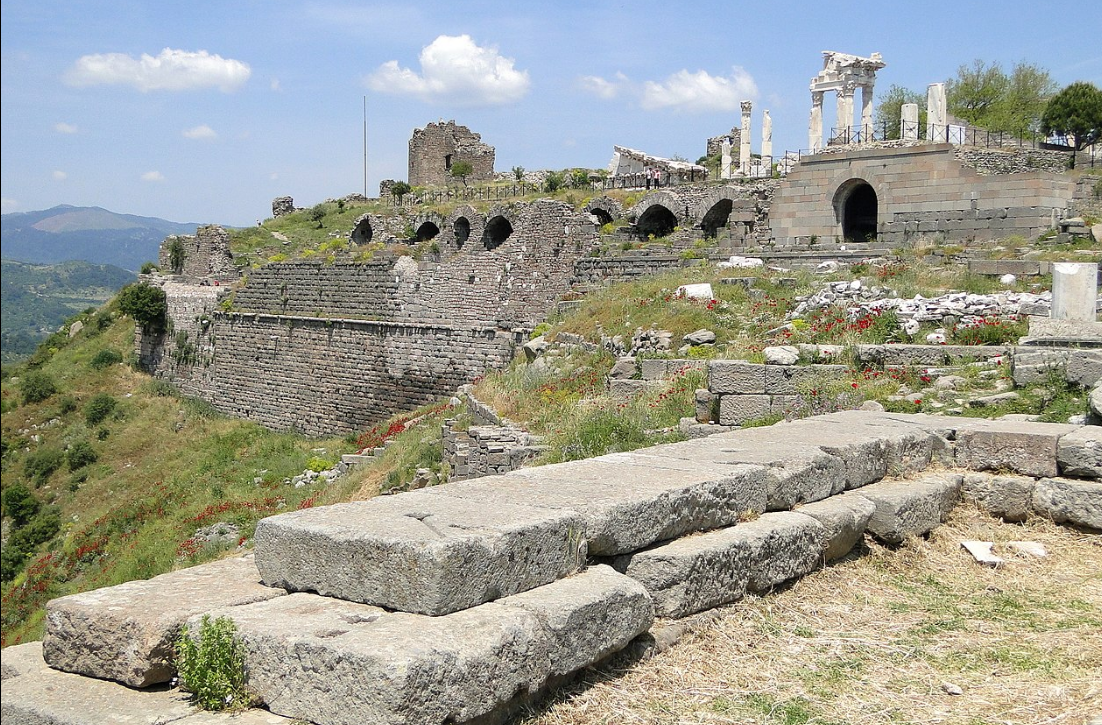
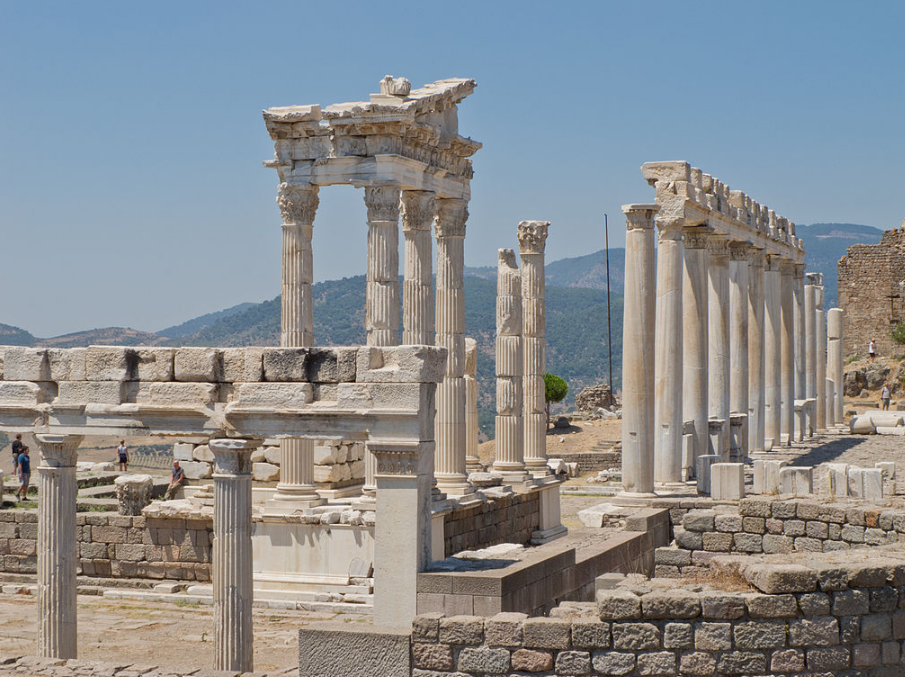
@ Pergamon and its Multi-Layered Cultural Landscape
기원전 3세기에 헬레니즘 아탈리드 왕조의 수도로 세워진 페르가몬은 고대 세계에서 가장 중요한 도시들 중 하나였습니다. 기원전 133년 로마인들에게 유산을 남긴 후, 그 도시는 주요 치료 중심지로 알려지며 더욱 발전하는 것을 목격했습니다.
Founded in the 3rd century BC as the capital of the Hellenistic Attalid dynasty, Pergamon was one of the most important cities of the ancient world. After its bequest to the Romans in 133 BC, the city witnessed further development, becoming known as a major therapeutic centre.


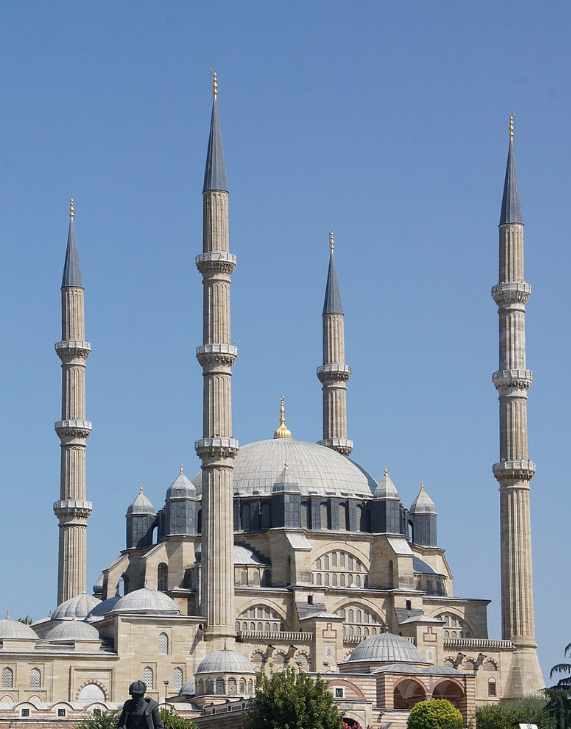
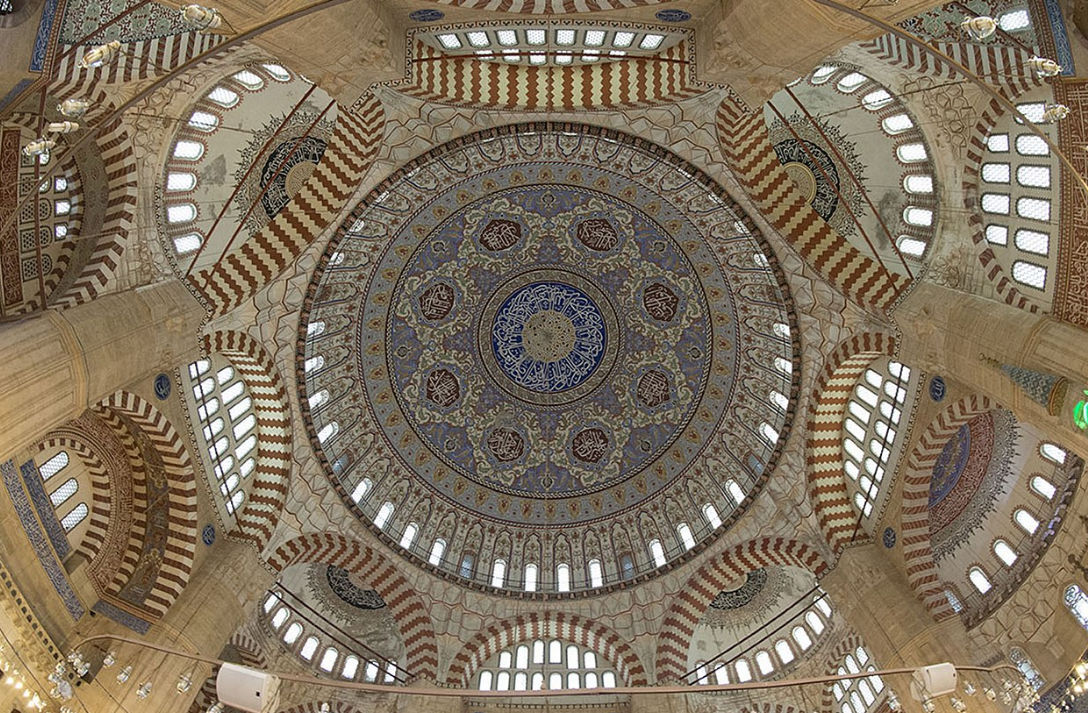
@ Selimiye Mosque and its Social Complex
16세기에 건설된 에디르네의 셀리미예 모스크 단지는 건축가 미마르 시난에 의해 그의 걸작으로 간주되며 오스만 건축의 가장 높은 성취를 나타냅니다.
Constructed during the 16th century, the Selimiye Mosque complex at Edirne is considered by the architect Mimar Sinan to be his masterpiece and represents the highest achievement of Ottoman architecture.


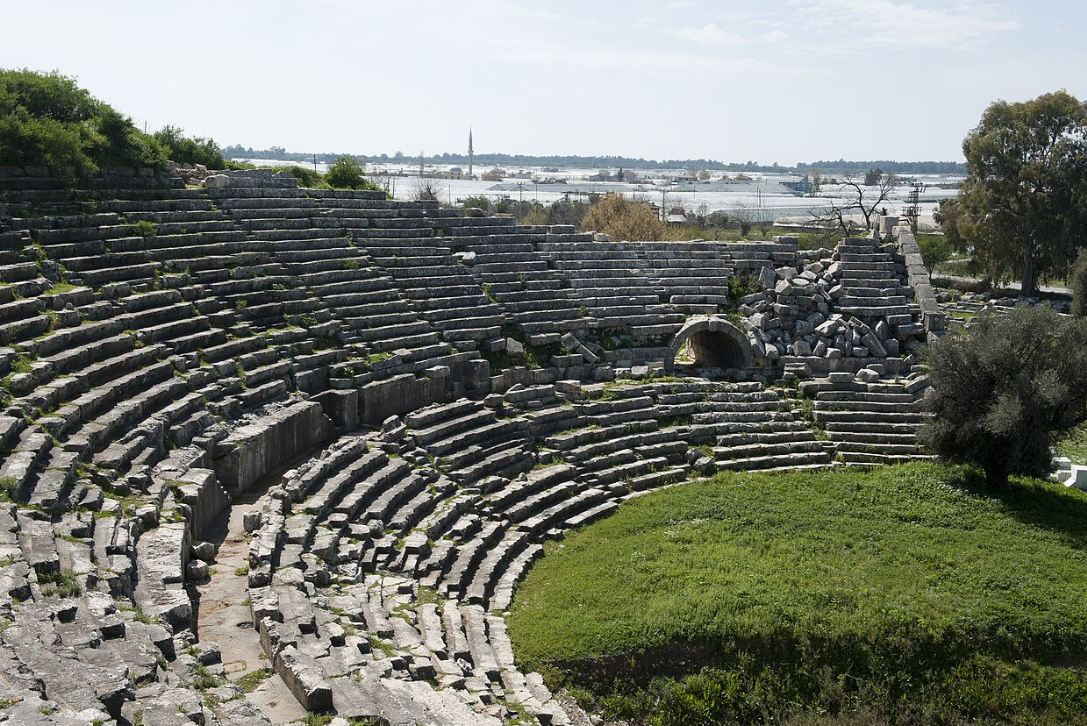
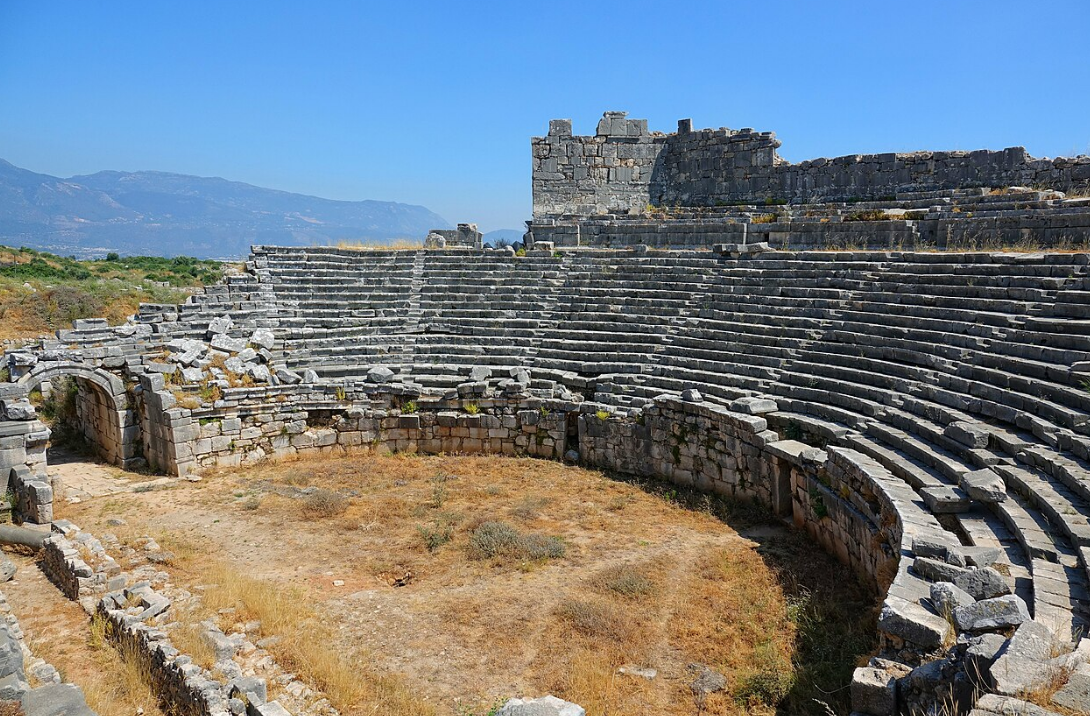
@ Xanthos-Letoon
그 장소는 두 개의 이웃 정착지로 구성되어 있습니다. 리키아 문명의 중심지인 크산토스는 네레이드 기념비가 카리아의 할리카르나소스에 있는 묘에 직접적인 영감을 주면서 이 지역의 다른 도시들에 중요한 건축적인 영향을 미쳤습니다. 리키아의 중요한 종교 중심지인 레툰은 오랫동안 멸종된 리키아 언어를 해독하는 열쇠를 제공했던 레툰 삼중 언어를 개최합니다.
The site consists of two neighboring settlements. Xanthos, the centre of the Lycian civilization, exerted significant architectural influences upon other cities of the region, with the Nereid Monument directly inspiring the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus in Caria. Letoon, an important religious centre in Lycia, hosts the Letoon trilingual, which provided the key in deciphering the long-extinct Lycian language.


@ 2023년 현재 유네스코에 등재된 터키 21개의 유적지 (21 sites in Turkey listed on UNESCO as of 2023)
참고 : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_World_Heritage_Sites_in_Turkey
'여행' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 유네스코 세계문화유산 그리스 (UNESCO in Greece) (20) | 2024.10.18 |
|---|---|
| 유네스코 세계 문화유산 호주(UNESCO in Australia) (4) | 2024.08.23 |
| 유네스코 세계 문화유산 캐나다 (UNESCO in Canada) (2) | 2024.07.04 |
| 유네스코 세계 문화유산 브라질 (UNESCO in Brazil) (0) | 2024.05.16 |
| 유네스코 세계 문화유산 미국 (UNESCO in UnitedStates) (0) | 2024.04.24 |



